
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781133939146
Author: Katz, Debora M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 25, Problem 26PQ
Three point charges q1 = 2.0 nC, q2 = −4.0 nC, and q3 = −3.0 nC are placed as shown in Figure P25.26. Find the electric flux through each of the closed Gaussian surfaces C1, C2, C3, and C4.
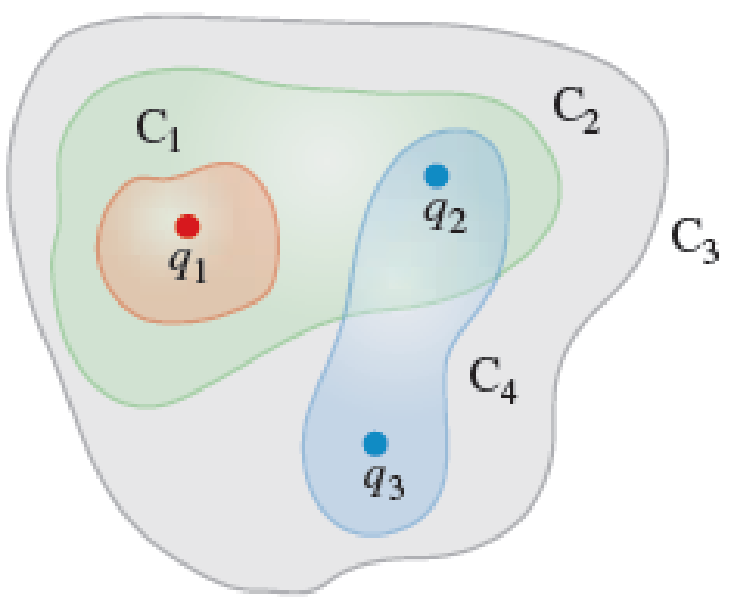
FIGURE P25.26
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Can I get help with how to calculate total displacement? The answer is 78.3x-4.8y
2.70 Egg Drop. You are on the Figure P2.70
roof of the physics building, 46.0 m
above the ground (Fig. P2.70). Your
physics professor, who is 1.80 m tall,
is walking alongside the building at
a constant speed of 1.20 m/s. If you
wish to drop an egg on your profes-
sor's head, where should the profes-
sor be when you release the egg?
Assume that the egg is in free fall.
2.71 CALC The acceleration
of a particle is given by ax(t) =
-2.00 m/s² +(3.00 m/s³)t. (a)
Find the initial velocity Vox such that
v = 1.20 m/s
1.80 m
46.0 m
One has to push down a ball with a force of 470 Newtons in order to hold the ball still, completely submerged under the surface of the water. What is the volume of the styrofoam ball in cubic meters? Use 997 kg/m3 as the density of water, 95 kg/m3 for the density of the styrofoam, and g = 9.8 m/s2.
Chapter 25 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
Ch. 25.1 - a. List all the uppercase letters that have the...Ch. 25.2 - The terms electric force, electric field, and...Ch. 25.2 - Prob. 25.3CECh. 25.3 - Which of the following expressions are correct...Ch. 25.3 - Find the electric flux through the three Gaussian...Ch. 25.4 - Prob. 25.6CECh. 25.7 - Is it possible for the charged solid sphere in...Ch. 25 - Which word or name has the same symmetry as the...Ch. 25 - Prob. 2PQCh. 25 - Prob. 3PQ
Ch. 25 - Prob. 4PQCh. 25 - Prob. 5PQCh. 25 - Prob. 6PQCh. 25 - A positively charged sphere and a negatively...Ch. 25 - A circular hoop of radius 0.50 m is immersed in a...Ch. 25 - Prob. 9PQCh. 25 - If the hemisphere (surface C) in Figure 25.10...Ch. 25 - A Ping-Pong paddle with surface area 3.80 102 m2...Ch. 25 - Prob. 12PQCh. 25 - A pyramid has a square base with an area of 4.00...Ch. 25 - Prob. 14PQCh. 25 - Prob. 15PQCh. 25 - A circular loop with radius r is rotating with...Ch. 25 - A circular loop with radius r is rotating with...Ch. 25 - Prob. 18PQCh. 25 - What is the net electric flux through each of the...Ch. 25 - Prob. 20PQCh. 25 - The colored regions in Figure P25.21 represent...Ch. 25 - Prob. 22PQCh. 25 - Prob. 23PQCh. 25 - Three particles and three Gaussian surfaces are...Ch. 25 - A Using Gausss law, find the electric flux through...Ch. 25 - Three point charges q1 = 2.0 nC, q2 = 4.0 nC, and...Ch. 25 - Prob. 27PQCh. 25 - A very long, thin wire fixed along the x axis has...Ch. 25 - Figure P25.29 shows a wry long tube of inner...Ch. 25 - Two very long, thin, charged rods lie in the same...Ch. 25 - Prob. 31PQCh. 25 - Two long, thin rods each have linear charge...Ch. 25 - Figure P25.33 shows a very long, thick rod with...Ch. 25 - A very long line of charge with a linear charge...Ch. 25 - Two infinitely long, parallel lines of charge with...Ch. 25 - An infinitely long wire with uniform linear charge...Ch. 25 - Prob. 37PQCh. 25 - Prob. 38PQCh. 25 - Prob. 39PQCh. 25 - Prob. 40PQCh. 25 - Two uniform spherical charge distributions (Fig....Ch. 25 - FIGURE P25.41 Problems 41 and 42. Two uniform...Ch. 25 - The nonuniform charge density of a solid...Ch. 25 - Prob. 44PQCh. 25 - What is the magnitude of the electric field just...Ch. 25 - Prob. 46PQCh. 25 - The infinite sheets in Figure P25.47 are both...Ch. 25 - Prob. 48PQCh. 25 - Prob. 49PQCh. 25 - Prob. 50PQCh. 25 - A very large, flat slab has uniform volume charge...Ch. 25 - FIGURE P25.41 Problems 51 and 52. Find the surface...Ch. 25 - Prob. 53PQCh. 25 - Prob. 54PQCh. 25 - If the magnitude of the surface charge density of...Ch. 25 - A spherical conducting shell with a radius of...Ch. 25 - A charged rod is placed in the center along the...Ch. 25 - A charged rod is placed in the center along the...Ch. 25 - A thick spherical conducting shell with an inner...Ch. 25 - A thick spherical conducting shell with an inner...Ch. 25 - A rectangular plate with sides 0.60 m and 0.40 m...Ch. 25 - Prob. 62PQCh. 25 - Prob. 63PQCh. 25 - A uniform spherical charge distribution has a...Ch. 25 - A rectangular surface extends from x = 0 to x =...Ch. 25 - A uniform electric field E = 1.57 104 N/C passes...Ch. 25 - A solid plastic sphere of radius R1 = 8.00 cm is...Ch. 25 - Examine the summary on page 780. Why are...Ch. 25 - Prob. 69PQCh. 25 - Prob. 70PQCh. 25 - Prob. 71PQCh. 25 - A coaxial cable is formed by a long, straight wire...Ch. 25 - Prob. 73PQCh. 25 - Prob. 74PQCh. 25 - A solid sphere of radius R has a spherically...Ch. 25 - A solid sphere of radius R has a spherically...Ch. 25 - A very large, horizontal conducting square plate...Ch. 25 - Prob. 78PQCh. 25 - A particle with charge q = 7.20 C is surrounded by...Ch. 25 - A sphere with radius R has a charge density given...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The cube is placed in a bucket of water and find that it floats, with 33% of its volume submerged below the surface of the water. What is the density of the mystery material? The material is uniformly distributed throughout the solid cube, with the number of kg/m3.arrow_forward2.82 A ball is thrown straight up from the ground with speed Up. At the same instant, a second ball is dropped from rest from a height H, directly above the point where the first ball was thrown upward. There is no air resistance. (a) Find the time at which the two balls collide. (b) Find the value of H in terms of un, and g such that at the instant when the balls collide, the first ball is at the highest point of its motion.arrow_forwardThe small piston has an area A1=0.033 m2 and the large piston has an area A2= 4.0 m2. What force F2 will the large piston provide if the small piston is pushed down with a force of 15 Newtons with an answer in Newtons?arrow_forward
- 2.23 BIO Automobile Airbags. The human body can survive an acceleration trauma incident (sudden stop) if the magnitude of the ac- celeration is less than 250 m/s². If you are in an automobile accident with an initial speed of 105 km/h (65 mi/h) and are stopped by an air- bag that inflates from the dashboard, over what minimum distance must the airbag stop you for you to survive the crash?arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer these problems correctly.Thank you!!arrow_forward2.2. In an experiment, a shearwater (a seabird) was taken from its nest, flown 5150 km away, and released. The bird found its way back to its nest 13.5 days after release. If we place the origin at the nest and extend the +x-axis to the release point, what was the bird's average ve- locity in m/s (a) for the return flight and (b) for the whole episode, from leaving the nest to returning?arrow_forward
- Use relevant diagrams where necessary and go through it in detailsarrow_forwardYour blood pressure (usually given in units of "mm of Hg") is a result of the heart muscle pushing on your blood. The left side of the heart creates a pressure of 115 mm Hg by exerting a force directly on the blood over an effective area of 14.5 cm2. What force does it exert to accomplish this? (Give your answer as the number of Newtons and note that you will need to do some unit conversions.)arrow_forwardWhat is the absolute (total) pressure experienced by a diver at a depth of 17 meters below the surface of a lake? Assume that atmospheric pressure at the surface of the lake is 101,000 Pascals, g= 9.8 m/s2, and the density of the water in the lake is 997 kg/m3. Give your answer as the number of Pascals.arrow_forward
- A particular solid cube has an edge of length 0.59 meters and is made of a material whose density is 3500 kg/m3. What is the mass of the cube? Give your answer as the number of kilograms.arrow_forwardSolve and answer correctly please.Thank you!!arrow_forwardA cart on wheels (assume frictionless) with a mass of 20 kg is pulled rightward with a 50N force. What is its acceleration?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY