
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337594318
Author: Barry J. Goodno; James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 3.4.19P
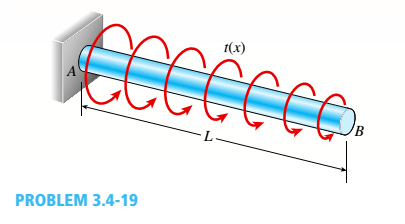
A prismatic bar AB with a solid circular cross section (diameter d) is loaded by a distributed torque (see figure). The intensity of the torque, that is, the torque per unit distance, is denoted i(x) and varies linearly from a maximum value iAat end A to zero at end B. Also, the length of the bar is L and the shear modulus of elasticity of the material is G.
- Determine the maximum shear stress in the bar.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 3 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
Ch. 3 - A circular tube is subjected to torque Tat its...Ch. 3 - -2. A plastic bar of diameter d = 56 mm is to be...Ch. 3 - A copper rod of length L = 18.0 in. is to be...Ch. 3 - A circular steel tube of length L = 1.0 m is...Ch. 3 - Solve the preceding problem if the length L = 56...Ch. 3 - A circular aluminum tube subjected to pure torsion...Ch. 3 - A solid steel bar of circular cross section has...Ch. 3 - A solid copper bar of circular cross section has...Ch. 3 - Repeat Problem 3.3-1, but now use a circular tube...Ch. 3 - A copper tube with circular cross section has...
Ch. 3 - A prospector uses a hand-powered winch (see...Ch. 3 - When drilling a hole in a table leg, a furniture...Ch. 3 - While removing a wheel to change a tire, a driver...Ch. 3 - -8 An aluminum bar of solid circular cross section...Ch. 3 - A high-strength steel drill rod used for boring a...Ch. 3 - The steel shaft of a socket wrench has a diameter...Ch. 3 - A circular tube of aluminum is subjected to...Ch. 3 - A propeller shaft for a small yacht is made of a...Ch. 3 - Three identical circular disks A, B, and Care...Ch. 3 - The steel axle of a large winch on an ocean liner...Ch. 3 - A hollow steel shaft used in a construction auger...Ch. 3 - Solve the preceding problem if the shaft has an...Ch. 3 - A vertical pole of solid, circular cross section...Ch. 3 - A vertical pole of solid, circular cross section...Ch. 3 - A solid brass bar of diameter d = 1.25 in. is...Ch. 3 - A hollow aluminum tube used in a roof structure...Ch. 3 - A circular tube of inner radius r1and outer radius...Ch. 3 - .1 A stepped shaft ABC consisting of two solid...Ch. 3 - A circular tube of outer diameter d3= 70 mm and...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft ABCD consisting of solid circular...Ch. 3 - A solid, circular bar ABC consists of two...Ch. 3 - A hollow tube ABCDE constructed of monel metal is...Ch. 3 - A shaft with a solid, circular cross section...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.4.7PCh. 3 - Two sections of steel drill pipe, joined by bolted...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.4.9PCh. 3 - -10. A tapered bar AB with a solid circular cross...Ch. 3 - A tapered bar AB with a solid circular cross...Ch. 3 - The bar shown in the figure is tapered linearly...Ch. 3 - The non prismatic, cantilever circular bar shown...Ch. 3 - A uniformly tapered tube AB with a hollow circular...Ch. 3 - A uniformly tapered aluminum-alloy tube AB with a...Ch. 3 - For the thin nonprismatic steel pipe of constant...Ch. 3 - .17 A mountain-bike rider going uphill applies...Ch. 3 - A prismatic bar AB of length L and solid circular...Ch. 3 - A prismatic bar AB with a solid circular cross...Ch. 3 - A magnesium-alloy wire of diameter d = 4mm and...Ch. 3 - A nonprismatic bar ABC with a solid circular cross...Ch. 3 - -22 Two tubes (AB, BC) of the same material arc...Ch. 3 - A circular copper bar with diameter d = 3 in. is...Ch. 3 - A circular steel tube with an outer diameter of 75...Ch. 3 - A hollow aluminum shaft (see figure) has an...Ch. 3 - A hollow steel bar (G = 80 GPa ) is twisted by...Ch. 3 - A tubular bar with outside diameterd2= 4.0 in, is...Ch. 3 - A solid circular bar of diameter d = 50 mm (see...Ch. 3 - -7 A steel tube (G = 11.5 x 106 psi) has an outer...Ch. 3 - A solid circular bar of steel (G = 78 GPa)...Ch. 3 - The normal strain in the 45n direction on the...Ch. 3 - An aluminum tube has inside diameter dx= 50 mm,...Ch. 3 - -11 A solid steel bar (G = 11.8 X 106 psi ) of...Ch. 3 - A solid aluminum bar (G = 27 GPa ) of diameter d =...Ch. 3 - Two circular aluminum pipes of equal length L = 24...Ch. 3 - A generator shaft in a small hydroelectric plant...Ch. 3 - A motor drives a shaft at 12 Hz and delivers 20 kW...Ch. 3 - A motor driving a solid circular steel shaft with...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.7.4PCh. 3 - The propeller shaft of a large ship has an outside...Ch. 3 - The drive shaft for a truck (outer diameter 60 mm...Ch. 3 - A hollow circular shaft for use in a pumping...Ch. 3 - A tubular shaft being designed for use on a...Ch. 3 - A propeller shaft of solid circular cross section...Ch. 3 - What is the maximum power that can be delivered by...Ch. 3 - A motor delivers 275 hp at 1000 rpm to the end of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.7.12PCh. 3 - A solid circular bar ABCD with fixed supports is...Ch. 3 - A solid circular bar A BCD with fixed supports at...Ch. 3 - A solid circular shaft AB of diameter d is fixed...Ch. 3 - A ho 1 low st e el shaft ACB of outside diameter...