
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The step (of steps 1 through 4) and turn (second or third) of the β-oxidation pathway in which the following compound is encountered as a reactant if the degraded fatty acid is decanoic acid has to be determined.
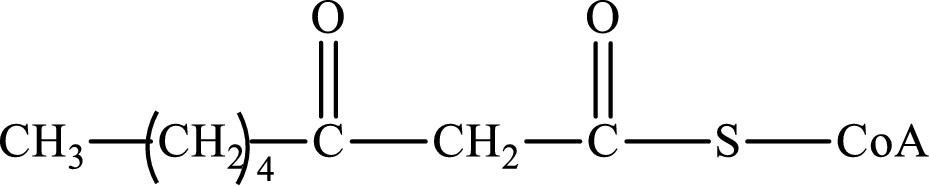
Concept introduction:
The β-oxidation pathway is defined as a repetitive series of four biochemical reactions in which acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA by the removal of two carbon atoms at a time. NADH and FADH2 are also produced in this pathway.
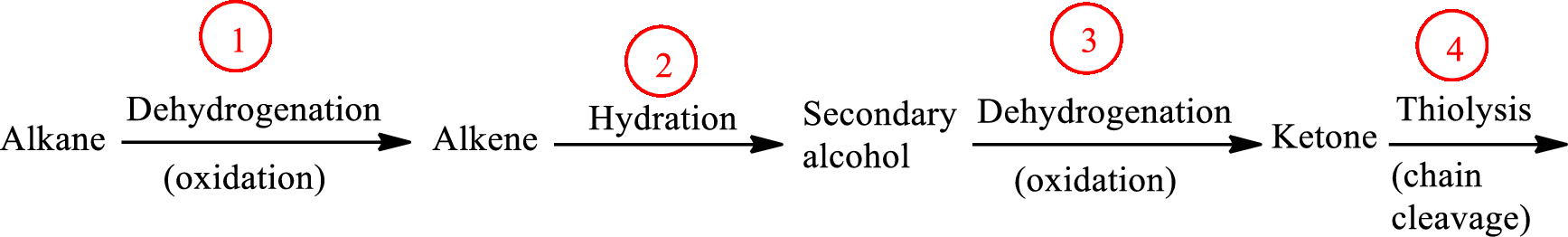
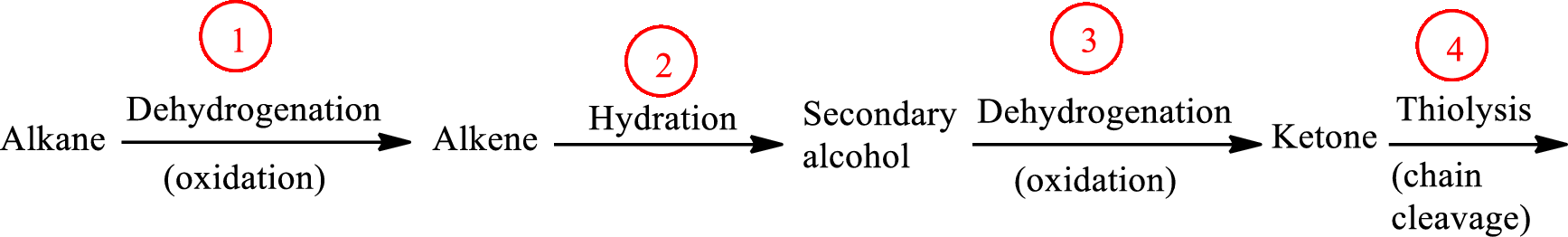
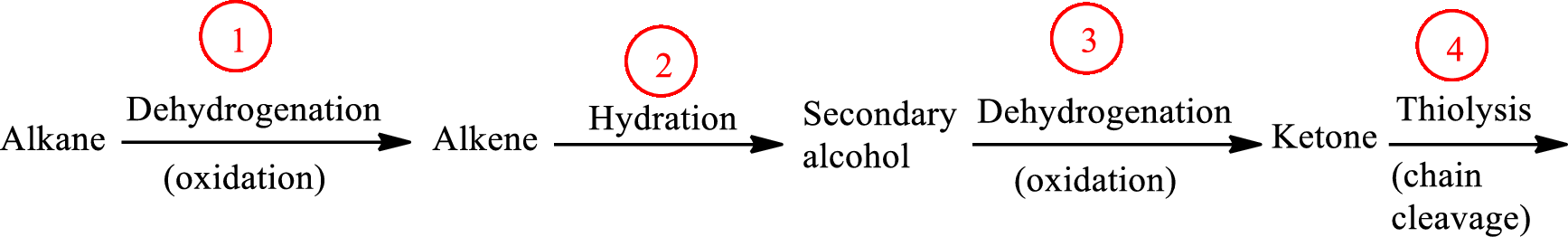
The functional group change in the β-oxidation pathway is as follows:
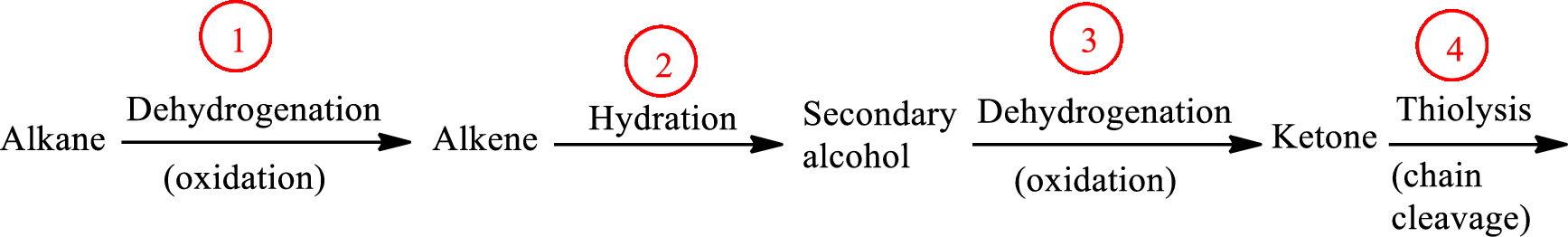
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In
(b)
Interpretation:
The step (of steps 1 through 4) and turn (second or third) of the β-oxidation pathway in which the following compound is encountered as a reactant if the degraded fatty acid is decanoic acid has to be determined.
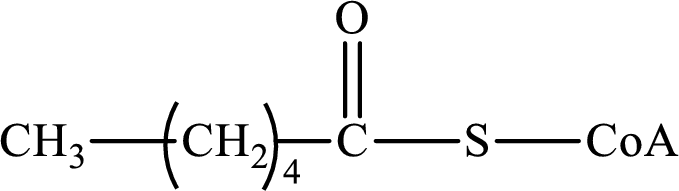
Concept introduction:
The β-oxidation pathway is defined as a repetitive series of four biochemical reactions in which acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA by the removal of two carbon atoms at a time. NADH and FADH2 are also produced in this pathway.
