
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether NAD+ is involved in (1) glycerol
Concept introduction:
Triacylglycerol mobilization is an ongoing process in which triacylglycerols that are stored in the adipose tissue are hydrolyzed. Fatty acids and glycerol are the products of triacylglycerol mobilization. The products are released into the bloodstream.
After entering the bloodstream, the glycerol travels to the kidneys or liver. The first stage of glycerol metabolism occurs in the liver or kidney. The first stage of glycerol metabolism is a two-step process. After the first stage, the remaining stages of glycerol metabolism are the same as glucose pathways. The overall equation for glycerol metabolism is as follows:
Fatty acids are molecules that are long hydrocarbon chain of
The fatty acids are broken down to provide energy. The breakdown of fatty acids is a three parts process. In the first part, the fatty acid is activated. In the second part, the transportation of fatty acid into the mitochondrial matrix is facilitated by a shuttle mechanism. In the third part, the fatty acid is readily oxidized, cycling through a series of four reactions. In these series of reactions, acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA. This pathway is termed as a β-oxidation pathway. Acetyl CoA, FADH2, and NADH are produced in this pathway.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is associated with the
(a)
Answer to Problem 25.47EP
NAD+ is involved in (3) both glycerol metabolism and fatty acid metabolism.
Explanation of Solution
The first stage of glycerol metabolism is a two-step process. In step 1, glycerol-3-phosphate is formed as the intermediate compound that further reacts to form dihydroxyacetone phosphate in step 2. The reaction for the conversion of glycerol is as follows:
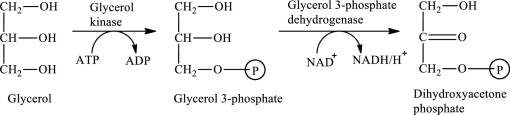
Here, represents
represents
In step 2 of glycerol metabolism, NAD+ oxidized glycerol-3-phosphate to dihydroxyacetone phosphate. Therefore, NAD+ is involved in glycerol metabolism.
The reaction in step 3 of a turn of the β-oxidation pathway is a dehydrogenation reaction in which two hydrogen atoms are removed from L-β-hydroxyacyl CoA. In this reaction, the β-hydroxy group is converted to a β-keto group. NAD+ is used as an oxidizing agent. This reaction is catalyzed by β-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase enzyme. The reaction for step 3 is as follows:
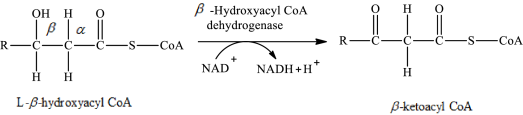
Therefore, NAD+ is involved in (3) both glycerol metabolism and fatty acid metabolism.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether ADP is involved in (1) glycerol metabolism to dihydroxyacetone phosphate, (2) fatty acid metabolism to acetyl CoA, or (3) both glycerol metabolism and fatty acid metabolism has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Triacylglycerol mobilization is an ongoing process in which triacylglycerols that are stored in the adipose tissue are hydrolyzed. Fatty acids and glycerol are the products of triacylglycerol mobilization. The products are released into the bloodstream.
After entering the bloodstream, the glycerol travels to the kidneys or liver. The first stage of glycerol metabolism occurs in the liver or kidney. The first stage of glycerol metabolism is a two-step process. After the first stage, the remaining stages of glycerol metabolism are the same as glucose pathways. The overall equation for glycerol metabolism is as follows:
Fatty acids are molecules that are long hydrocarbon chain of carboxylic acid. They are building blocks of fat in humans and animals.
The fatty acids are broken down to provide energy. The breakdown of fatty acids is a three parts process. In the first part, the fatty acid is activated. In the second part, the transportation of fatty acid into the mitochondrial matrix is facilitated by a shuttle mechanism. In the third part, the fatty acid is readily oxidized, cycling through a series of four reactions. In these series of reactions, acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA. This pathway is termed as a β-oxidation pathway. Acetyl CoA, FADH2, and NADH are produced in this pathway.
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) provides energy to carry out the metabolic processes in the living cells.
(b)
Answer to Problem 25.47EP
ADP is involved in (1) glycerol metabolism to dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
Explanation of Solution
The first stage of glycerol metabolism is a two-step process. In step 1, glycerol-3-phosphate is formed as the intermediate compound that further reacts to form dihydroxyacetone phosphate in step 2. The reaction for the conversion of glycerol is as follows:
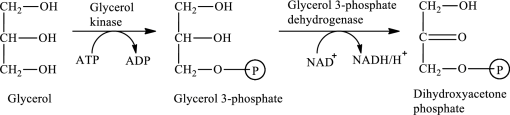
Here, represents
represents
In step 1 of glycerol metabolism, ATP is converted to ADP. Therefore, ADP is involved in glycerol metabolism.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether kinase is involved in (1) glycerol metabolism to dihydroxyacetone phosphate, (2) fatty acid metabolism to acetyl CoA, or (3) both glycerol metabolism and fatty acid metabolism has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Triacylglycerol mobilization is an ongoing process in which triacylglycerols that are stored in the adipose tissue are hydrolyzed. Fatty acids and glycerol are the products of triacylglycerol mobilization. The products are released into the bloodstream.
