
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: Nature of below alkyl radical along with names and most stable radical should be described by orbital description.

Concept introduction: The carbon radical linked to one alkyl/carbon while other two
The carbon radical linked to two alkyl/carbon atoms and one
The various kinds of alkyl radicals are indicated below:
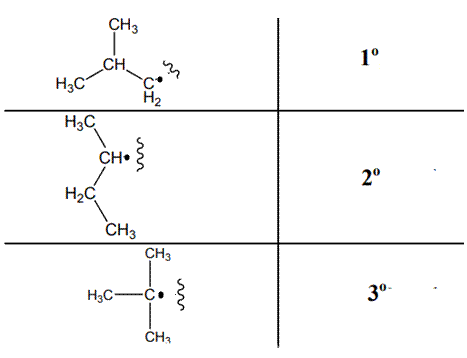
The tertiary radicals are most stable followed by secondary and least stable is primary methyl radical. This is because there is maximum stabilization through delocalization via hyperconjugation. The phenomenon of hyperconjugation refers to donation of
(b)
Interpretation: Nature of below alkyl radical along with names and most stable radical should be described by orbital description.
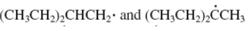
Concept introduction: The carbon radical linked to one alkyl/carbon while other two
The carbon radical linked to two alkyl/carbon atoms and one
The various kinds of alkyl radicals are indicated below:
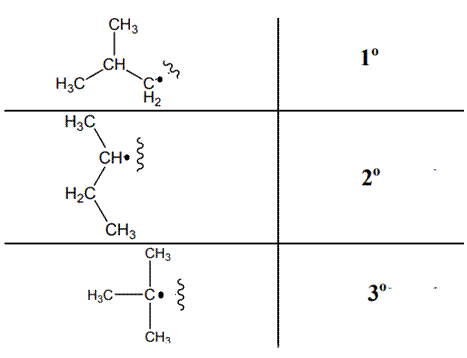
The tertiary radicals are most stable followed by secondary and least stable is primary methyl radical. This is because there is maximum stabilization through delocalization via hyperconjugation. The phenomenon of hyperconjugation refers to donation of
(c)
Interpretation: Nature of below alkyl radical along with names and most stable radical should be described by orbital description.
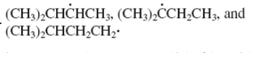
Concept introduction: The carbon radical linked to one alkyl/carbon while other two
The carbon radical linked to two alkyl/carbon atoms and one
The various kinds of alkyl radicals are indicated below:
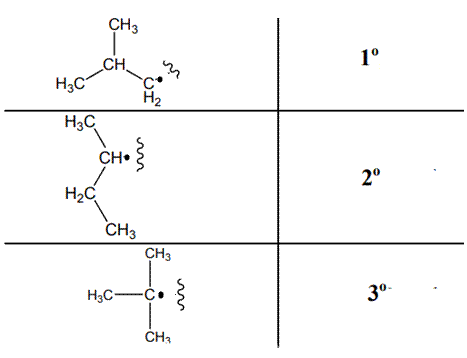
The tertiary radicals are most stable followed by secondary and least stable is primary methyl radical. This is because there is maximum stabilization through delocalization via hyper conjugation. The phenomenon of hyperconjugation refers to donation of
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- 5. Write the formation reaction of the following complex compounds from the following reactants: 6. AgNO₃ + K₂CrO₂ + NH₄OH → 7. HgNO₃ + excess KI → 8. Al(NO₃)₃ + excess NaOH →arrow_forwardIndicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. CO₂C2H5 + CH3-NH-NH,arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction N-(cyclohex-1-en-1-yl)-1-(pyrrolidino) reacts with CH2=CHCHO, heat, H3O+arrow_forward
- Draw the starting material that would be needed to make this product through an intramolecular Dieckmann reactionarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Nitropropane reacts + pent-3-en-2-one reacts with NaOCH2CH3, CH3CHOHarrow_forwardIndicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. OC2H5 + CoHs-NH-NH,arrow_forward
- Explain how substitutions at the 5-position of barbituric acid increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forwardExplain how substitutions at the 5-position of phenobarbital increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forwardName an interesting derivative of barbituric acid, describing its structure.arrow_forward
- Briefly describe the synthesis mechanism of barbituric acid from the condensation of urea with a β-diketone.arrow_forwardGiven the hydrazones indicated, draw the structures of the enamines that can be formed. Indicate the most stable enamine (explain). C6H5 C6H5 H C6H5 Harrow_forward4. Propose a Synthesis for the molecule below. You may use any starting materials containing 6 carbons or less (reagents that aren't incorporated into the final molecule such as PhзP do not count towards this total, and the starting material can have whatever non-carbon functional groups you want), and any of the reactions you have learned so far in organic chemistry I, II, and III. Your final answer should show each step separately, with intermediates and conditions clearly drawn.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

