
Concept explainers
Compute the power absorbed by each element in the circuit of Fig. 3.68 if the mysterious element X is (a) a 13 Ω resistor; (b) a dependent voltage source labeled 4v1, “+” reference on top; (c) a dependent voltage source labeled 4ix, “+” reference on top.
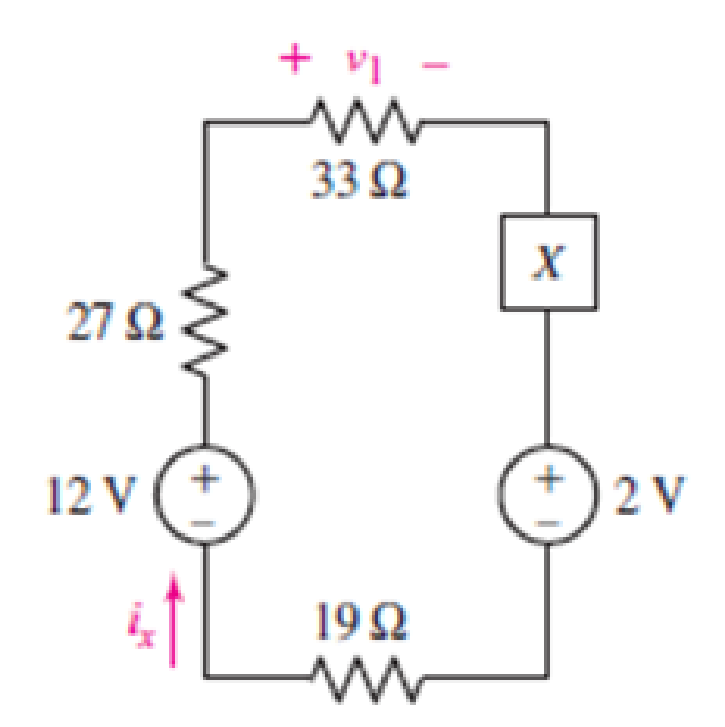
FIGURE 3.68
(a)
Find the power absorbed by each element.
Answer to Problem 28E
Power absorbed by
Explanation of Solution
Given Data:
Element
Formula used:
The expression for power absorbed by voltage source is as follows.
Here,
The expression for power absorbed by resistor is as follows.
Here,
Calculation:
The circuit diagram is redrawn as shown in Figure 1.
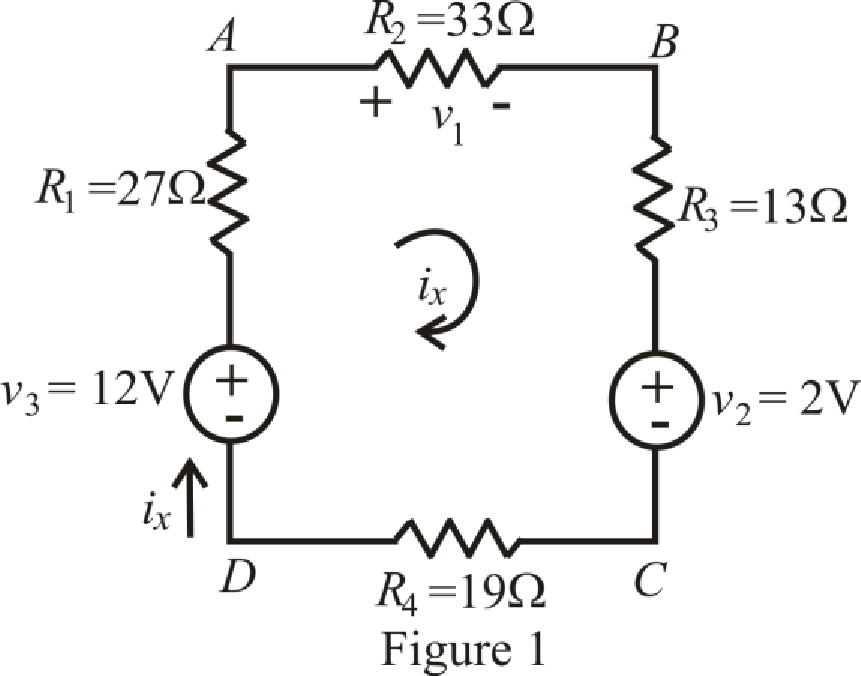
Refer to the redrawn Figure 1.
