
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781133939146
Author: Katz, Debora M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 25.7, Problem 25.7CE
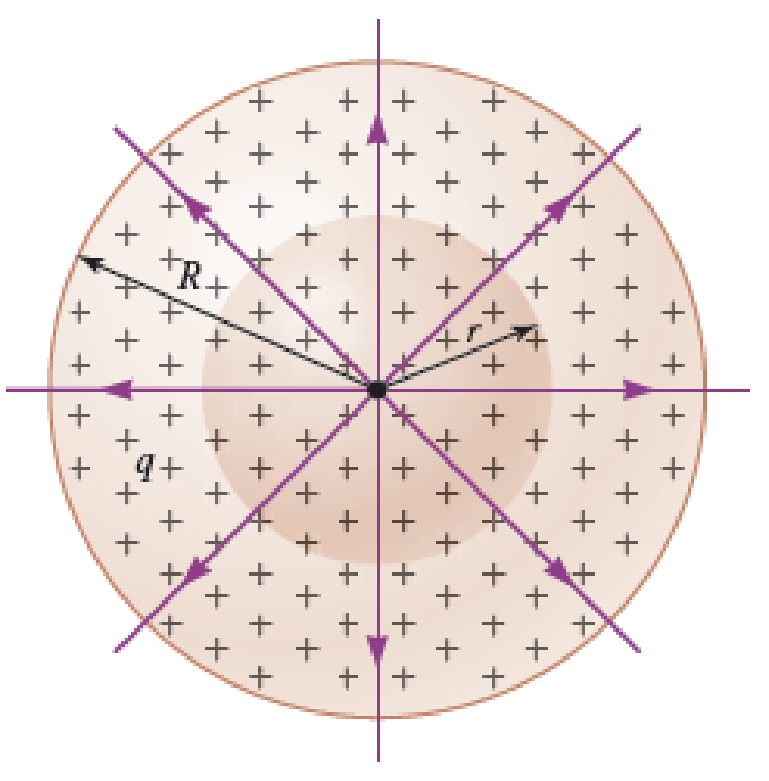
Is it possible for the charged solid sphere in Figure 25.23 to be a conductor in electrostatic equilibrium? Explain.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
4.) The diagram shows the electric field lines of a positively charged conducting sphere of
radius R and charge Q.
A
B
Points A and B are located on the same field line.
A proton is placed at A and released from rest. The magnitude of the work done by the electric field in
moving the proton from A to B is 1.7×10-16 J. Point A is at a distance of 5.0×10-2m from the centre of
the sphere. Point B is at a distance of 1.0×10-1 m from the centre of the sphere.
(a) Explain why the electric potential decreases from A to B. [2]
(b) Draw, on the axes, the variation of electric potential V with distance r from the centre of the
sphere.
R
[2]
(c(i)) Calculate the electric potential difference between points A and B. [1]
(c(ii)) Determine the charge Q of the sphere. [2]
(d) The concept of potential is also used in the context of gravitational fields. Suggest why scientists
developed a common terminology to describe different types of fields. [1]
3.) The graph shows how current I varies with potential difference V across a component X.
904
80-
70-
60-
50-
I/MA
40-
30-
20-
10-
0+
0
0.5
1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
VIV
Component X and a cell of negligible internal resistance are placed in a circuit.
A variable resistor R is connected in series with component X. The ammeter reads 20mA.
4.0V
4.0V
Component X and the cell are now placed in a potential divider circuit.
(a) Outline why component X is considered non-ohmic. [1]
(b(i)) Determine the resistance of the variable resistor. [3]
(b(ii)) Calculate the power dissipated in the circuit. [1]
(c(i)) State the range of current that the ammeter can measure as the slider S of the potential divider
is moved from Q to P. [1]
(c(ii)) Describe, by reference to your answer for (c)(i), the advantage of the potential divider
arrangement over the arrangement in (b).
1.) Two long parallel current-carrying wires P and Q are separated by 0.10 m. The current in wire P is 5.0 A.
The magnetic force on a length of 0.50 m of wire P due to the current in wire Q is 2.0 × 10-s N.
