
(a)
Interpretation: The
Concept introduction: At extremely elevated temperature, the
The phenomenon of hyperconjugation refers to donation of
(b)
Interpretation: The preferred product formed from attack of
Concept introduction: After the homolytic cleavage radicals may recombine with one another and result in variety of
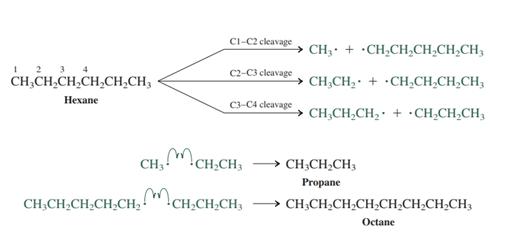
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- pls helparrow_forwardIndicate the compound resulting from the bromination of 3,5-dimethylpyrazolearrow_forward31) The reaction profile for a given chemical reaction is shown below A Energy Reactants Products B Progress of reaction a. Which arrow represents the activation energy for the forward reaction? b. Which arrow represents the activation energy for the backward reaction? c. Is the forward reaction exothermic or endothermic? d. Is the reverse reaction exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forward
- pls helparrow_forward10) What is the [OH-] concentration of a solution with a pH of 12.0? 1.0 x 10¹² M a. b. 1.0 x 10-12 M C. 1.0 x 10² M d. 1.0 x 102M 11) In which block of the periodic table would you find the element gold? a. b. s block P block C. d block d. f blockarrow_forward5) Who was responsible for the first model of the atom that included electrons? a. Dalton b. Thomson c. Bohr d. Rutherford 6) Which of the following rate laws is a fourth-order reaction? a. r = k[X][Y]²[Z] b._r= k[X]²[Y]³ C. r = k[X][Y]² d._r= k[X][Y]²[Z]ª 7) The activation energy of a particular reaction will decrease if: a. A catalyst is used. b. Temperature is increased. c. Reactant concentration is increased. d. All of the abovearrow_forward
- pls helparrow_forwardState the reason why compound A (m.p. 99-100°C) is heated under vacuum.1. So that the sample heating temperature is not too high when heated under vacuum.2. So that the temperature is higher than the melting point of compound A.3. So that cold water is not required in the sublimator.arrow_forwardTo find the theoretical % yield of a given reaction:1. actual amount obtained once crystallized2. (actual amount obtained / theoretical amount) x 1003. maximum amount of product that can be obtained / amount of initial reactantarrow_forward
- The reason activated carbon decolorizes and purifies a product is:1. It helps dissolve the product and then recrystallize it.2. It reacts with impurities in the product and removes them.3. It retains impurities by adsorption, purifying the product.arrow_forwardThe principle of a rotary evaporator is the same as that of:1. vacuum distillation2. reflux3. fractional distillationarrow_forwardAnhydrous MgSO4 is used to:1. Form a salt with the compound dissolved in the solution2. Remove water from a solution3. Neutralize a solutionarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