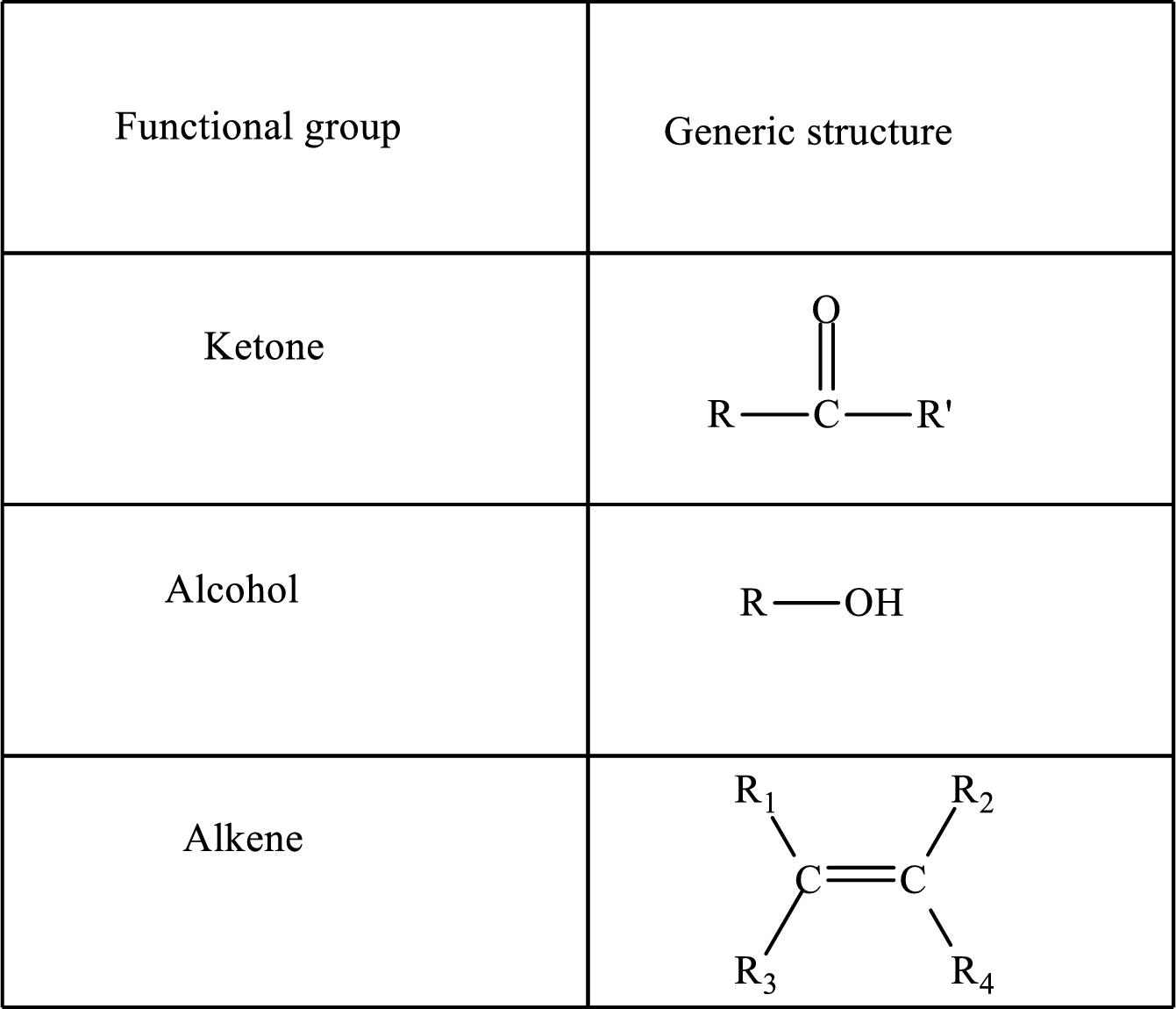
The functional group change in the β-oxidation pathway is as follows:
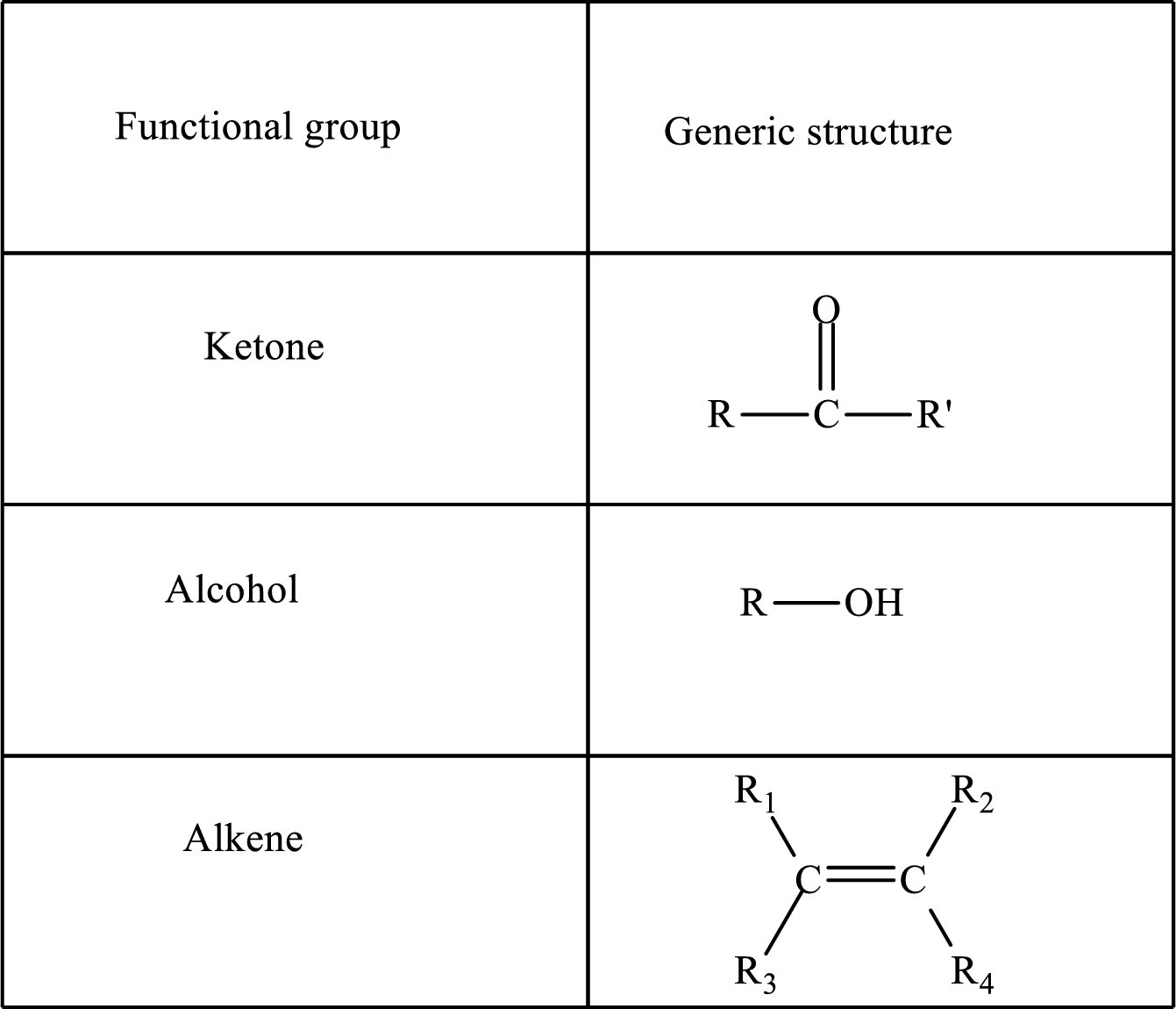
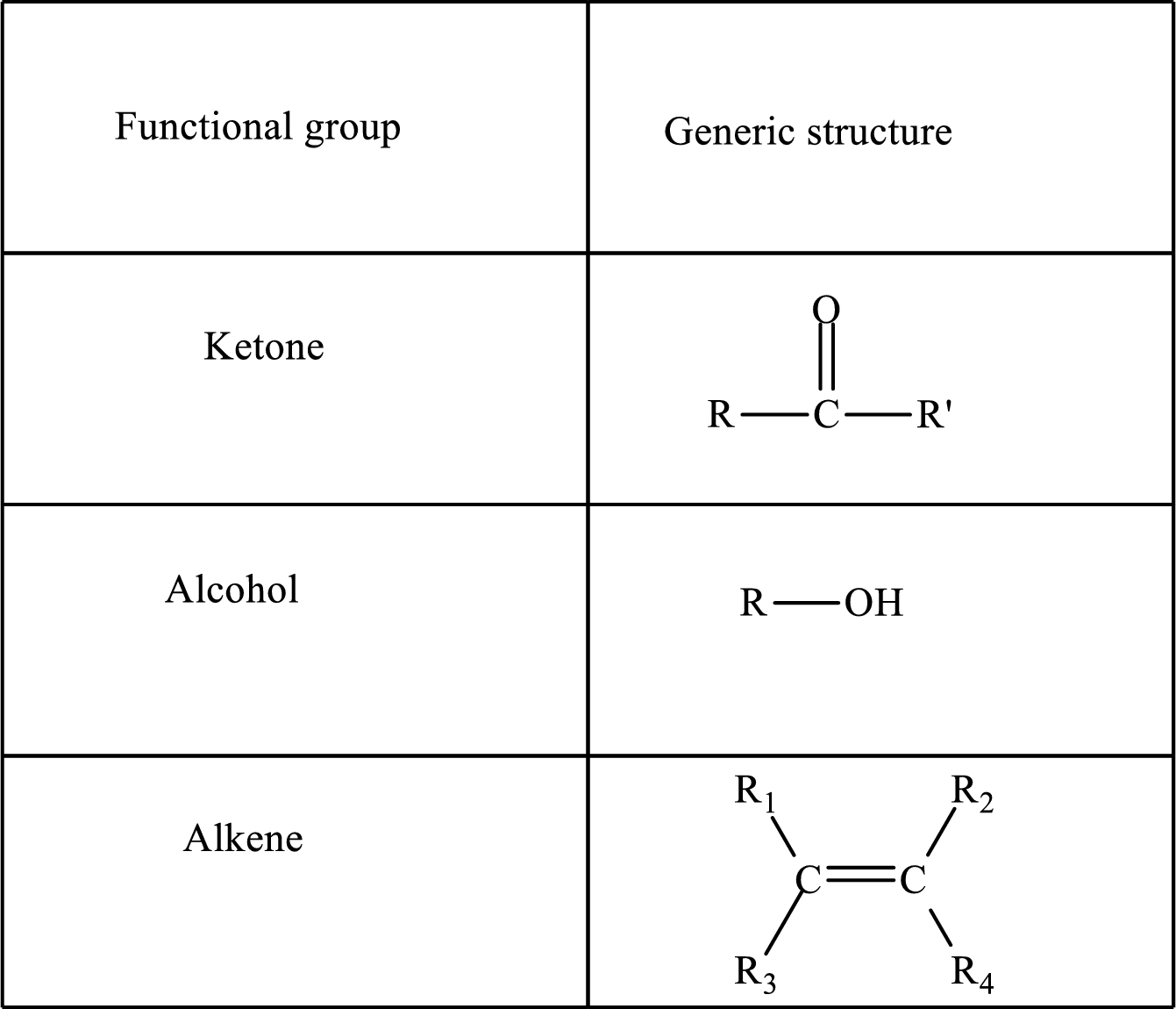
Functional groups are defined as the group of atoms which are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds. These are generally heteroatoms which are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain. Some examples of functional groups are as follows:
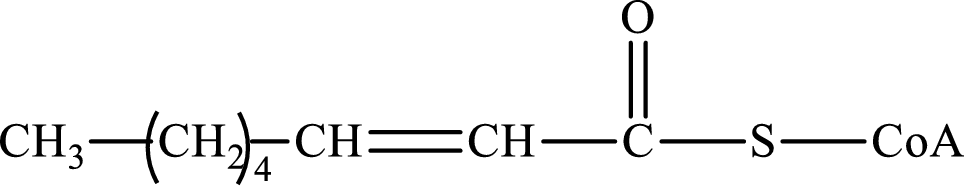
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen.
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain covalently bonded hydrogen and carbon atoms. In secondary alcohol, the carbon atom of the hydroxyl group
(c)
Interpretation:
The step (of steps 1 through 4) and turn (second or third) of the β-oxidation pathway in which the following compound is encountered as a reactant if the degraded fatty acid is decanoic acid has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The β-oxidation pathway is defined as a repetitive series of four biochemical reactions in which acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA by the removal of two carbon atoms at a time. NADH and FADH2 are also produced in this pathway.
The functional group change in the β-oxidation pathway is as follows:
Functional groups are defined as the group of atoms which are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds. These are generally heteroatoms which are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain. Some examples of functional groups are as follows:
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen.
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain covalently bonded hydrogen and carbon atoms. In secondary alcohol, the carbon atom of the hydroxyl group
(d)
Interpretation:
The step (of steps 1 through 4) and turn (second or third) of the β-oxidation pathway in which the following compound is encountered as a reactant if the degraded fatty acid is decanoic acid has to be determined.
