
Concept explainers
Classify each terpene and terpenoid in Problem 31.26 (e.g., as a monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.).
(a)
Interpretation: The terpene and terpenoid are to be classified as monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.
Concept introduction: Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are present in plants and animals. Terpenes contain one or more isoprene units. Terpenoids are derivatives of terpenes with oxygen containing functional group such as carbonyl groups. Monoterpenes contain two isoprene units, sesquiterpene contain three isoprene units etc.
Answer to Problem 31.27P
Neral is classified as monoterpene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isoprene is,
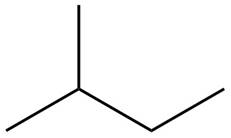
Figure 1
The isoprene unit contains four carbon atoms in the long chain and one carbon atom in branch. Isoprene unit in a terpene consists of carbon-carbon sigma or pi bonds.
The isoprene units in the given compound are shown below.
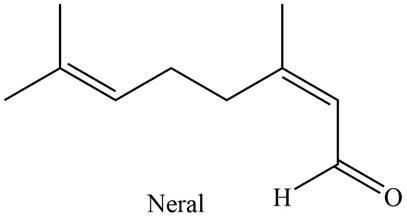
Figure 2
The highlighted bonds represent the isoprene unit. There are two isoprene units present in the given compound. Neral is classified as monoterpene.
Neral is classified as monoterpene.
(b)
Interpretation: The terpene and terpenoid are to be classified as monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.
Concept introduction: Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are present in plants and animals. Terpenes contain one or more isoprene units. Terpenoids are derivatives of terpenes with oxygen containing functional group such as carbonyl groups. Monoterpenes contain two isoprene units, sesquiterpene contain three isoprene units etc.
Answer to Problem 31.27P
Carvone is classified as monoterpene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isoprene is,
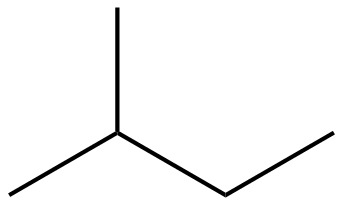
Figure 1
The isoprene unit contains four carbon atoms in the long chain and one carbon atom in branch. Isoprene unit in a terpene consists of carbon-carbon sigma or pi bonds.
The isoprene units in the given compound are shown below.
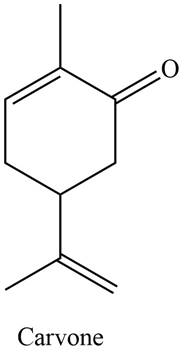
Figure 3
The highlighted bonds represent the isoprene unit. There are two isoprene units present in the given compound. Carvone is classified as monoterpene.
Carvone is classified as monoterpene.
(c)
Interpretation: The terpene and terpenoid are to be classified as monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.
Concept introduction: Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are present in plants and animals. Terpenes contain one or more isoprene units. Terpenoids are derivatives of terpenes with oxygen containing functional group such as carbonyl groups. Monoterpenes contain two isoprene units, sesquiterpene contain three isoprene units etc.
Answer to Problem 31.27P
Lycopene is classified as tetraterpene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isoprene is,
Figure 1
The isoprene unit contains four carbon atoms in the long chain and one carbon atom in branch. Isoprene unit in a terpene consists of carbon-carbon sigma or pi bonds.
The isoprene units in the given compound are shown below.
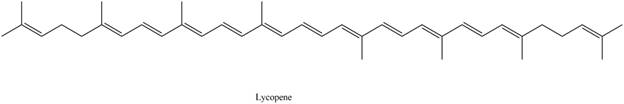
Figure 4
The highlighted bonds represent the isoprene unit. There are eight isoprene units present in the given compound. Lycopene is classified as tetraterpene.
Lycopene is classified as tetraterpene.
(d)
Interpretation: The terpene and terpenoid are to be classified as monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.
Concept introduction: Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are present in plants and animals. Terpenes contain one or more isoprene units. Terpenoids are derivatives of terpenes with oxygen containing functional group such as carbonyl groups. Monoterpenes contain two isoprene units, sesquiterpene contain three isoprene units etc.
Answer to Problem 31.27P
The
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isoprene is,

Figure 1
The isoprene unit contains four carbon atoms in the long chain and one carbon atom in branch. Isoprene unit in a terpene consists of carbon-carbon sigma or pi bonds.
The isoprene units in the given compound are shown below.
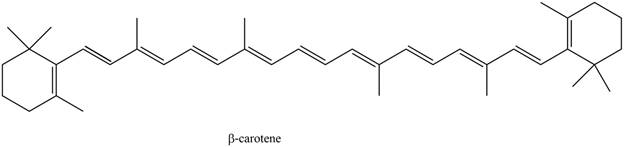
Figure 5
The highlighted bonds represent the isoprene unit. There are eight isoprene units present in the given compound. The
The
(e)
Interpretation: The terpene and terpenoid are to be classified as monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.
Concept introduction: Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are present in plants and animals. Terpenes contain one or more isoprene units. Terpenoids are derivatives of terpenes with oxygen containing functional group such as carbonyl groups. Monoterpenes contain two isoprene units, sesquiterpene contain three isoprene units etc.
Answer to Problem 31.27P
Patchouli alcohol is classified as sesquiterpene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isoprene is,

Figure 1
The isoprene unit contains four carbon atoms in the long chain and one carbon atom in branch. Isoprene unit in a terpene consists of carbon-carbon sigma or pi bonds.
The isoprene units in the given compound are shown below.
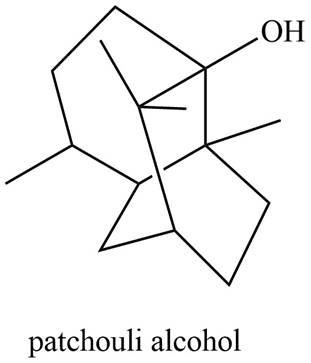
Figure 6
The highlighted bonds represent the isoprene unit. There are three isoprene units present in the given compound. Patchouli alcohol is classified as sesquiterpene.
Patchouli alcohol is classified as sesquiterpene.
(f)
Interpretation: The terpene and terpenoid are to be classified as monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.
Concept introduction: Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are present in plants and animals. Terpenes contain one or more isoprene units. Terpenoids are derivatives of terpenes with oxygen containing functional group such as carbonyl groups. Monoterpenes contain two isoprene units, sesquiterpene contain three isoprene units etc.
Answer to Problem 31.27P
Periplanone B is classified as sesquiterpene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isoprene is,
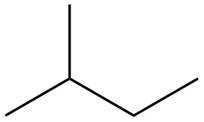
Figure 1
The isoprene unit contains four carbon atoms in the long chain and one carbon atom in branch. Isoprene unit in a terpene consists of carbon-carbon sigma or pi bonds.
The isoprene units in the given compound are shown below.
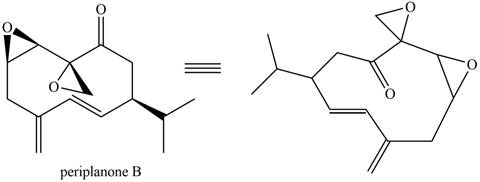
Figure 7
The highlighted bonds represent the isoprene unit. There are three isoprene units present in the given compound. Periplanone B is classified as sesquiterpene.
Periplanone B is classified as sesquiterpene.
(g)
Interpretation: The terpene and terpenoid are to be classified as monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.
Concept introduction: Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are present in plants and animals. Terpenes contain one or more isoprene units. Terpenoids are derivatives of terpenes with oxygen containing functional group such as carbonyl groups. Monoterpenes contain two isoprene units, sesquiterpene contain three isoprene units etc.
Answer to Problem 31.27P
Dextropimaric acid is classified as diterpene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isoprene is,

Figure 1
The isoprene unit contains four carbon atoms in the long chain and one carbon atom in branch. Isoprene unit in a terpene consists of carbon-carbon sigma or pi bonds.
The isoprene units in the given compound are shown below.
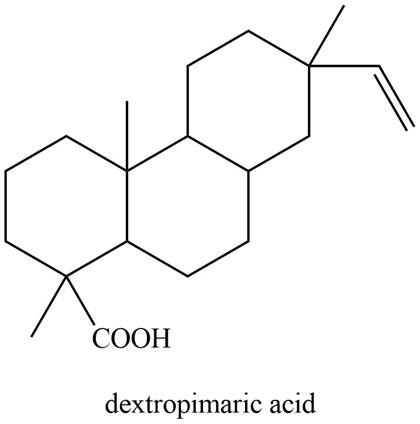
Figure 8
The highlighted bonds represent the isoprene unit. There are four isoprene units present in the given compound. Dextropimaric acid is classified as diterpene.
