
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The reaction between
Concept introduction:
Deuterium is an isotope of hydrogen. Deuterium contains one neutron and one proton in its nucleus while hydrogen has only one proton in its nucleus but the number of electrons in hydrogen and deuterium is one.
Isotopic substitution is a reaction in which one isotope is substituted by the other
Answer to Problem 26.34AP
The complete reaction between
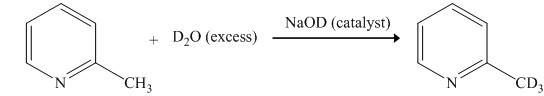
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
Figure 1
When

Figure 2
The complete reaction between
(b)
Interpretation:
The reaction between
Concept introduction:
Phenyllithium is an organometallic agent which is used to introduce metal into an organic compound during synthesis. It is used to give nucleophilic addition and substitution reactions.
Answer to Problem 26.34AP
The complete reaction between
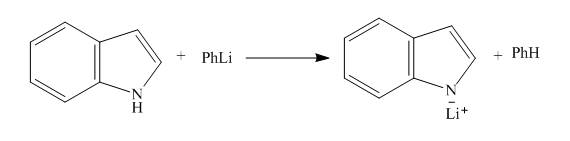
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
Figure 3
When indole reacts with phenyllithium, phenyllithium abstracts a proton bonded to nitrogen atom and a lithium salt of indole is formed as a conjugate base. The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 4
The complete reaction between
(c)
Interpretation:
The reaction of
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction involves the substitution of an electrophile on an aromatic ring. The
Answer to Problem 26.34AP
The complete reaction of
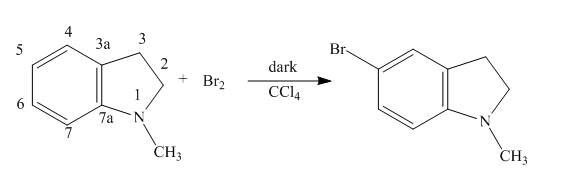
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
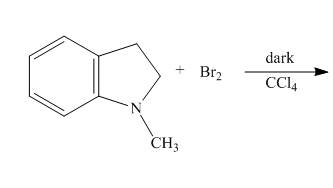
Figure 5
When
The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 6
The complete reaction of
(d)
Interpretation:
The reaction of pyrrolizine with hydrogen in presence of platinum and carbon catalyst is to be completed by giving the major product.
Concept introduction:
Catalytic hydrogenation is a reduction process of addition of hydrogen atoms in an
Answer to Problem 26.34AP
The complete reaction of pyrrolizine with hydrogen in presence of platinum and carbon catalyst is shown below.
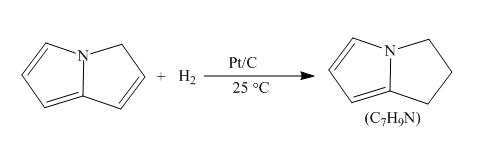
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
c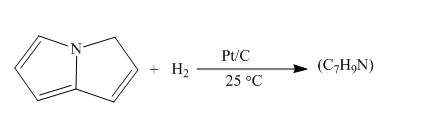
Figure 7
When pyrrolizine reacts with hydrogen in presence of

Figure 8
The complete reaction of pyrrolizine with hydrogen in presence of platinum and carbon catalyst is shown in Figure 8.
(e)
Interpretation:
The reaction of
Concept introduction:
Nitration is a process in which an
Answer to Problem 26.34AP
The complete reaction of
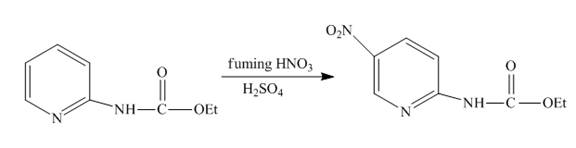
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
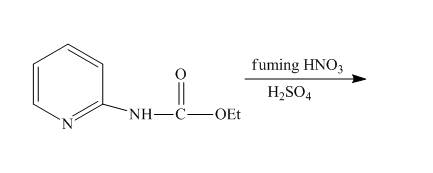
Figure 9
Nitration occurs when

