
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (8th Edition)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780321885326
Author: Jane B. Reece, Martha R. Taylor, Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, Kelly A. Hogan
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 10TYK
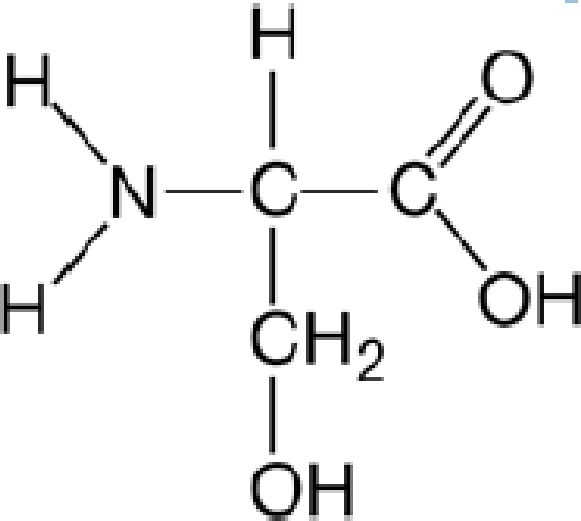
Circle and name the
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In order to establish the expiration date of perishable food, growth curve data must be collected. Once the microbial load is so high that it poses a hazard to human health, the food item is no longer considered safe (expired). Generally a load of x50,000
bacteria/gram is considered unsafe.
Your task is to determine the microbial growth curves for MicroYo, a new brand of yogurt. The growth is determined by sampling the yogurt and growing the bacterial isolates in broth culture which is then serially diluted by a total of x10,000 and inoculated onto
standard petri plates of nutrient agar. The following colony counts are measured:
Time (days)
MicroYo colony count#
1
1
4
1
12
2
16
20
4
7
What day should you recommend expiring the yogurt (the last possible date before the microbial load is unsafe).
12
4
20
16
9. Chicken combs in chickens is an example where you see interactions between genes.
See potential genotypes and phenotypes below. Which genotype, when mated to a
rose comb chicken, will produce progeny that are 50% walnut comb and 50% pea comb?
walnut
(RRPP)
walnut
(RrPP)
pea
(rrPP)
walnut
(RRPP)
walnut
(RrPp)
pea
(rrPp)
rose
rose
single
(RRPP)
(Rrpp)
(rrpp)
Describe a compound light microscope and its importance in microbiology (2) examples of at least two microbes viewed under a compound light microscope and their general characteristics (note: the microbes you choose do not need to be the ones outlined in the above tutorial video) and (3) at least one source you used for the information included in your infographic.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (8th Edition)
Ch. 3 - Complete the following table to help you review...Ch. 3 - A glucose molecule is to starch as (Explain your...Ch. 3 - What makes a fatty acid an acid? a. It does not...Ch. 3 - Prob. 4TYKCh. 3 - Of the following functional groups, which is/are...Ch. 3 - Prob. 6TYKCh. 3 - Prob. 7TYKCh. 3 - Prob. 8TYKCh. 3 - Which structural level of a protein would be least...Ch. 3 - Circle and name the functional groups in this...
Ch. 3 - Most proteins are soluble in the aqueous...Ch. 3 - Sucrose is broken down in your intestine to the...Ch. 3 - The diversity of life is staggering. Yet the...Ch. 3 - How can a cell make many different kinds of...Ch. 3 - Given that the function of egg yolk is to nourish...Ch. 3 - Enzymes usually function best at an optimal pH and...Ch. 3 - SCIENTIFIC THINKING Another aspect of the Nurses...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Price of visit Number of visits $700 0 $600 [1 $500 2 $400 3 $300 4 00000 The Table blow gives the demand curve for doctor visits for Elena. If the price of a doctor's visit is $600, and Elena does not have health insurance, she will visit the doctor times. If Elena obtains 50% coinsurance (the company pays 50% of the medical bill, Elena pays 50%), then Elena will visit the doctor times. 1; 2 0; 3 0; 2 1;4 2; 1arrow_forwardP 200 150- 100 50 w/instrance/ w/insurance 2 100 Demand Assume that the white curve (labeled "Demand") represents an individual's true demand for this particular health care service. The coinsurance associated with insurance option 1 (in blue) is likely _. 0000 100% 25% 50% 0%arrow_forwardUse the figure below. Bob and Nancy have the same income and total utility.. willingness to pay for an insurance premium will be lower than because they are. risk- averse. Total utility Current utility Bob's utility Nancy's utility 0000 Bob; Nancy; less Nancy; Bob; less Nancy; Bob; more Bob; Nancy; more Current Income incomearrow_forward
- Consider the figure below. Suppose the true price of a health care service is P1. Suppose further that the individual has obtained insurance that has a fixed copayment for this particular service. The copayment is represented by price P2. represents the quantity of the service the individual would consume without insurance. quantity of the service the individual would consume with the insurance. Health Care Service represents the P. P₂ a Q1;Q2 Q2; Q3 Q1; Q3 Q3; Q1 Q2; Q1 फ f Q ८ g d h Q3\D 7Q 00000arrow_forwardThe table shows the utility Jordan receives at various income levels, but they do not know what their income will be next year. There is a 15% chance their income will be $25,000, a 20% chance their income will be $35,000, and a 65% chance their income will be $45,000. We know that Jordan is Income $25,000 Utility 2,800 30,000 3,200 35,000 3,500 40,000 3,700 45,000 3,800 ☐ none of the above 0 000 risk taker (lover) because their marginal utility of income is increasing risk neutral because their marginal utility of income is constant risk averse because their marginal utility of income is decreasing risk neutral because their marginal utility of income is decreasingarrow_forwardOOOO a d+e d a+b+c Consider the figure below. Suppose the true price of a health care service is P1. Suppose further that the individual has obtained insurance that has a fixed copayment for this particular service. The copayment is represented by price P2. The social loss from moral hazard if the individual has copayment P2 is represented graphically by the area(s): Health Care Service P. a No 4 ८ e g Q2 Q3 Darrow_forward
- OOO O The table shows the utility Jordan receives at various income levels, but they do not know what their income will be next year. There is a 15% chance their income will be $25,000, a 20% chance their income will be $35,000, and a 65% chance their income will be $45,000. We know that Jordan's expected income is. Their utility from their expected income is_ Income $25,000 Utility 2,800 30,000 3,200 35,000 3,500 40,000 3,700 45,000 3,800 $45,000; 3,800 $40,000; 3,700 $25,000; 2,800 $35,000; 3,500 $30,000; 3,200arrow_forwardQuestion 1 Classify the Bird Mark 7; how is it: Powered Triggered Cycled Classify brid mark 7 Powered: By gas (oxygen) Triggered: Negative Pressure, caused by the patient’s inspiratory effort Cycled: The machine stops delivering gas and allows for exhalationarrow_forwardHypothetical "pedigree" for Sickle Cellarrow_forward
- would this be considered a novel protein and if not how can I fix it so it is and can you draw the corrections pleasearrow_forwardIn as much detail as possible, hand draw a schematic diagram of the hypothalamic-pituitary- gonad (HPG) axis in the human male. Be sure to include all the relevant structures and hormones. You must define all abbreviations the first time you use them. Please include (and explain) the feedback loops.arrow_forwardA negligence action was brought by a mother against a hospital on behalf of her minor daughter. It alleged that when the mother was 13 years of age, the hospital negligently transfused her with Rh-positive blood. The mother's Rh-negative blood was incompatible with and sensitized by the Rh-positive blood. The mother discovered her condition 8 years later during a routine blood screening ordered by her healthcare provider in the course of prenatal care. The resulting sensitization of the mother's blood allegedly caused damage to the fetus, resulting in physical defects and premature birth. Did a patient relationship with the transfusing hospital exist?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College


Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Macromolecules | Classes and Functions; Author: 2 Minute Classroom;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V5hhrDFo8Vk;License: Standard youtube license