
Concept explainers
GO Figure 28-52 gives the orientation energy U of a magnetic dipole in an external magnetic field
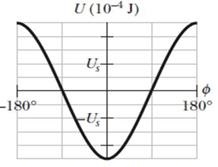
Figure 28-52 Problem 64.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardthe cable may break and cause severe injury. cable is more likely to break as compared to the [1] ds, inclined at angles of 30° and 50° to the vertical rings by way of a scaled diagram. [4] I 30° T₁ 3cm 3.8T2 cm 200 N 50° at it is headed due North and its airspeed indicat 240 km/h. If there is a wind of 100 km/h from We e relative to the Earth? [3]arrow_forwardCan you explain this using nodal analysis With the nodes I have present And then show me how many KCL equations I need to write, I’m thinking 2 since we have 2 dependent sourcesarrow_forward
- The shear leg derrick is used to haul the 200-kg net of fish onto the dock as shown in. Assume the force in each leg acts along its axis. 5.6 m. 4 m- B Part A Determine the compressive force along leg AB. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FAB = Value Submit Request Answer Part B Units ? Determine the compressive force along leg CB. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FCB= Value Submit Request Answer Part C ? Units Determine the tension in the winch cable DB. Express your answer with the appropriate units. 2marrow_forwardPart A (Figure 1) shows a bucket suspended from a cable by means of a small pulley at C. If the bucket and its contents have a mass of 10 kg, determine the location of the pulley for equilibrium. The cable is 6 m long. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 4 m B НА x = Value Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback < 1 of 1 T 1 m Units ?arrow_forwardThe particle in is in equilibrium and F4 = 165 lb. Part A Determine the magnitude of F1. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. ΑΣΦ tvec F₁ = Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the magnitude of F2. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. ΑΣΦ It vec F2 = Submit Request Answer Part C Determine the magnitude of F3. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. ? ? lb lb F₂ 225 lb 135° 45° 30° -60°-arrow_forward
- The 10-lb weight is supported by the cord AC and roller and by the spring that has a stiffness of k = 10 lb/in. and an unstretched length of 12 in. as shown in. Part A Determine the distance d to maintain equilibrium. Express your answer in inches to three significant figures. 節 ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ d = *k J vec 5 t 0 ? d C A in. 12 in. Barrow_forwardThe members of a truss are connected to the gusset plate as shown in . The forces are concurrent at point O. Take = 90° and T₁ = 7.5 kN. Part A Determine the magnitude of F for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. F = Value Submit Request Answer Part B 0 ? Units Determine the magnitude of T2 for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? T₂ = Value Units T₁ Carrow_forwardpls help on botharrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