Figure 10
The complete reaction of
(f)
Interpretation:
The reaction between
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction involves the substitution of an electrophile on an aromatic ring. The
Answer to Problem 26.34AP
The complete reaction between
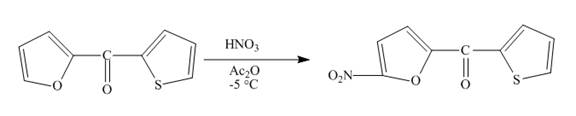
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
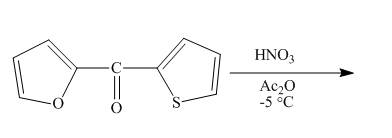
Figure 11
Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction will occur in Furan since it is more reactive than thiophene. Therefore, nitration will occur at carbon

Figure 12
The complete reaction between
(g)
Interpretation:
The reaction of
Concept introduction:
Nitration is a process in which an aromatic compound is nitrated by electrophilic substitution mechanism in presence of concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid. Electron donating groups substituted on the aromatic ring are those which donates electron to the aromatic ring. Electron donating groups are ortho and para-directing.
Answer to Problem 26.34AP
The complete reaction of
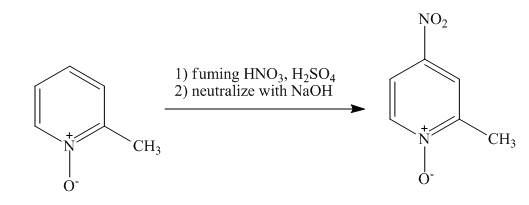
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
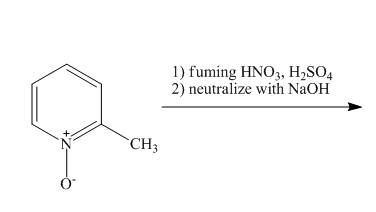
Figure 13
The pyridine ring activates towards electrophilic aromatic substitution due to the presence of pyridinium

Figure 14
The complete reaction of
(h)
Interpretation:
The reaction of
Concept introduction:
Wolff Kishner reduction is a reaction in which
Answer to Problem 26.34AP
The complete reaction of
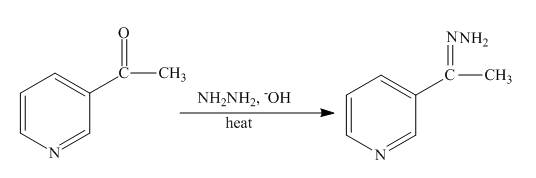
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
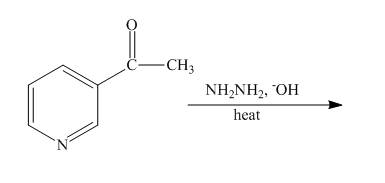
Figure 15
The Wolff-Kishner reduction takes place when

Figure 16
The complete reaction of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- 1. For each of the reaction "railroads" below, you are either asked to give the structure(s) of the starting material(s) or product(s), or provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the transformation, as indicated by the boxes. a. NaOMe H+ .CO,H HO₂C MeOH (excess) MeOH H3C Br يع CH3 1. LiAlH4 2. H3O+ 3. PBг3 H3C 1. Et-Li 2. H3O+ -CO₂Me -CO₂Me OH CH3 CH3 ল CH3arrow_forwardPredict the intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this organic reaction: NaOMe ག1, ད།་, - + H You can draw 1 and 2 in any arrangement you like. 2 work up Note: if either 1 or 2 consists of a pair of enantiomers, just draw one structure using line bonds instead of 3D (dash and wedge) bonds at the chiral center. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Parrow_forwardWhat is the total energy cost associated with the compound below adopting the shown conformation? CH3 HH DH CH3arrow_forward
- ΗΝ, Draw Final Product C cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Edit Enamine H3O+ CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H Edit Iminium Ionarrow_forwardHow many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?arrow_forwardIdentify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forward
- Identify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forwardWhy isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