(a) State and explain the magnitude of the force on a length of 0.50 m of wire Q due to the current in P. [2]
(b) Calculate the current in wire Q. [2]
(c) Another current-carrying wire R is placed parallel to wires P and Q and halfway between them as shown.
wire P
wire R
wire Q
0.05 m
0.05 m
The net magnetic force on wire Q is now zero.
(c.i) State the direction of the current in R, relative to the current in P.[1]
(c.ii) Deduce the current in R. [2]
Chapter 25 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
Ch. 25.1 - a. List all the uppercase letters that have the...Ch. 25.2 - The terms electric force, electric field, and...Ch. 25.2 - Prob. 25.3CECh. 25.3 - Which of the following expressions are correct...Ch. 25.3 - Find the electric flux through the three Gaussian...Ch. 25.4 - Prob. 25.6CECh. 25.7 - Is it possible for the charged solid sphere in...Ch. 25 - Which word or name has the same symmetry as the...Ch. 25 - Prob. 2PQCh. 25 - Prob. 3PQ
Ch. 25 - Prob. 4PQCh. 25 - Prob. 5PQCh. 25 - Prob. 6PQCh. 25 - A positively charged sphere and a negatively...Ch. 25 - A circular hoop of radius 0.50 m is immersed in a...Ch. 25 - Prob. 9PQCh. 25 - If the hemisphere (surface C) in Figure 25.10...Ch. 25 - A Ping-Pong paddle with surface area 3.80 102 m2...Ch. 25 - Prob. 12PQCh. 25 - A pyramid has a square base with an area of 4.00...Ch. 25 - Prob. 14PQCh. 25 - Prob. 15PQCh. 25 - A circular loop with radius r is rotating with...Ch. 25 - A circular loop with radius r is rotating with...Ch. 25 - Prob. 18PQCh. 25 - What is the net electric flux through each of the...Ch. 25 - Prob. 20PQCh. 25 - The colored regions in Figure P25.21 represent...Ch. 25 - Prob. 22PQCh. 25 - Prob. 23PQCh. 25 - Three particles and three Gaussian surfaces are...Ch. 25 - A Using Gausss law, find the electric flux through...Ch. 25 - Three point charges q1 = 2.0 nC, q2 = 4.0 nC, and...Ch. 25 - Prob. 27PQCh. 25 - A very long, thin wire fixed along the x axis has...Ch. 25 - Figure P25.29 shows a wry long tube of inner...Ch. 25 - Two very long, thin, charged rods lie in the same...Ch. 25 - Prob. 31PQCh. 25 - Two long, thin rods each have linear charge...Ch. 25 - Figure P25.33 shows a very long, thick rod with...Ch. 25 - A very long line of charge with a linear charge...Ch. 25 - Two infinitely long, parallel lines of charge with...Ch. 25 - An infinitely long wire with uniform linear charge...Ch. 25 - Prob. 37PQCh. 25 - Prob. 38PQCh. 25 - Prob. 39PQCh. 25 - Prob. 40PQCh. 25 - Two uniform spherical charge distributions (Fig....Ch. 25 - FIGURE P25.41 Problems 41 and 42. Two uniform...Ch. 25 - The nonuniform charge density of a solid...Ch. 25 - Prob. 44PQCh. 25 - What is the magnitude of the electric field just...Ch. 25 - Prob. 46PQCh. 25 - The infinite sheets in Figure P25.47 are both...Ch. 25 - Prob. 48PQCh. 25 - Prob. 49PQCh. 25 - Prob. 50PQCh. 25 - A very large, flat slab has uniform volume charge...Ch. 25 - FIGURE P25.41 Problems 51 and 52. Find the surface...Ch. 25 - Prob. 53PQCh. 25 - Prob. 54PQCh. 25 - If the magnitude of the surface charge density of...Ch. 25 - A spherical conducting shell with a radius of...Ch. 25 - A charged rod is placed in the center along the...Ch. 25 - A charged rod is placed in the center along the...Ch. 25 - A thick spherical conducting shell with an inner...Ch. 25 - A thick spherical conducting shell with an inner...Ch. 25 - A rectangular plate with sides 0.60 m and 0.40 m...Ch. 25 - Prob. 62PQCh. 25 - Prob. 63PQCh. 25 - A uniform spherical charge distribution has a...Ch. 25 - A rectangular surface extends from x = 0 to x =...Ch. 25 - A uniform electric field E = 1.57 104 N/C passes...Ch. 25 - A solid plastic sphere of radius R1 = 8.00 cm is...Ch. 25 - Examine the summary on page 780. Why are...Ch. 25 - Prob. 69PQCh. 25 - Prob. 70PQCh. 25 - Prob. 71PQCh. 25 - A coaxial cable is formed by a long, straight wire...Ch. 25 - Prob. 73PQCh. 25 - Prob. 74PQCh. 25 - A solid sphere of radius R has a spherically...Ch. 25 - A solid sphere of radius R has a spherically...Ch. 25 - A very large, horizontal conducting square plate...Ch. 25 - Prob. 78PQCh. 25 - A particle with charge q = 7.20 C is surrounded by...Ch. 25 - A sphere with radius R has a charge density given...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2.) A 50.0 resistor is connected to a cell of emf 3.00 V. The voltmeter and the ammeter in the circuit are ideal. V A 50.00 (a) The current in the ammeter is 59.0 mA. Calculate the internal resistance of the cell. The circuit is changed by connecting another resistor R in parallel to the 50.0 resistor. V A 50.00 R (b) Explain the effect of this change on R is made of a resistive wire of uniform cross-sectional area 3.1 × 10-8 m², resistivity 4.9 × 10-70m and length L. The resistance of R is given by the equation R = KL where k is a constant. (b.i) the reading of the ammeter. [2] (b.ii) the reading of the voltmeter. [2] (c) Calculate k. State an appropriate unit for your answer. [3] [2]arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- A rod 12.0 cm long is uniformly charged and has a total charge of -20.0 μc. Determine the magnitude and direction of the electric field along the axis of the rod at a point 32.0 cm from its center. 361000 ☑ magnitude What is the general expression for the electric field along the axis of a uniform rod? N/C direction toward the rodarrow_forwardA certain brand of freezer is advertised to use 730 kW h of energy per year. Part A Assuming the freezer operates for 5 hours each day, how much power does it require while operating? Express your answer in watts. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? P Submit Request Answer Part B W If the freezer keeps its interior at a temperature of -6.0° C in a 20.0° C room, what is its theoretical maximum performance coefficient? Enter your answer numerically. K = ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer Part C What is the theoretical maximum amount of ice this freezer could make in an hour, starting with water at 20.0°C? Express your answer in kilograms. m = Ο ΑΣΦ kgarrow_forwardDescribe the development of rational choice theory in sociology. Please includearrow_forward
- A-E pleasearrow_forwardA 11.8 L gas tank containing 3.90 moles of ideal He gas at 26.0°C is placed inside a completely evacuated insulated bell jar of volume 39.0 L .A small hole in the tank allows the He to leak out into the jar until the gas reaches a final equilibrium state with no more leakage. Part A What is the change in entropy of this system due to the leaking of the gas? ■ ΜΕ ΑΣΦ AS = ? J/K Submit Request Answer Part B Is the process reversible or irreversible?arrow_forwardA-E pleasearrow_forward
- Three moles of an ideal gas undergo a reversible isothermal compression at 20.0° C. During this compression, 1900 J of work is done on the gas. For related problem-solving tips and strategies, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of Entropy change in a free expansion. Part A What is the change of entropy of the gas? ΤΕ ΑΣΦ AS = Submit Request Answer J/Karrow_forward5.97 Block A, with weight 3w, slides down an inclined plane S of slope angle 36.9° at a constant speed while plank B, with weight w, rests on top of A. The plank is attached by a cord to the wall (Fig. P5.97). (a) Draw a diagram of all the forces acting on block A. (b) If the coefficient of kinetic friction is the same between A and B and between S and A, determine its value. Figure P5.97 B A S 36.9°arrow_forwardPlease take your time and solve each part correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics Capacitor & Capacitance part 7 (Parallel Plate capacitor) CBSE class 12; Author: LearnoHub - Class 11, 12;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JoW6UstbZ7Y;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY