
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 28, Problem 6Q
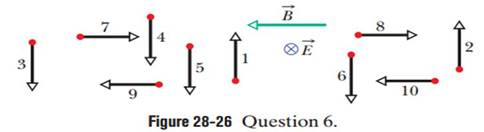 |
Figure 28-26 Question 6.
Table 28-3 Question 6
| Particle | Charge | Speed | Particle | Charge | Speed |
| 1 | + | Less | 6 | - | Greater |
| 2 | + | Greater | 7 | + | Less |
| 3 | + | Less | 8 | + | Greater |
| 4 | + | Greater | 9 | - | Less |
| 5 | - | Less | 10 | - | Greater |
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
You are working with a team that is designing a new roller coaster-type amusement park ride for a major theme park. You are present for the testing of the ride, in which an empty 150 kg car is sent along the entire ride. Near the end of the ride, the car is at near rest at the top of a 100 m
tall track. It then enters a final section, rolling down an undulating hill to ground level. The total length of track for this final section from the top to the ground is 250 m. For the first 230 m, a constant friction force of 370 N acts from computer-controlled brakes. For the last 20 m, which is
horizontal at ground level, the computer increases the friction force to a value required for the speed to be reduced to zero just as the car arrives at the point on the track at which the passengers exit.
(a) Determine the required constant friction force (in N) for the last 20 m for the empty test car.
N
(b) Find the highest speed (in m/s) reached by the car during the final section of track length…
A player kicks a football at the start of the game. After a 4 second flight, the ball touches the ground 50 m from the kicking tee. Assume air resistance is negligible and the take-off and landing height are the same (i.e., time to peak = time to fall = ½ total flight time). (Note: For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.) Calculate and answer all parts. Only use equations PROVIDED:
Chapter 28 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 28 - Prob. 1QCh. 28 - Prob. 2QCh. 28 - Prob. 3QCh. 28 - Prob. 4QCh. 28 - In Module 28-2, we discussed a charged particle...Ch. 28 - Figure 28-26 shows crossed uniform electic and...Ch. 28 - Figure 28-27 shows the path of an electron that...Ch. 28 - Figure 28-28 shows the path of an electron in a...Ch. 28 - a In Checkpoint 5, if the dipole moment is rotated...Ch. 28 - Particle round about. Figure 28-29 shows 11 paths...
Ch. 28 - Prob. 11QCh. 28 - Prob. 12QCh. 28 - Prob. 1PCh. 28 - A particle of mass 10 g and charge 80 C moves...Ch. 28 - An electron that has an instantaneous velocity of...Ch. 28 - An alpa particle travels at a velocity of...Ch. 28 - GO An electron moves through a unifrom magnetic...Ch. 28 - GO A proton moves through a uniform magnetic field...Ch. 28 - Prob. 7PCh. 28 - An electric field of 1.50 kV/m and a perpendicular...Ch. 28 - ILW In Fig. 28-32, an electron accelerated from...Ch. 28 - A proton travels through uniform magnetic and...Ch. 28 - Prob. 11PCh. 28 - Go At time t1 an electron is sent along the...Ch. 28 - Prob. 13PCh. 28 - A metal strip 6.50 cm long, 0.850 cm wide, and...Ch. 28 - Prob. 15PCh. 28 - Prob. 16PCh. 28 - An alpha particle can be produced in certain...Ch. 28 - Prob. 18PCh. 28 - Prob. 19PCh. 28 - Prob. 20PCh. 28 - SSM An electron of kinetic energy 1.20 keV circles...Ch. 28 - In a nuclear