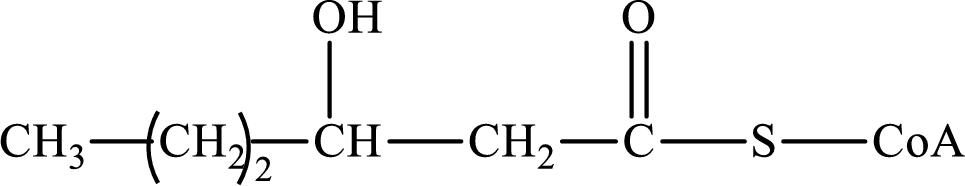
Concept introduction:
The β-oxidation pathway is defined as a repetitive series of four biochemical reactions in which acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA by the removal of two carbon atoms at a time. NADH and FADH2 are also produced in this pathway.
The functional group change in the β-oxidation pathway is as follows:
Functional groups are defined as the group of atoms which are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds. These are generally heteroatoms which are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain. Some examples of functional groups are as follows:
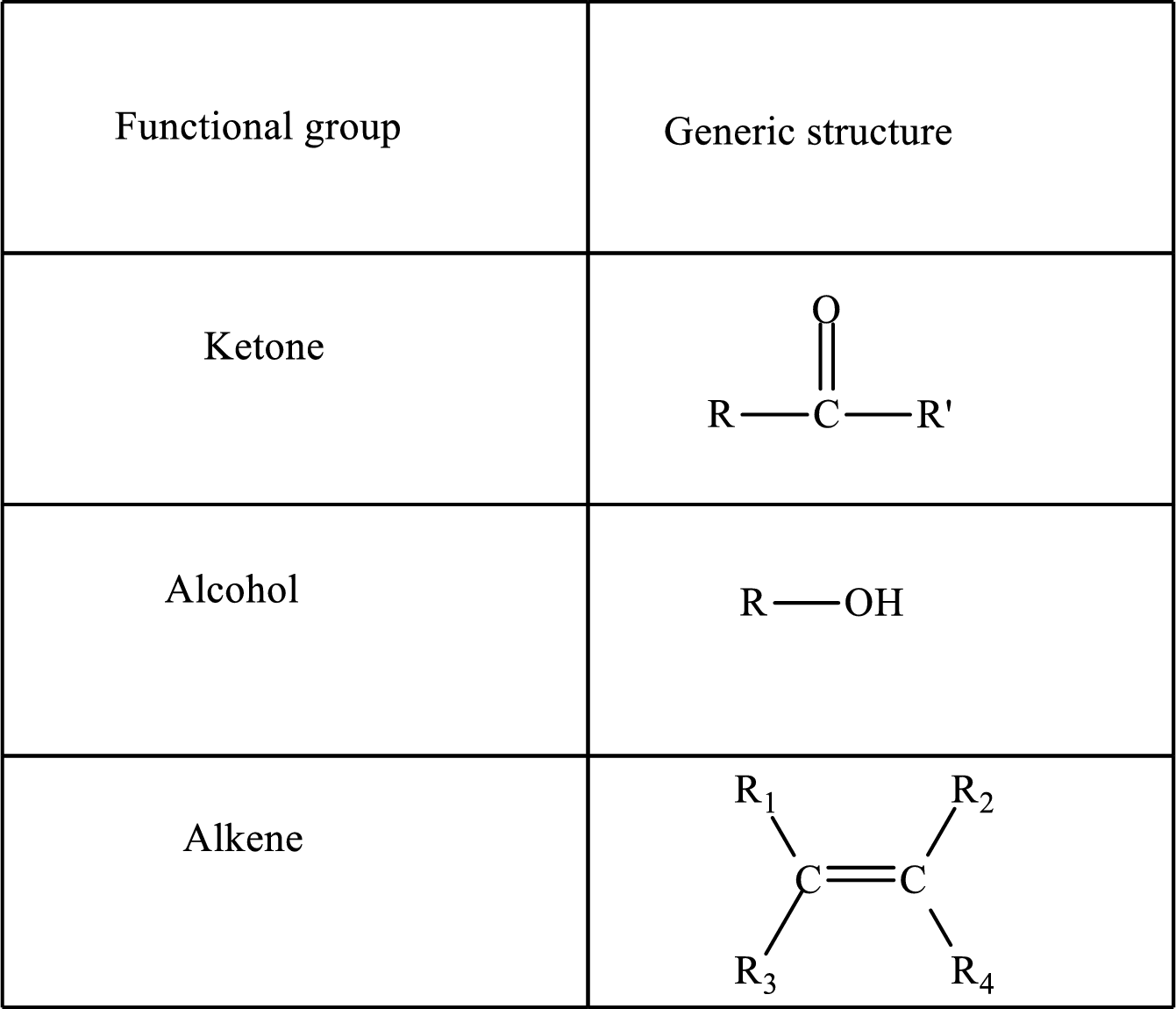
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen.
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain covalently bonded hydrogen and carbon atoms. In secondary alcohol, the carbon atom of the hydroxyl group
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 25 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, AND BIOLOGICAL CH
- Which does NOT describe a mole? A. a unit used to count particles directly, B. Avogadro’s number of molecules of a compound, C. the number of atoms in exactly 12 g of pure C-12, D. the SI unit for the amount of a substancearrow_forward5 What would the complete ionic reaction be if aqueous solutions of potassium sulfate and barium acetate were mixed? ed of Select one: O a 2 K SO4 + Ba2 +2 C₂H3O21 K+SO4 + Ba2+ + 2 C2H3O21 K+SO42 + Ba2 +2 C2H3O2 BaSO4 +2 K+ + 2 C2H3O estion Ob. O c. Od. 2 K SO4 +Ba2 +2 C₂H₂O₂ BaSO4 + K+ + 2 C2H3O BaSO4 + K + 2 C2H301 →Ba² +SO42 +2 KC2H3O s pagearrow_forward(28 pts.) 7. Propose a synthesis for each of the following transformations. You must include the reagents and product(s) for each step to receive full credit. The number of steps is provided. (OC 4) 4 steps 4 steps OH b.arrow_forward
- LTS Solid: AT=Te-Ti Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Average ΔΗ Mass water, g 24.096 23.976 23.975 Moles of solid, mol 0.01763 001767 0101781 Temp. change, °C 2.9°C 11700 2.0°C Heat of reaction, J -292.37J -170.473 -193.26J AH, kJ/mole 16.58K 9.647 kJ 10.85 kr 16.58K59.64701 KJ mol 12.35k Minimum AS, J/mol K 41.582 mol-k Remember: q = mCsAT (m = mass of water, Cs=4.184J/g°C) & qsin =-qrxn & Show your calculations for: AH in J and then in kJ/mole for Trial 1: qa (24.0969)(4.1845/g) (-2.9°C)=-292.37J qsin = qrxn = 292.35 292.37J AH in J = 292.375 0.2923kJ 0.01763m01 =1.65×107 AH in kJ/mol = = 16.58K 0.01763mol mol qrx Minimum AS in J/mol K (Hint: use the average initial temperature of the three trials, con Kelvin.) AS=AHIT (1.65×10(9.64×103) + (1.0 Jimaiarrow_forwardFor the compound: C8H17NO2 Use the following information to come up with a plausible structure: 8 This compound has "carboxylic acid amide" and ether functional groups. The peaks at 1.2ppm are two signals that are overlapping one another. One of the two signals is a doublet that represents 6 hydrogens; the other signal is a quartet that represents 3 hydrogens.arrow_forwardVnk the elements or compounds in the table below in decreasing order of their boiling points. That is, choose 1 next to the substance with the highest bolling point, choose 2 next to the substance with the next highest boiling point, and so on. substance C D chemical symbol, chemical formula or Lewis structure. CH,-N-CH, CH, H H 10: H C-C-H H H H Cale H 10: H-C-C-N-CH, Bri CH, boiling point (C) Сен (C) B (Choosearrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





