
Concept explainers
A 9 ft thick fill is to be placed on the soil shown in Figure 3.22. Once it is compacted, this fill will have a unit weight of
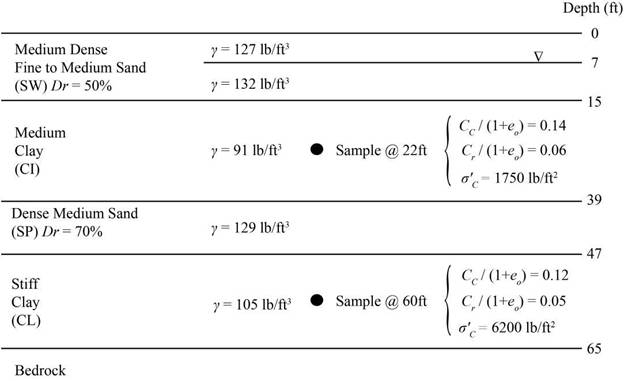
Figure 3.22 Soil profile for Problem 3.18.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 3 Solutions
Foundation Design: Principles and Practices (3rd Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Problem Solving with C++ (10th Edition)
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- P.3.3 Oil of sp.gr. 0.9 flows through a vertical pipe (upwards). Two points A and B one above the other 40 cm apart in a pipe are connected by a U-tube carrying mercury. If the difference of pressure between A and B is 0.2 kg/cm², 1- Find the reading of the manometer. 2- If the oil flows through a horizontal pipe, find the reading in manometer for the same difference in pressure between A and B. Ans. 1- R= 0.12913 m, 2- R = 0.1575 m,arrow_forwardPlease solve the question by hand with a detailed explanation of the steps.arrow_forwardPlease solve the question by hand with a detailed explanation of the steps.arrow_forward
- P.3.4 A mercury U-tube manometer is used to measure the pressure drop across an orifice in pipe. If the liquid that flowing through the orifice is brine of sp.gr. 1.26 and upstream pressure is 2 psig and the downstream pressure is (10 in Hg) vacuum, find the reading of manometer. Ans. R=394 mm Hgarrow_forwardProject management questionarrow_forwardQ5/B with Explantion plsarrow_forward
- project management question Q5/Barrow_forwardProblem 1: Given: In a given floor system, a 5-in concrete slab supported by T-beams of 24-ft spans, supporting 354 psf live load. The T-beams are spaced 2x4 ft on center, and bw (width of the beam web) = 15 inches. Total T-beam height is 25 inches. f'c = 4,000psi, fy = 60,000psi. Design the T-beam. Show all steps. Sketch your Design. Problem 2: Given: A 25"x25" column is subject to a factored axial load of Pu=1,200 kips, and factored design moment of Mu-354 kips-ft. f'c 4,000psi, fy = 60,000psi. Determine the required steel ratio (p) and ties. Sketch the design. 2.0 0.08 INTERACTION DIAGRAM R4-60.9 fc-4 ksi 1.8 1,- 60 ksi 0.07 Y=0.9 16 1.6 0.06 Kmax 0.05 1.4 f/f, = 0 0.04 00 K₁ = P₁/f'c Ag 1.2 12 0.03 0.25 1.0 10 0.02 0.01 0.8 0.6 0.4 €,= 0.0035 0.2 €,= 0.0050 0.0 h yh 0.50 0.75 1.0. 0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50 R₁ = P₁e/f'Agharrow_forwardGiven: In a given floor system, a 5-in concrete slab supported by T-beams of 24-ft spans, supporting 354 psf live load. The T-beams are spaced 2x4 ft on center, and bw (width of the beam web) = 15 inches. Total T-beam height is 25 inches. f'c = 4,000psi, fy = 60,000psi. Design the T-beam. Show all steps. Sketch your Design.arrow_forward
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning