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft ACB having solid circular cross...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft ACB having solid circular cross...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft ACE is held against rotation at...Ch. 3 - A solid circulai' aluminum bar AB is fixed at both...Ch. 3 - Two sections of steel drill pipe, joined by bolted...Ch. 3 - A circular bar AB of length L is fixed against...Ch. 3 - A circular bar AB with ends fixed against rotation...Ch. 3 - A solid steel bar of diameter d1= 25.0 mm is...Ch. 3 - A solid steel bar of diameter d1= 1.50 in. is...Ch. 3 - The composite shaft shown in the figure is...Ch. 3 - The composite shaft shown in the figure is...Ch. 3 - A steel shaft (Gs= 80 GPa) of total length L = 3.0...Ch. 3 - A uniformly tapered aluminum-ally tube AB of...Ch. 3 - Two pipes {L, = 2.5 m and L, = 1.5 m) are joined...Ch. 3 - A solid circular bar of steel (G = 1L4 × 106 psi)...Ch. 3 - A solid circular bar of copper (G = 45 GPa) with...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft of solid circular cross sections...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft of solid circular cross sections...Ch. 3 - A circular tube AB is fixed at one end and free at...Ch. 3 - A cantilever bar of circular cross section and...Ch. 3 - Obtain a formula for the strain energy U of the...Ch. 3 - A statically indeterminate stepped shaft ACE is...Ch. 3 - Derive a formula for the strain energy U of the...Ch. 3 - A thin-walled hollow tube AB of conical shape has...Ch. 3 - A hollow circular tube A fits over the end of a...Ch. 3 - A heavy flywheel rotating at n revolutions per...Ch. 3 - A hollow circular tube having an inside diameter...Ch. 3 - A solid circular bar having diameter d is to be...Ch. 3 - A thin-walled aluminum tube of rectangular cross...Ch. 3 - A thin-walled steel tube of rectangular cross...Ch. 3 - A square tube section has side dimension of 20 in....Ch. 3 - A thin-walled circular tube and a solid circular...Ch. 3 - A thin-walled steel tube having an elliptical...Ch. 3 - Calculate the shear stress and the angle of twist...Ch. 3 - A torque T is applied to a thin-walled tube having...Ch. 3 - Compare the angle of twist 1 for a thin-walled...Ch. 3 - A tubular aluminum bar (G = 4 × 106 psi) of square...Ch. 3 - A thin tubular shaft with a circular cross section...Ch. 3 - A thin-walled rectangular tube has uniform...Ch. 3 - A long, thin-walled tapered tube AB with a...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft consisting of solid circular...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft with diameters D1= 40 mm and D2=...Ch. 3 - A full quarter-circular fillet is used at the...Ch. 3 - The stepped shaft shown in the figure is required...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft (see figure) has diameter D2= 1.5...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- -11 A solid steel bar (G = 11.8 X 106 psi ) of diameter d = 2,0 in. is subjected to torques T = 8.0 kip-in. acting in the directions shown in the figure. Determine the maximum shear, tensile, and compressive stresses in the bar and show these stresses on sketches of properly oriented stress elements. Determine the corresponding maximum strains (shear, tensile, and compressive) in the bar and show these strains on sketches of the deformed elements.arrow_forwardA cylindrical pressure vessel having a radius r = 14 in. and wall thickness t = 0,5 in, is subjected to internal pressure p = 375 psi, In addition, a torque T = 90 kip-ft acts at each end of the cylinder (see figure), (a) Determine the maximum tensile stress ctniXand the maximum in-plane shear stress Tmjv in the wall of the cylinder. (b) If the allowable in-plane shear stress is 4.5 ksi, what is the maximum allowable torque T\ (c) If 7 = 150 kip-ft and allowable in-plane shear and allowable normal stresses are 4.5 ksi and 11.5 ksi, respectively, what is the minimum required wall thicknessarrow_forwardA vertical pole of solid, circular cross section is twisted by horizontal forces P = 5kN acting at the ends of a rigid horizontal arm AB (see figure part a). The distance from the outside of the pole to the line of action of each force is c = 125 mm (sec figure part b) and the pole height L = 350 mm. (a) If the allowable shear stress in the pole is 30 MPa, what is the minimum required diameter dminof the pole? (b) What is the torsional stiffness of the pole (kN · m/rad)? Assume that G = 28 GPa. (c) If two translation al springs, each with stiffness k =2550 kN/m, are added at 2c/5 from A and B (see figure part c), repeat part (a) to find dmin. Hint: Consider the pole and pair of springs as "springs in parallel."arrow_forward
- A vertical pole of solid, circular cross section is twisted by horizontal forces P = 1100 lb acting at the ends of a rigid horizontal arm AB (see figure part a). The distance from the outside of the pole to the line of action of each force is c = 5.0 in. (see figure part b) and the pole height is L = 14in. (a) If the allowable shear stress in the pole is 4500 psi, what is the minimum required diameter dminof the pole? Find the torsional stiffness of the pole (kip-in./rad). Assume that G = 10,800 ksi. If two translational springs, each with stiffness k = 33 kips/in., are added at 2(75 from A and B (see figure part c), repeat part (a) to find dmin. Hint: Consider the pole and pair of springs as "springs in parallel."arrow_forwardA solid circular bar of steel (G = 1L4 × 106 psi) with length L = 30 in, and diameter d = 1.75 in, is subjected to pure torsion by torques T acting at the ends (see figure). Calculate the amount of strain energy V stored in the bar when the maximum shear stress is 4500 psi. From the strain energy, calculate the angle of twist 0 (in degrees).arrow_forward-8 An aluminum bar of solid circular cross section is twisted by torques T acting at the ends (see figure). The dimensions and shear modulus of elasticity arc L = 1.4 m, d = 32 mm, and G = 28 GPa. Determine the torsional stiffness of the bar. If the angle of twist of the bar is 5º, what is the maximum shear stress? What is the maximum shear strain (in radians)? If a hole of diameter d/2 is drilled longitudinally through the bar, what is the ratio of the torsional stiffnesses of the hollow and solid bars? What is the ratio of their maximum shear stresses if both arc acted on by the same torque? If the hole diameter remains at d/2, what new outside diameter d2will result in equal stiffnesses of the hollow and solid bars?arrow_forward
- A solid circular bar of copper (G = 45 GPa) with length L = 315n m and diameter d = 40 mm is subjected to pure torsion by torques T acting at the ends (see figure). Calculate the amount of strain energy U stored in the bar when the maximum shear stress is 32 MPa. From the strain energy, calculate the angle of twist (in degrees).arrow_forwardThe length of the end segments of the bar (see figure) is 20 in. and the length of the prismatic middle segment is 50 in. Also, the diameters at cross sections A. B, C, and D are 0.5, 1.0, 1.0, and 0.5 in., respectively, and the modulus of elasticity is 18 ,000 ksi. (a) Calculate the elongation of a copper bar of solid circular cross section with tapered ends when it is stretched by axial loads of magnitude 3.0 kips (see figure). (b) If the total elongation of the bar cannot exceed 0.025 in., what are the required diameters at B and C? Assume that diameters at A and D remain at 0.5 in.arrow_forwardA flat brass bar has length L, constant thickness t, and a rectangular cross section whose width varies linearly between b2at the fixed support to b1at the free end (see figure). Assume that the taper of the bar is small. The bar has modulus of elasticity E. Calculate the displacements ??Band ??cif P = 200 kN, L = 2 m, t = 20 mm, b, = 100 mm, b, = 115 mm, and E = 96 GPa.arrow_forward
- A square steel tube of a length L = 20 ft and width b2= 10.0 in. is hoisted by a crane (see figure). The lube hangs from a pin of diameter d that is held by the cables at points A and B. The cross section is a hollow square with an inner dimension b1= 8.5 in. and outer dimension b2= 10,0 in. The allowable shear stress in the pin is 8,700 psi. and the allowable bearing stress between the pin and the tube is 13,000 psi. Determine the minimum diameter of the pin in order to support the weight of the tube. Note: Disregard the rounded corners of the tube when calculating its weight.arrow_forwardA thin-walled circular tube and a solid circular bar of the same material (see figure) are subjected to torsion. The tube and bar have the same cross-sectional area and the same length. What is the ratio of the strain energy U1in the tube to the strain energy U2in the solid bar if the maximum shear stresses are the same in both cases? (For the tube, use the approximate theory for thin-walled bars.)arrow_forwardA round bar ABC of length 2L (see figure) rotates about an axis through the midpoint C with constant angular speed w (radians per second). The material of the bar has weight density y. (a) Derive a formula for the tensile stress a’ in the bar as a function of the distance x from the midpoint C. (b) What is the maximum tensile stress a max?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Pressure Vessels Introduction; Author: Engineering and Design Solutions;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z1J97IpFc2k;License: Standard youtube license