The expression for KVL in mesh
Here,
Substitute
Rearrange equation (4) for
Current is leaving the positive terminal and we are calculating power absorbed hence current should leave by negative terminal so we will use magnitude of voltage with negative sign, therefore, value of
Substitute
So power absorbed by independent voltage source
Substitute
So, the power absorbed by resistor
Substitute
So power absorbed by resistor
Substitute
So power absorbed by resistor
Substitute
So power absorbed by independent voltage source
Substitute
So power absorbed by resistor
Conclusion:
Thus, power absorbed by
(b)
Find power absorbed by each element.
Answer to Problem 28E
Power absorbed by
Explanation of Solution
Given Data:
Element
Calculation:
The circuit diagram is redrawn as shown in Figure 2,
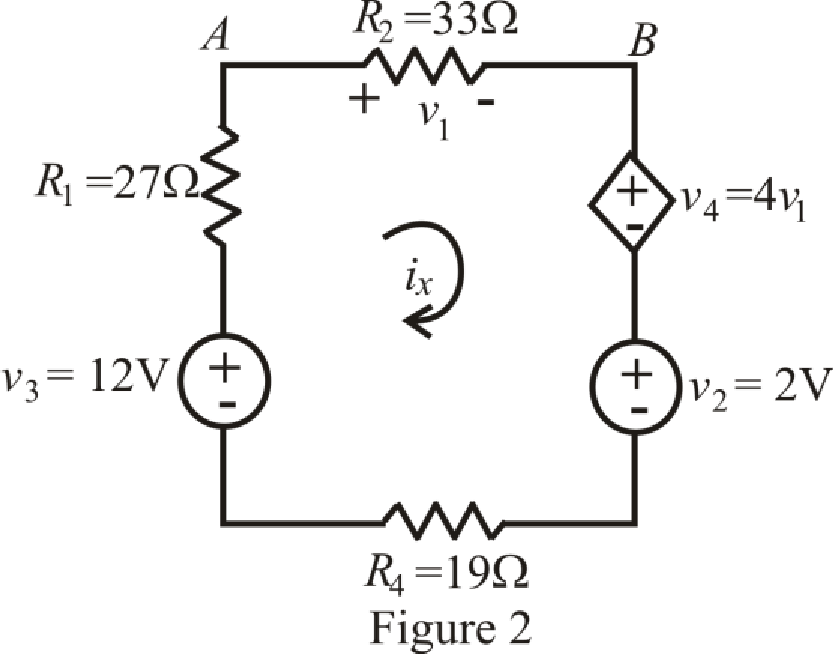
Refer to the redrawn Figure 2,
The expression for KVL in mesh
Here,
The expression for voltage
Here,
The expression for voltage
Here,
Refer to the redrawn Figure 2,
Substitute
Substitute
Rearrange equation (9) for
Current is leaving the positive terminal and we are calculating power absorbed hence current should leave by negative terminal so we will use magnitude of voltage with negative sign, therefore, value of
Substitute
So power absorbed by independent voltage source
Substitute
So power absorbed by resistor
Substitute
So power absorbed by resistor
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
So power absorbed by dependent voltage source
Substitute
So power absorbed by independent voltage source
Substitute
So power absorbed by resistor
Conclusion:
Thus, power absorbed by
(c)
Find power absorbed by each element.
Answer to Problem 28E
Power absorbed by
Explanation of Solution
Given Data:
Element
Calculation:
The circuit diagram is redrawn as shown in Figure 3.