experiment a proton with kinetic...Ch. 28 - What uniform magnetic field, applied perpendicular...Ch. 28 - An electron is accelerated from rest by a...Ch. 28 - a Find the frequency of revolution of an electron...Ch. 28 - Prob. 26PCh. 28 - A mass spectrometer Fig. 28-12 is used to separate...Ch. 28 - A particle undergoes uniform circular motion of...Ch. 28 - An electron follows a helical path in a uniform...Ch. 28 - GO In Fig. 28-40. an electron with an initial...Ch. 28 - A particular type of fundamental particle decays...Ch. 28 - An source injects an electron of speed v = 1.5 ...Ch. 28 - Prob. 33PCh. 28 - An electron follows a helical path in a uniform...Ch. 28 - A proton circulates in a cyclotron, beginning...Ch. 28 - Prob. 36PCh. 28 - Prob. 37PCh. 28 - In a certain cyclotron a proton moves in a circle...Ch. 28 - SSM A horizontal power line carries a current of...Ch. 28 - A wire 1.80 m long carries a current of 13.0 A and...Ch. 28 - Prob. 41PCh. 28 - Prob. 42PCh. 28 - A single-turn current loop, carrying a current of...Ch. 28 - Prob. 44PCh. 28 - ACA /ACwire 50.0 cm long carries a 0.500 A current...Ch. 28 - In Fig. 28-44, a metal wire of mass m = 24.1 mg...Ch. 28 - GO A 1.0 kg copper rod rests on two horizontal...Ch. 28 - GO A long, rigid conductor, lying along an x axis,...Ch. 28 - Prob. 49PCh. 28 - An electron moves in a circle of radius r = 5.29 ...Ch. 28 - Prob. 51PCh. 28 - Prob. 52PCh. 28 - Prob. 53PCh. 28 - A magnetic dipole with a dipole moment of...Ch. 28 - Prob. 55PCh. 28 - Prob. 56PCh. 28 - Prob. 57PCh. 28 - Prob. 58PCh. 28 - A Current loop, carrying a current of 5.0 A, is in...Ch. 28 - Prob. 60PCh. 28 - Prob. 61PCh. 28 - Prob. 62PCh. 28 - A circular loop of wire having a radius of 8.0 cm...Ch. 28 - GO Figure 28-52 gives the orientation energy U of...Ch. 28 - Prob. 65PCh. 28 - Prob. 66PCh. 28 - A stationary circular wall clock has a face with a...Ch. 28 - A wire lying along a y axis from y = 0 to y =...Ch. 28 - Atom 1 of mass 35 u and atom 2 of mass 37 u are...Ch. 28 - Prob. 70PCh. 28 - Physicist S. A. Goudsmit devised a method for...Ch. 28 - A beam of electrons whose kinetic energy is K...Ch. 28 - Prob. 73PCh. 28 - Prob. 74PCh. 28 - Prob. 75PCh. 28 - Prob. 76PCh. 28 - Prob. 77PCh. 28 - In Fig. 28-8, show that the ratio of the Hall...Ch. 28 - Prob. 79PCh. 28 - An electron is moving at 7.20 106 m/s in a...Ch. 28 - Prob. 81PCh. 28 - Prob. 82PCh. 28 - Prob. 83PCh. 28 - A write lying along an x axis from x = 0 to x =...Ch. 28 - At one instant, m/s is the velocity of a proton in...Ch. 28 - An electron has velocity km/s as it enters a...Ch. 28 - Prob. 87PCh. 28 - Prob. 88PCh. 28 - In Fig. 28-58, an electron of mass m, charge e,...Ch. 28 - Prob. 90PCh. 28 - Prob. 91PCh. 28 - An electron that is moving through a uniform...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Some organizations are starting to envision a sustainable societyone in which each generation inherits sufficie...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Prokaryotes lack mitochondria. What structure does perform the functions of mitochondria in prokaryotes?
Microbiology: Principles and Explorations
Liquid glycol flows around an engine, cooling it as it absorbs energy. The glycol enters the engine at 60°C and...
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
What two body structures contain flexible elastic cartilage?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
8. A human maintaining a vegan diet (containing no animal products) would be a:
a. producer
b. primary consume...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Two culture media were inoculated with four different bacteria. After incubation, the following results were ob...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please answer.arrow_forwardA shot putter releases a shot at 13 m/s at an angle of 42 degrees to the horizontal and from a height of 1.83 m above the ground. (Note: For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.) Calculate and answer all parts. Only use equations PROVIDED:arrow_forward"looks" like a particle.) ...32 GO In Fig. 22-55, positive charge q = 7.81 pC is spread uni- formly along a thin nonconducting rod of length L = 14.5 cm. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (relative to the positive direction of the x axis) of the electric field produced at point P, at distance R = 6.00 cm from the rod along its perpendicular bisector? R y Р + + + + + + + + +-× L Figure 22-55 Problem 32.arrow_forward
- 1) A horizontal wire carrying current I in +x direction on the x-axis from x=0 to x=2 2) A vertical wire carrying current I upward at along the x=2 line from y=0 to y=8 3) A diagonal straight wire started at the origin and it ends at y=8 x=2 carrying a current in SE direction ( diagonally downward); y=4x In a regional magnetic field that is given in vector notation by B = ( y i - x j )/(x^2+y^2+25) As components Bx = (y+1)/x^2+y^2+25) By = (1- x )/(x^2+y^2+25) Find the integral expression for the net force for each branch carrying 5 ampere current.arrow_forwardAn electric power station that operates at 30 KV and uses a 15:1 set step-up ideal transformer is producing 400MW (Mega-Watt) of power that is to be sent to a big city with only 2.0% loss. What which is located 270 km away is the resistance of the Two wires that are being used? 52arrow_forwardSlink, from Toy Story, is a slinky dog whose middle section is a giant spring with a spring constant of 10.9 N/m. Woody, who has a mass of 0.412 kg, grabs onto the tail end of Slink and steps off the bed (as shown in figure A) with no initial velocity and reaches the floor right as his velocity hits zero again (as shown in figure C).arrow_forward
- The character Min Min from Arms was a DLC character added to Super Smash Bros. Min Min’s arms are large springs, with a spring constant of 8.53 ⋅ 10^3 N/m, which she uses to punch and fling away her opponents. Min Min pushes her spring arm against Steve, who is not moving, compressing it 1.20 m as shown in figure A. Steve has a mass of 81.6 kg. Assuming she uses only the spring to launch Steve, how fast is Steve moving when the spring is no longer compressed? As Steve goes flying away he goes over the edge of the level, as shown in figure C. What is the magnitude of Steve’s velocity when he is 2.00 m below where he started?arrow_forwardCalculate the energy needed to melt 50 g of 0°C icearrow_forwardTwo very long line charges are set up along lines that areparallel to the z-axis, so they set up Electric fields strictly in the xy plane. One goes throughthe x-axis at x = −0.40 m and has charge a density λ1 = +12.0 μC/m, the other goesthrough the x-axis at x = +0.40 m has charge density λ2 = −8.0 μC/m.A. Find the Electric field at point A: (0.40, 0.80) (distances in meters). Give answersin unit vector notation and draw a graph of the x-y plane with the E-fields you justfound.B. Find a point on the x-axis at which the total E-field is 0.arrow_forward
- In order to increase the amount of exercise in her daily routine, Tara decides to walk up the four flights of stairs to her car instead of taking the elevator. Each of the steps she takes are 18.0 cm high, and there are 12 steps per flight. (a) If Tara has a mass of 77.0 kg, what is the change in the gravitational potential energy of the Tara-Earth system (in J) when she reaches her car? ] (b) If the human body burns 1.5 Calories (6.28 x 10³ J) for each ten steps climbed, how much energy (in J) has Tara burned during her climb? ] (c) How does the energy she burned compare to the change in the gravitational potential energy of the system? Eburned Δυarrow_forwardA 4.40 kg steel ball is dropped onto a copper plate from a height of 10.0 m. If the ball leaves a dent 2.75 mm deep, what is the average force exerted by the plate on the ball during the impact? Narrow_forwardA block of mass m = 7.00 kg is released from rest from point and slides on the frictionless track shown in the figure below. (Assume h₂ = 7.80 m.) a m ha 3.20 m 2.00 m i (a) Determine the block's speed at points ® and point B ©. m/s m/s point (b) Determine the net work done by the gravitational force on the block as it moves from point J A to pointarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781111794378
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Magnets and Magnetic Fields; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IgtIdttfGVw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY