
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To indicate whether B vitamin niacin is involved as a cofactor in the processes of (1) transamination, (2) oxidative deamination, (3) urea cycle, (4) carbon skeleton degradation to CAC intermediates, or (5) carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Concept introduction:
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. The coenzymes containing B-vitamin serve as temporary carriers of atoms or functional groups in the redox and group transfer reactions associated with the
Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide. The desired product of the urea cycle is urea.
There are 20 standard amino acids. Each amino acid has a different carbon skeleton and has a different degradation pathway for its carbon skeleton.
(a)
Answer to Problem 26.115EP
B vitamin niacin is involved as a cofactor in the process of oxidative deamination and in carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Explanation of Solution
Coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Oxidative deamination reaction of glutamate requires dehydrogenase enzyme. It is an oxidoreductase enzyme and works with either
The oxidative deamination reaction of glutamate amino acid is as follows:
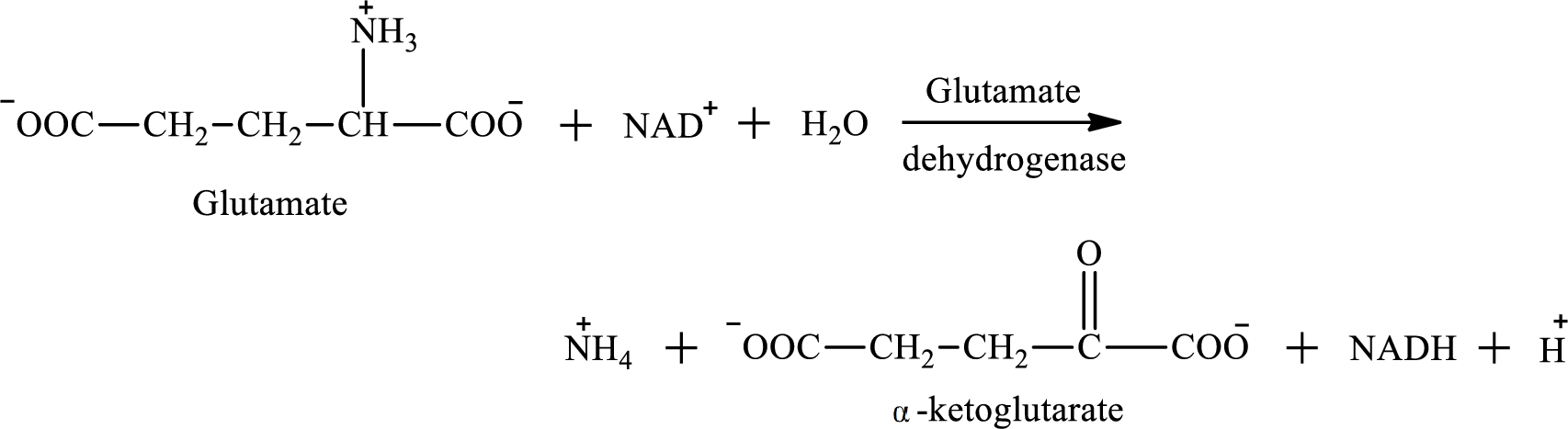
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
(b)
Interpretation:
To indicate whether B vitamin folate is involved as a cofactor in the processes of (1) transamination, (2) oxidative deamination, (3) urea cycle, (4) carbon skeleton degradation to CAC intermediates, or (5) carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Concept introduction:
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. The coenzymes containing B-vitamin serve as temporary carriers of atoms or functional groups in the redox and group transfer reactions associated with the metabolism of ingested food in order to obtain energy from the food.
Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide. The desired product of the urea cycle is urea.
There are 20 standard amino acids. Each amino acid has a different carbon skeleton and has a different degradation pathway for its carbon skeleton.
(b)
Answer to Problem 26.115EP
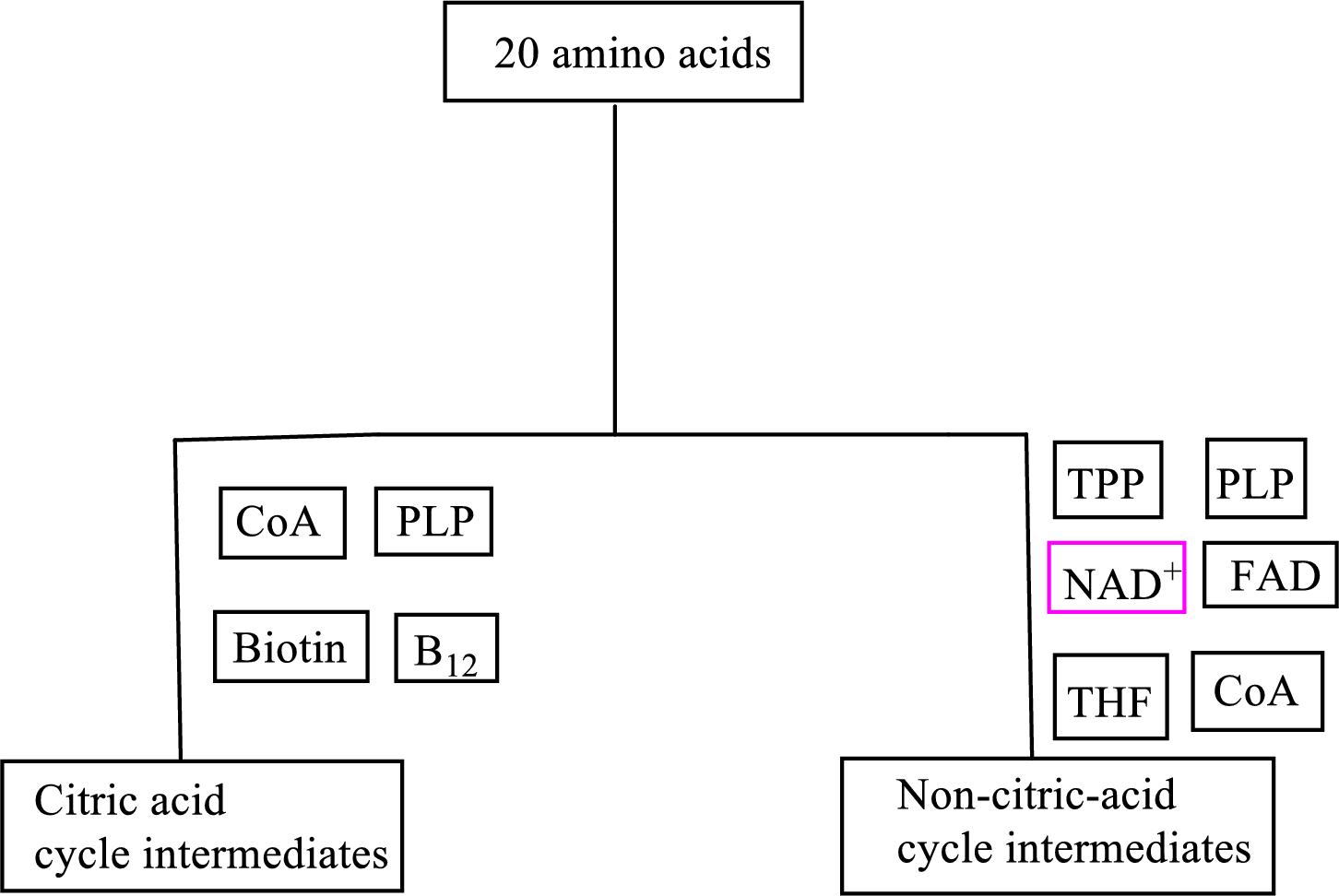
B vitamin folate is involved as a cofactor in carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Explanation of Solution
Coenzyme tetrahydrofolate
(c)
Interpretation:
To indicate whether B vitamin biotin is involved as a cofactor in the processes of (1) transamination, (2) oxidative deamination, (3) urea cycle, (4) carbon skeleton degradation to CAC intermediates, or (5) carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Concept introduction:
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. The coenzymes containing B-vitamin serve as temporary carriers of atoms or functional groups in the redox and group transfer reactions associated with the metabolism of ingested food in order to obtain energy from the food.
Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide. The desired product of the urea cycle is urea.
There are 20 standard amino acids. Each amino acid has a different carbon skeleton and has a different degradation pathway for its carbon skeleton.
(c)
Answer to Problem 26.115EP
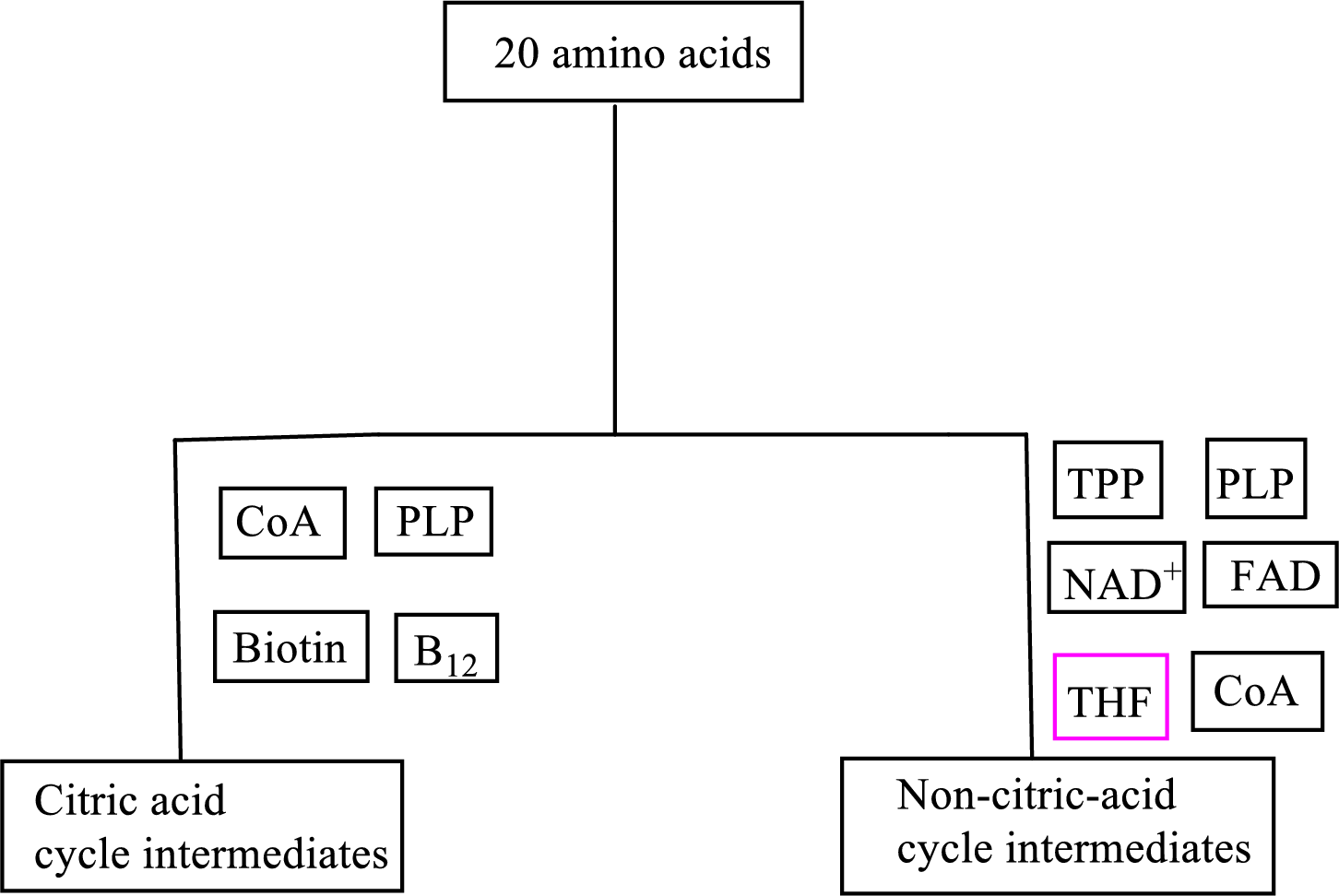
B vitamin biotin is involved as a cofactor in carbon skeleton degradation to CAC intermediates.
Explanation of Solution
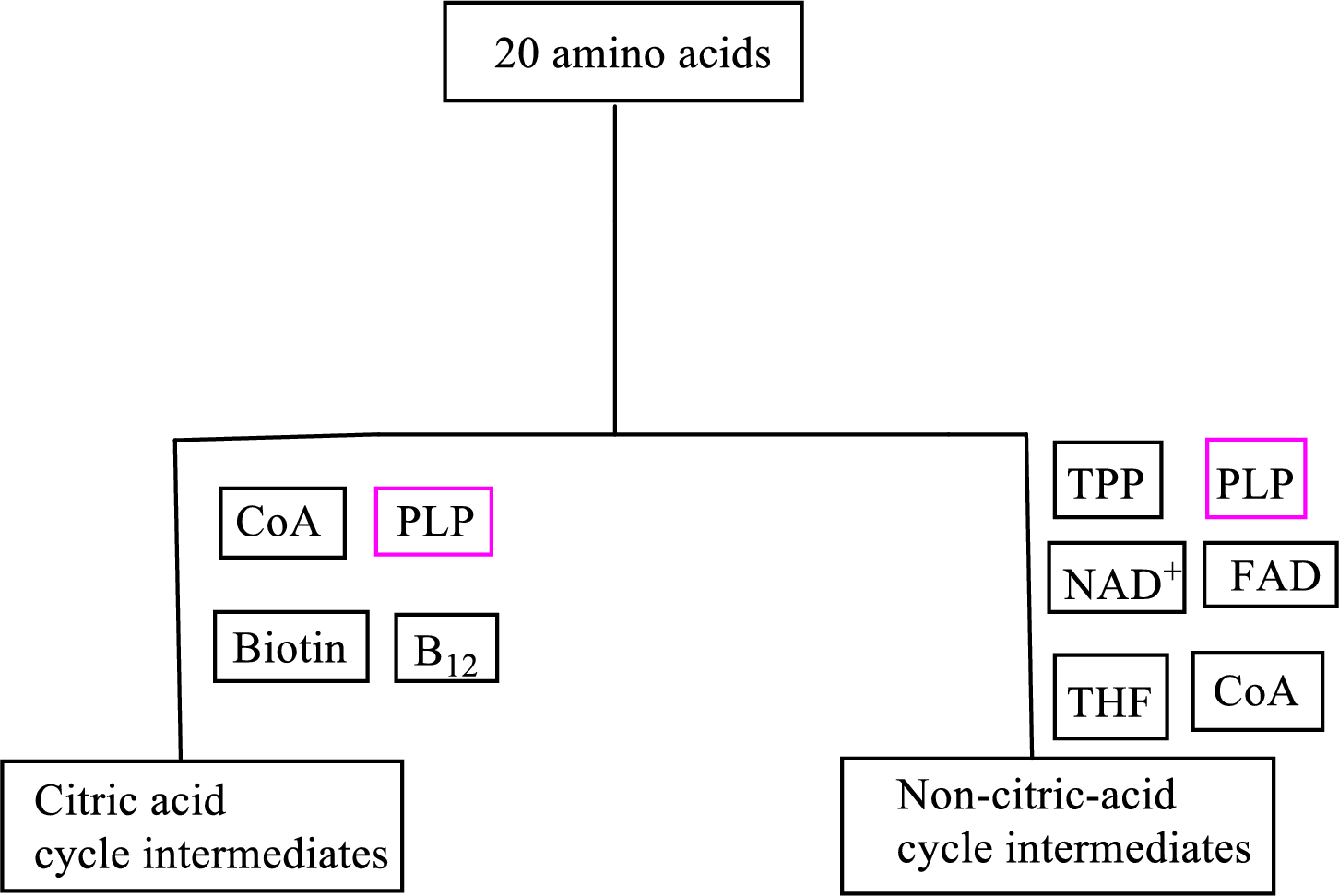
Biotin is involved in the carbon skeleton degradation pathway to CAC intermediates. An overview of the B vitamin participations in the degradation pathways for the carbon skeletons of the 20 standard amino acids is as follows:
(d)
Interpretation:
To indicate whether B vitamin
Concept introduction:
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. The coenzymes containing B-vitamin serve as temporary carriers of atoms or functional groups in the redox and group transfer reactions associated with the metabolism of ingested food in order to obtain energy from the food.
Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide. The desired product of the urea cycle is urea.
There are 20 standard amino acids. Each amino acid has a different carbon skeleton and has a different degradation pathway for its carbon skeleton.
(d)
Answer to Problem 26.115EP
Explanation of Solution
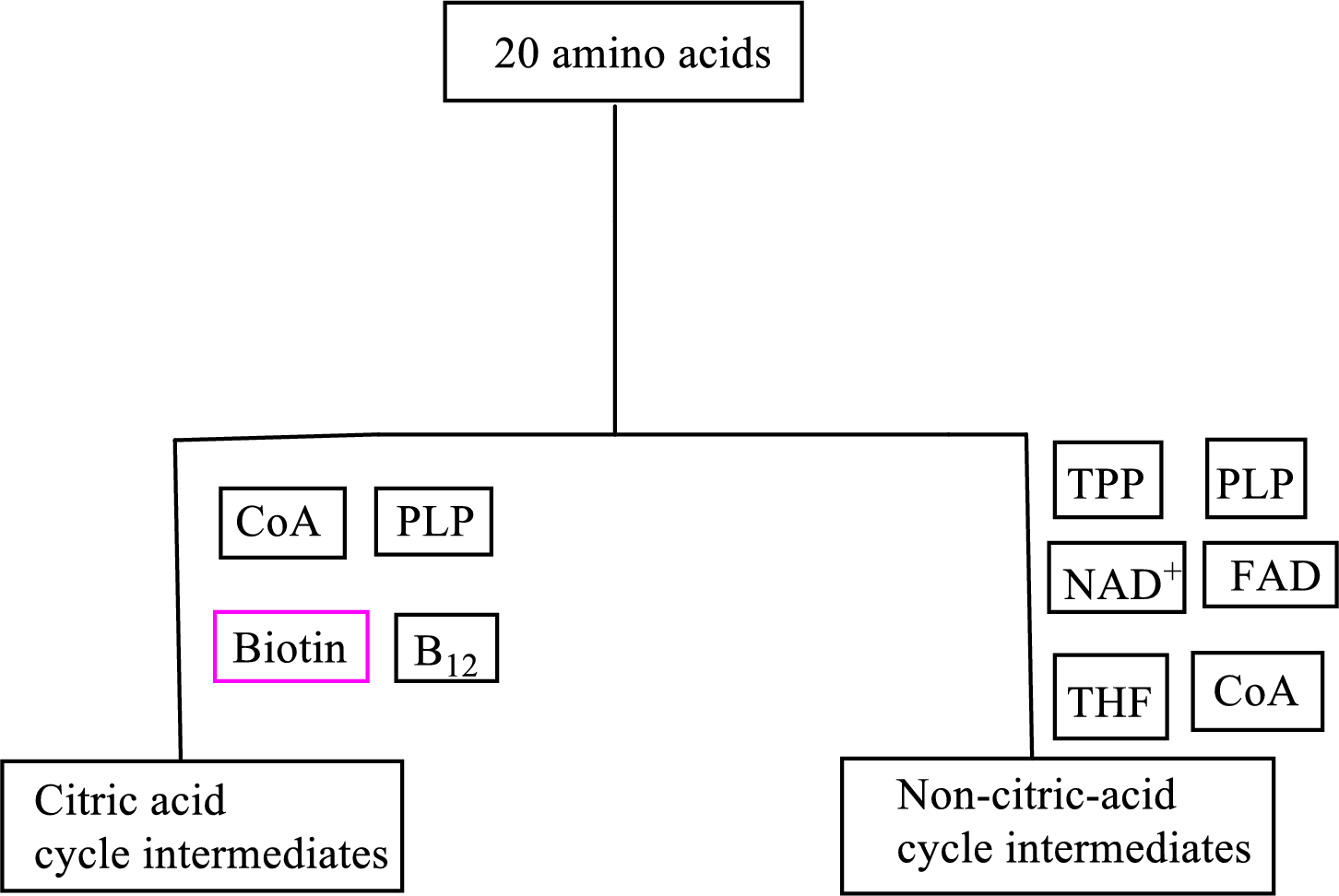
Coenzyme
Transamination reaction involves a simple transfer of amino groups but the overall reaction occurs in several steps and also requires
Coenzyme
An overview of the B vitamin participations in the degradation pathways for the carbon skeletons of the 20 standard amino acids is as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, AND BIOLOGICAL CH
- 9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Vanctions +H₂504 4.50+ T C. +212 Fellz 237 b. Praw the potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Rauctions and account For any differences that appear in the two potential Puergy Diagrams which of here two reactions 19 Found to be Reversable, Rationalice your answer based upon the venation mechanisms and the potential energy diagrams.arrow_forward9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Veritious +H2504 4.50+ + 1/₂ Felly ◎+ 7 b. Praw he potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Ronctions and account for any differences that appeak in the two potential Puergy Diagramsarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining 1. excess Br2, NaOH 2. neutralizing workup Qarrow_forward
- Given the electrode Pt | Ag | Ag+ (aq), describe it.arrow_forwardAt 25°C, the reaction Zn2+ + 2e ⇄ Zn has a normal equilibrium potential versus the saturated calomel electrode of -1.0048 V. Determine the normal equilibrium potential of Zn versus the hydrogen electrode.Data: The calomel electrode potential is E° = 0.2420 V versus the normal hydrogen electrode.arrow_forwardElectrochemistry. State the difference between E and E0.arrow_forward
- In an electrolytic cell, the positive pole is always assumed to be on the right side of the battery notation. Is that correct?arrow_forwardIn an electrolytic cell, the positive pole is always assumed to be on the right side of the battery. Is that correct?arrow_forwardCalculate the free energy of formation of 1 mol of Cu in cells where the electrolyte is 1 mol dm-3 Cu2+ in sulfate solution, pH 0. E° for the Cu2+/Cu pair in this medium is +142 mV versus ENH.Assume the anodic reaction is oxygen evolution.Data: EH2 = -0.059 pH (V) and EO2 = 1.230 - 0.059 pH (V); 2.3RT/F = 0.059 Varrow_forward
- If the normal potential for the Fe(III)/Fe(II) pair in acid at zero pH is 524 mV Hg/Hg2Cl2 . The potential of the saturated calomel reference electrode is +246 mV versus the NHE. Calculate E0 vs NHE.arrow_forwardGiven the galvanic cell whose scheme is: (-) Zn/Zn2+ ⋮⋮ Ag+/Ag (+). If we know the normal potentials E°(Zn2+/Zn) = -0.76V and E°(Ag+/Ag) = 0.799 V. Indicate the electrodes that are the anode and the cathode and calculate the E0battery.arrow_forwardIndicate the functions that salt bridges have in batteries.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