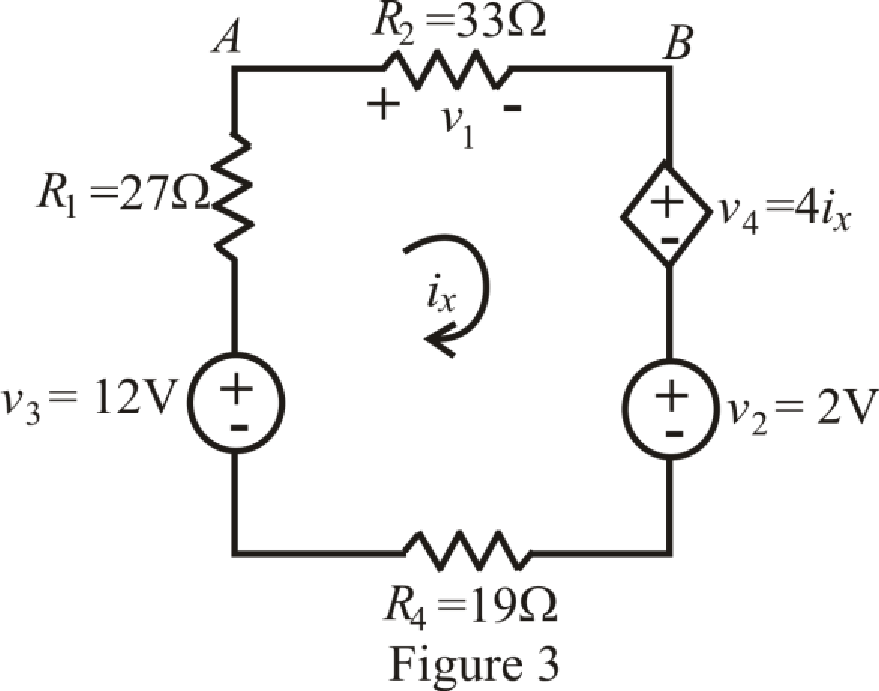
Refer to the redrawn Figure 3,
The expression for KVL in mesh
Here,
The expression for voltage
Here,
Refer to the redrawn Figure 2,
Substitute
Rearrange equation (12) for
Current is leaving the positive terminal and we are calculating power absorbed hence current should leave by negative terminal so we will use magnitude of voltage with negative sign, therefore, value of
Substitute
So power absorbed by independent voltage source
Substitute
So power absorbed by resistor
Substitute
So power absorbed by resistor
Substitute
Substitute
So power absorbed by dependent voltage source
Substitute
So power absorbed by independent voltage source
Substitute
So power absorbed by resistor
Conclusion:
Thus, power absorbed by
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
- NO AI PLEASE.arrow_forward2-3) For each of the two periodic signals in the figures below, find the exponential Fourier series and sketch the magnitude and angle spectra. -5 ΟΙ 1 1- (a) (b) -20π -10x -π Π 10m 20m 1-arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forward
- In the op-amp circuit shown in Fig. P8.32,uin(t) = 12cos(1000t) V,R = 10 k Ohm , RL = 5 k Ohm, and C = 1 μF. Determine the complexpower for each of the passive elements in the circuit. Isconservation of energy satisfied?arrow_forward2-4) Similar to Lathi & Ding prob. 2.9-4 (a) For signal g(t)=t, find the exponential Fourier series to represent g(t) over the interval(0, 1). (b) Sketch the original signal g(t) and the everlasting signal g'(t) represented by the same Fourier series. (c) Verify Parseval's theorem [eq. (2.103b)] for g'(t), given that: = n 1 6arrow_forward8.24 In the circuit of Fig. P8.24, is(t) = 0.2sin105t A,R = 20 W, L = 0.1 mH, and C = 2 μF. Show that the sum ofthe complex powers for the three passive elements is equal to thecomplex power of the source.arrow_forward
- 3. VEB (on) 0.7 V, VEC (sat) = 0.2 V, and ẞ = 150. RB = 50 kQ, Rc = 2 kQ, and Vcc = 5 V. a) Find the range of V₁ for the cut-off. Forward active, and saturation regions. (20 points) b) Draw the voltage transfer characteristic (VTC) graph. (10 points) Vcc VEB V₁ RB www 。 Vo Rc Figure 3arrow_forward2-1) Lathi & Ding prob. 2.5-2 For the signals y(t) and x(t) shown below, find the component of the form y(t) contained in x(t). In other words, find the optimum value of c in the approximation x(t) = cy(t) so that the error signal energy is minimum. Also compute the error signal energy. y(t) x(t) 0 1 0 1arrow_forward1. Is1 = 2ls2 = 4 × 10-16 A, B₁ = ẞ2 = 100, and R₁ = 5 kQ. Find the VB such that lx = 1 mA. (30 points) R1 ww Q2 + VB Figure 1arrow_forward
- 2-2) Lathi & Ding prob. 2.6-1 2.6-1 Find the correlation coefficient p between of signal x(t) and each of the four pulses g1(1), 82(1), 83(1), and g4(f) shown in Fig. P2.6-1. To provide maximum margin against the noise along the transmission path, which pair of pulses would you select for a binary communication? Figure P.2.6-1 x(f) (a) 8(1) (b) 82(1) (c) 1 1 sin 2πt sin 4πt -sin 2 0 0.707 83(1) 0 1 (d) 0 M P 0.707 84(1) (e) 0 0.5 -0.707arrow_forward2. Determine the operation point and the small-signal model of Q₁ for each of the circuits shown in Fig. 2. Assume Is = 8 × 10-16 A, B = 100 and VA = ∞. a) 20 points b) 20 points 0.8 V RC 50 Ω + Vcc = 2.5 V 4A" Figure 2-a Rc1kQ + Vcc = 2.5 V Figure 2-barrow_forwardPlease explain in detail how to solve this question. Show detailed steps in terms of calculation and theory. thank youarrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