Dextropimaric acid is classified as diterpene.
(h)
Interpretation: The terpene and terpenoid are to be classified as monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.
Concept introduction: Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are present in plants and animals. Terpenes contain one or more isoprene units. Terpenoids are derivatives of terpenes with oxygen containing functional group such as carbonyl groups. Monoterpenes contain two isoprene units, sesquiterpene contain three isoprene units etc.
Answer to Problem 31.27P
The
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isoprene is,
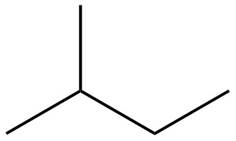
Figure 1
The isoprene unit contains four carbon atoms in the long chain and one carbon atom in branch. Isoprene unit in a terpene consists of carbon-carbon sigma or pi bonds.
The isoprene units in the given compound are shown below.
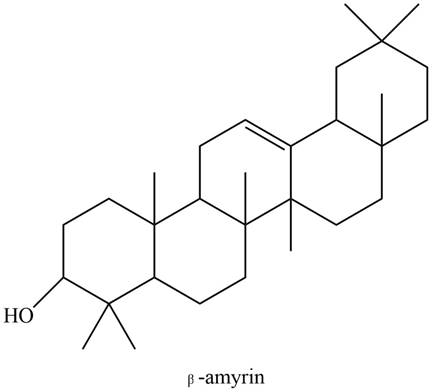
Figure 9
The highlighted bonds represent the isoprene unit. There are four isoprene units present in the given compound. The
The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 31 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward5. A solution of sucrose is fermented in a vessel until the evolution of CO2 ceases. Then, the product solution is analyzed and found to contain, 45% ethanol; 5% acetic acid; and 15% glycerin by weight. If the original charge is 500 kg, evaluate; e. The ratio of sucrose to water in the original charge (wt/wt). f. Moles of CO2 evolved. g. Maximum possible amount of ethanol that could be formed. h. Conversion efficiency. i. Per cent excess of excess reactant. Reactions: Inversion reaction: C12H22O11 + H2O →2C6H12O6 Fermentation reaction: C6H12O6 →→2C2H5OH + 2CO2 Formation of acetic acid and glycerin: C6H12O6 + C2H5OH + H₂O→ CH3COOH + 2C3H8O3arrow_forward
- Show work. don't give Ai generated solution. How many carbons and hydrogens are in the structure?arrow_forward13. (11pts total) Consider the arrows pointing at three different carbon-carbon bonds in the molecule depicted below. Bond B 2°C. +2°C. cleavage Bond A •CH3 + 26.← Cleavage 2°C. + Bond C +3°C• CH3 2C Cleavage E 2°C. 26. weakest bond Intact molecule Strongest 3°C 20. Gund Largest argest a. (2pts) Which bond between A-C is weakest? Which is strongest? Place answers in appropriate boxes. C Weakest bond A Produces Most Bond Strongest Bond Strongest Gund produces least stable radicals Weakest Stable radical b. (4pts) Consider the relative stability of all cleavage products that form when bonds A, B, AND C are homolytically cleaved/broken. Hint: cleavage products of bonds A, B, and C are all carbon radicals. i. Which ONE cleavage product is the most stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. 13°C. formed in bound C cleavage ii. Which ONE cleavage product is the least stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. • CH3 methyl radical Formed in Gund A Cleavage c.…arrow_forwardBr. COOH Br, FCH COOH E FeBr ASOCI B NH (CH,CO),OD Br₂ 2 C alcKOHarrow_forward
- Find A to F (all)arrow_forwardShow work. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardHi!! Please provide a solution that is handwritten. Ensure all figures, reaction mechanisms (with arrows and lone pairs please!!), and structures are clearly drawn to illustrate the synthesis of the product as per the standards of a third year organic chemistry course. ****the solution must include all steps, mechanisms, and intermediate structures as required. Please hand-draw the mechanisms and structures to support your explanation. Don’t give me AI-generated diagrams or text-based explanations, no wordy explanations on how to draw the structures I need help with the exact mechanism hand drawn by you!!! I am reposting this—ensure all parts of the question are straightforward and clear or please let another expert handle it thanks!!arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