After entering the bloodstream, the glycerol travels to the kidneys or liver. The first stage of glycerol metabolism occurs in the liver or kidney. The first stage of glycerol metabolism is a two-step process. After the first stage, the remaining stages of glycerol metabolism are the same as glucose pathways. The overall equation for glycerol metabolism is as follows:
Fatty acids are molecules that are long hydrocarbon chain of carboxylic acid. They are building blocks of fat in humans and animals.
The fatty acids are broken down to provide energy. The breakdown of fatty acids is a three parts process. In the first part, the fatty acid is activated. In the second part, the transportation of fatty acid into the mitochondrial matrix is facilitated by a shuttle mechanism. In the third part, the fatty acid is readily oxidized, cycling through a series of four reactions. In these series of reactions, acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA. This pathway is termed as a β-oxidation pathway. Acetyl CoA, FADH2, and NADH are produced in this pathway.
The transfer of a phosphoryl group
(c)
Answer to Problem 25.47EP
Kinase is involved in (1) glycerol metabolism to dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
Explanation of Solution
The first stage of glycerol metabolism is a two-step process. In step 1, glycerol-3-phosphate is formed as the intermediate compound that further reacts to form dihydroxyacetone phosphate in step 2. The reaction for the conversion of glycerol is as follows:
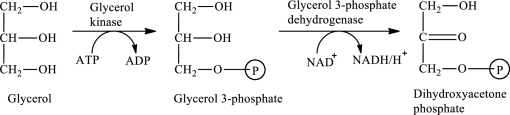
Here, represents
represents
In step 1 of glycerol metabolism, glycerol kinase enzyme catalyzed the conversion of glycerol to glycerol-3-phosphate. Therefore, the kinase is involved in glycerol metabolism.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether ketoacyl CoA is involved in (1) glycerol metabolism to dihydroxyacetone phosphate, (2) fatty acid metabolism to acetyl CoA, or (3) both glycerol metabolism and fatty acid metabolism has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Triacylglycerol mobilization is an ongoing process in which triacylglycerols that are stored in the adipose tissue are hydrolyzed. Fatty acids and glycerol are the products of triacylglycerol mobilization. The products are released into the bloodstream.
After entering the bloodstream, the glycerol travels to the kidneys or liver. The first stage of glycerol metabolism occurs in the liver or kidney. The first stage of glycerol metabolism is a two-step process. After the first stage, the remaining stages of glycerol metabolism are the same as glucose pathways. The overall equation for glycerol metabolism is as follows:
Fatty acids are molecules that are long hydrocarbon chain of carboxylic acid. They are building blocks of fat in humans and animals.
The fatty acids are broken down to provide energy. The breakdown of fatty acids is a three parts process. In the first part, the fatty acid is activated. In the second part, the transportation of fatty acid into the mitochondrial matrix is facilitated by a shuttle mechanism. In the third part, the fatty acid is readily oxidized, cycling through a series of four reactions. In these series of reactions, acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA. This pathway is termed as a β-oxidation pathway. Acetyl CoA, FADH2, and NADH are produced in this pathway.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is associated with the redox reactions in metabolism. Its reduced form is NADH and oxidized form is NAD+.
(d)
Answer to Problem 25.47EP
Ketoacyl CoA is involved in (2) fatty acid metabolism to acetyl CoA.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction in step 3 of a turn of the β-oxidation pathway is a dehydrogenation reaction in which two hydrogen atoms are removed from L-β-hydroxyacyl CoA. In this reaction, the β-hydroxy group is converted to a β-keto group. NAD+ is used as an oxidizing agent. This reaction is catalyzed by β-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase enzyme. The reaction for step 3 is as follows:
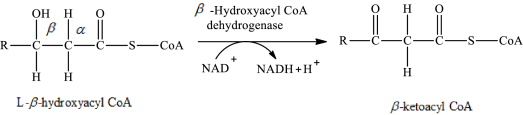
Therefore, ketoacyl CoA is involved in (2) fatty acid metabolism to acetyl CoA.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC,+BIO.CHEM.-MINDTAP
- What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.arrow_forwardWhat is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forward
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



