
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337594318
Author: Barry J. Goodno; James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 3.3.17P
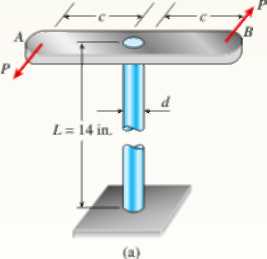
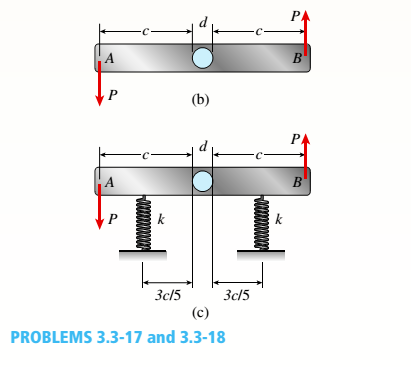
A vertical pole of solid, circular cross section is twisted by horizontal forces P = 1100 lb acting at the ends of a rigid horizontal arm AB (see figure part a). The distance from the outside of the pole to the line of action of each force is c = 5.0 in. (see figure part b) and the pole height is L = 14in.
(a) If the allowable shear stress in the pole is 4500 psi, what is the minimum required diameter dminof the pole?
- Find the torsional stiffness of the pole (kip-in./rad). Assume that G = 10,800 ksi.
- If two translational springs, each with stiffness k = 33 kips/in., are added at 2(75 from A and B (see figure part c), repeat part (a) to find dmin. Hint: Consider the pole and pair of springs as "springs in parallel."
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
A particle, starting from rest, travels along a straight track and for 14 s has an
acceleration as shown. Draw the v-t graph that describes the motion and find the distance traveled in 14
S.
a
8
11 уг
(0.8)
11 ут
(6,8
6.
4+
2
*2 Ye
(1.0)
t
2
4
6
8
10
12 14
dre
dec
dec dec
Mechanical engineering,Use paper sheet.
No chatgpt.
Mechanical engineering question.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
Ch. 3 - A circular tube is subjected to torque Tat its...Ch. 3 - -2. A plastic bar of diameter d = 56 mm is to be...Ch. 3 - A copper rod of length L = 18.0 in. is to be...Ch. 3 - A circular steel tube of length L = 1.0 m is...Ch. 3 - Solve the preceding problem if the length L = 56...Ch. 3 - A circular aluminum tube subjected to pure torsion...Ch. 3 - A solid steel bar of circular cross section has...Ch. 3 - A solid copper bar of circular cross section has...Ch. 3 - Repeat Problem 3.3-1, but now use a circular tube...Ch. 3 - A copper tube with circular cross section has...
Ch. 3 - A prospector uses a hand-powered winch (see...Ch. 3 - When drilling a hole in a table leg, a furniture...Ch. 3 - While removing a wheel to change a tire, a driver...Ch. 3 - -8 An aluminum bar of solid circular cross section...Ch. 3 - A high-strength steel drill rod used for boring a...Ch. 3 - The steel shaft of a socket wrench has a diameter...Ch. 3 - A circular tube of aluminum is subjected to...Ch. 3 - A propeller shaft for a small yacht is made of a...Ch. 3 - Three identical circular disks A, B, and Care...Ch. 3 - The steel axle of a large winch on an ocean liner...Ch. 3 - A hollow steel shaft used in a construction auger...Ch. 3 - Solve the preceding problem if the shaft has an...Ch. 3 - A vertical pole of solid, circular cross section...Ch. 3 - A vertical pole of solid, circular cross section...Ch. 3 - A solid brass bar of diameter d = 1.25 in. is...Ch. 3 - A hollow aluminum tube used in a roof structure...Ch. 3 - A circular tube of inner radius r1and outer radius...Ch. 3 - .1 A stepped shaft ABC consisting of two solid...Ch. 3 - A circular tube of outer diameter d3= 70 mm and...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft ABCD consisting of solid circular...Ch. 3 - A solid, circular bar ABC consists of two...Ch. 3 - A hollow tube ABCDE constructed of monel metal is...Ch. 3 - A shaft with a solid, circular cross section...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.4.7PCh. 3 - Two sections of steel drill pipe, joined by bolted...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.4.9PCh. 3 - -10. A tapered bar AB with a solid circular cross...Ch. 3 - A tapered bar AB with a solid circular cross...Ch. 3 - The bar shown in the figure is tapered linearly...Ch. 3 - The non prismatic, cantilever circular bar shown...Ch. 3 - A uniformly tapered tube AB with a hollow circular...Ch. 3 - A uniformly tapered aluminum-alloy tube AB with a...Ch. 3 - For the thin nonprismatic steel pipe of constant...Ch. 3 - .17 A mountain-bike rider going uphill applies...Ch. 3 - A prismatic bar AB of length L and solid circular...Ch. 3 - A prismatic bar AB with a solid circular cross...Ch. 3 - A magnesium-alloy wire of diameter d = 4mm and...Ch. 3 - A nonprismatic bar ABC with a solid circular cross...Ch. 3 - -22 Two tubes (AB, BC) of the same material arc...Ch. 3 - A circular copper bar with diameter d = 3 in. is...Ch. 3 - A circular steel tube with an outer diameter of 75...Ch. 3 - A hollow aluminum shaft (see figure) has an...Ch. 3 - A hollow steel bar (G = 80 GPa ) is twisted by...Ch. 3 - A tubular bar with outside diameterd2= 4.0 in, is...Ch. 3 - A solid circular bar of diameter d = 50 mm (see...Ch. 3 - -7 A steel tube (G = 11.5 x 106 psi) has an outer...Ch. 3 - A solid circular bar of steel (G = 78 GPa)...Ch. 3 - The normal strain in the 45n direction on the...Ch. 3 - An aluminum tube has inside diameter dx= 50 mm,...Ch. 3 - -11 A solid steel bar (G = 11.8 X 106 psi ) of...Ch. 3 - A solid aluminum bar (G = 27 GPa ) of diameter d =...Ch. 3 - Two circular aluminum pipes of equal length L = 24...Ch. 3 - A generator shaft in a small hydroelectric plant...Ch. 3 - A motor drives a shaft at 12 Hz and delivers 20 kW...Ch. 3 - A motor driving a solid circular steel shaft with...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.7.4PCh. 3 - The propeller shaft of a large ship has an outside...Ch. 3 - The drive shaft for a truck (outer diameter 60 mm...Ch. 3 - A hollow circular shaft for use in a pumping...Ch. 3 - A tubular shaft being designed for use on a...Ch. 3 - A propeller shaft of solid circular cross section...Ch. 3 - What is the maximum power that can be delivered by...Ch. 3 - A motor delivers 275 hp at 1000 rpm to the end of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.7.12PCh. 3 - A solid circular bar ABCD with fixed supports is...Ch. 3 - A solid circular bar A BCD with fixed supports at...Ch. 3 - A solid circular shaft AB of diameter d is fixed...Ch. 3 - A ho 1 low st e el shaft ACB of outside diameter...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft ACB having solid circular cross...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft ACB having solid circular cross...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft ACE is held against rotation at...Ch. 3 - A solid circulai' aluminum bar AB is fixed at both...Ch. 3 - Two sections of steel drill pipe, joined by bolted...Ch. 3 - A circular bar AB of length L is fixed against...Ch. 3 - A circular bar AB with ends fixed against rotation...Ch. 3 - A solid steel bar of diameter d1= 25.0 mm is...Ch. 3 - A solid steel bar of diameter d1= 1.50 in. is...Ch. 3 - The composite shaft shown in the figure is...Ch. 3 - The composite shaft shown in the figure is...Ch. 3 - A steel shaft (Gs= 80 GPa) of total length L = 3.0...Ch. 3 - A uniformly tapered aluminum-ally tube AB of...Ch. 3 - Two pipes {L, = 2.5 m and L, = 1.5 m) are joined...Ch. 3 - A solid circular bar of steel (G = 1L4 × 106 psi)...Ch. 3 - A solid circular bar of copper (G = 45 GPa) with...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft of solid circular cross sections...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft of solid circular cross sections...Ch. 3 - A circular tube AB is fixed at one end and free at...Ch. 3 - A cantilever bar of circular cross section and...Ch. 3 - Obtain a formula for the strain energy U of the...Ch. 3 - A statically indeterminate stepped shaft ACE is...Ch. 3 - Derive a formula for the strain energy U of the...Ch. 3 - A thin-walled hollow tube AB of conical shape has...Ch. 3 - A hollow circular tube A fits over the end of a...Ch. 3 - A heavy flywheel rotating at n revolutions per...Ch. 3 - A hollow circular tube having an inside diameter...Ch. 3 - A solid circular bar having diameter d is to be...Ch. 3 - A thin-walled aluminum tube of rectangular cross...Ch. 3 - A thin-walled steel tube of rectangular cross...Ch. 3 - A square tube section has side dimension of 20 in....Ch. 3 - A thin-walled circular tube and a solid circular...Ch. 3 - A thin-walled steel tube having an elliptical...Ch. 3 - Calculate the shear stress and the angle of twist...Ch. 3 - A torque T is applied to a thin-walled tube having...Ch. 3 - Compare the angle of twist 1 for a thin-walled...Ch. 3 - A tubular aluminum bar (G = 4 × 106 psi) of square...Ch. 3 - A thin tubular shaft with a circular cross section...Ch. 3 - A thin-walled rectangular tube has uniform...Ch. 3 - A long, thin-walled tapered tube AB with a...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft consisting of solid circular...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft with diameters D1= 40 mm and D2=...Ch. 3 - A full quarter-circular fillet is used at the...Ch. 3 - The stepped shaft shown in the figure is required...Ch. 3 - A stepped shaft (see figure) has diameter D2= 1.5...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- correct answer only. I will upvote.arrow_forwardCorrect answer only. I will upvote.arrow_forwardI really don't know how to approach this problem i've tried approaching it with some of the torsional stress equations I know but i'm comming up with awnsers that don't make any sence can you please help me with this?arrow_forward
- I tried this problem and don't know what I did wrong or how else I could approach it can you please help me out?arrow_forwardQ3: An engine produce 750 kW power and uses gaseous C12H26 as a fuel at 25 C; 200% theoretical air is used and air enters at 500 K. The products of combustion leave at 800 K. The heat loss from the engine is 175 kW. Determine the fuel consumption for complete combustion.arrow_forwardQu 5 Determine the carburizing time necessary to achieve a carbon concentration of 0.30 wt% at a position 4 mm into an iron carbon alloy that initially contains 0.10 wt% C. The surface concentration is to be maintained at 0.90 wt% C, and the treatment is to be conducted at 1100°C. Use the data for the diffusion of carbon into y-iron: Do = 2.3 x10-5 m2/s and Qd = 148,000 J/mol. Express your answer in hours to three significant figures. show all work step by step problems formula material sciencearrow_forward
- (Read Question)arrow_forwardIn figure A, the homogeneous rod of constant cross section is attached to unyielding supports. In figure B, a homogeneous bar with a cross-sectional area of 600 mm2 is attached to rigid supports. The bar carries the axial loads P1 = 20 kN and P2 = 60 kN, as shown.1. In figure A, derive the expression that calculates the reaction R1 in terms of P, and the given dimensions.2. In figure B, calculate the reaction (kN) at A.3. In figure B, calculate the maximum axial stress (MPa) in the rod.arrow_forward(Read image)arrow_forward
- (Read Image)arrow_forwardM16x2 grade 8.8 bolts No. 25 C1- Q.2. The figure is a cross section of a grade 25 cast-iron pressure vessel. A total of N, M16x2.0 grade 8.8 bolts are to be used to resist a separating force of 160 kN. (a) Determine ks, km, and C. (b) Find the number of bolts required for a load factor of 2 where the bolts may be reused when the joint 19 mm is taken apart. (c) with the number of bolts obtained in (b), determine the realized load factor for overload, the yielding factor of safety, and the separation factor of safety. 19 mmarrow_forwardProblem4. The thin uniform disk of mass m = 1-kg and radius R = 0.1m spins about the bent shaft OG with the angular speed w2 = 20 rad/s. At the same time, the shaft rotates about the z-axis with the angular speed 001 = 10 rad/s. The angle between the bent portion of the shaft and the z-axis is ẞ = 35°. The mass of the shaft is negligible compared to the mass of the disk. a. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point G, based on the axis orientation as shown. Include an MVD in your solution. b. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point O, based on the axis orientation as shown. (Note: O is NOT the center of fixed-point rotation.) c. Find the kinetic energy of the assembly. z R R 002 2R x Answer: H = -0.046ĵ-0.040 kg-m²/sec Ho=-0.146-0.015 kg-m²/sec T 0.518 N-m =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Everything About COMBINED LOADING in 10 Minutes! Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N-PlI900hSg;License: Standard youtube license