
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether crotonate, a C4 species is a (1) hydroxy acid, (2) keto acid, (3) saturated acid, or (4) unsaturated acid has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional groups are defined as the group of atoms which are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds. These are generally heteroatoms which are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain. Some examples of functional groups are as follows:
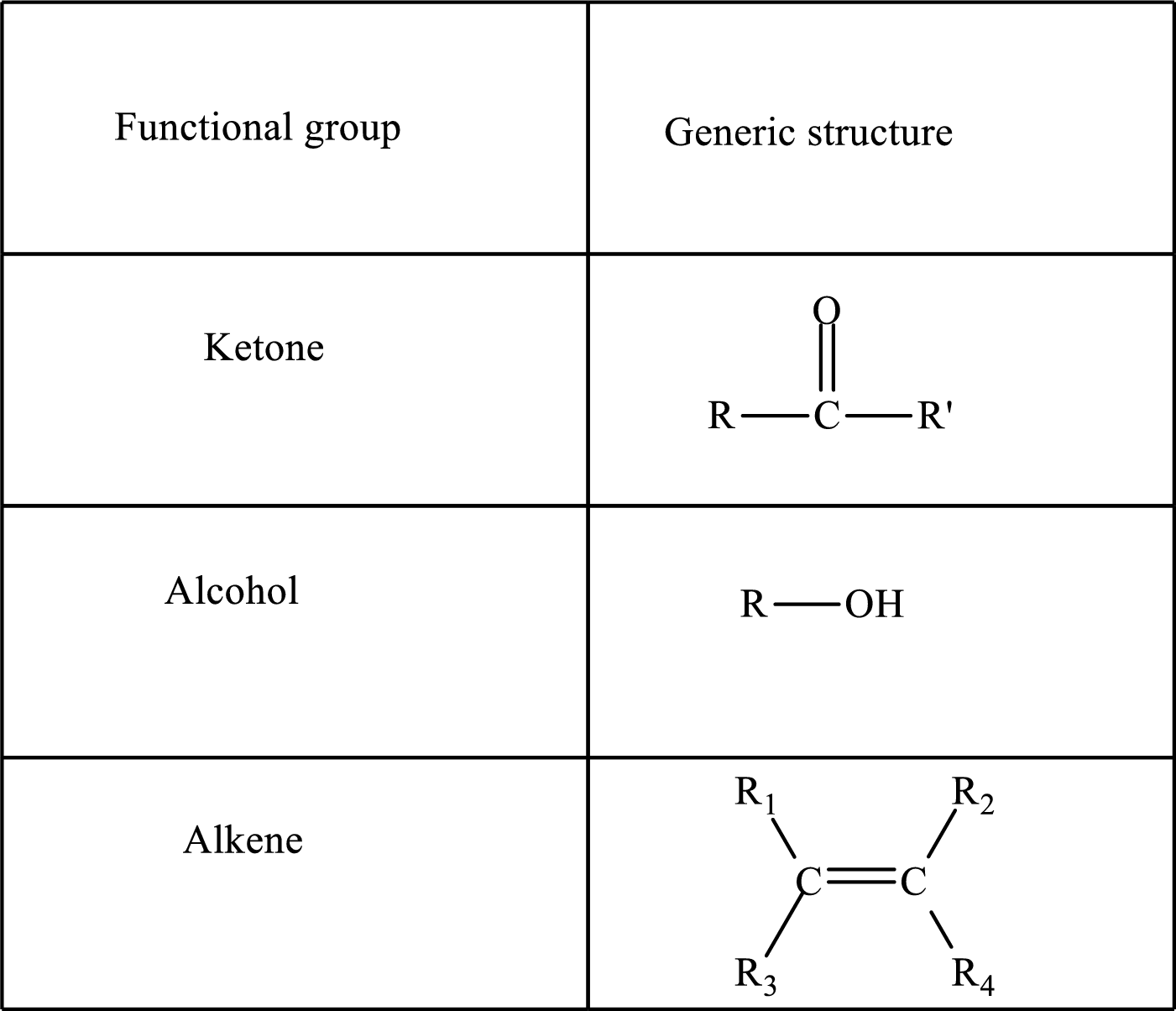
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen.
Keto acid has a
A carboxylate group is formed by the removal of the acidic hydrogen from the carboxylic group. The conjugate base is formed by the removal of acidic hydrogen from the corresponding acid.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether oxaloacetate, a C4 species is a (1) hydroxy acid, (2) keto acid, (3) saturated acid, or (4) unsaturated acid has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional groups are defined as the group of atoms which are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds. These are generally heteroatoms which are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain. Some examples of functional groups are as follows:
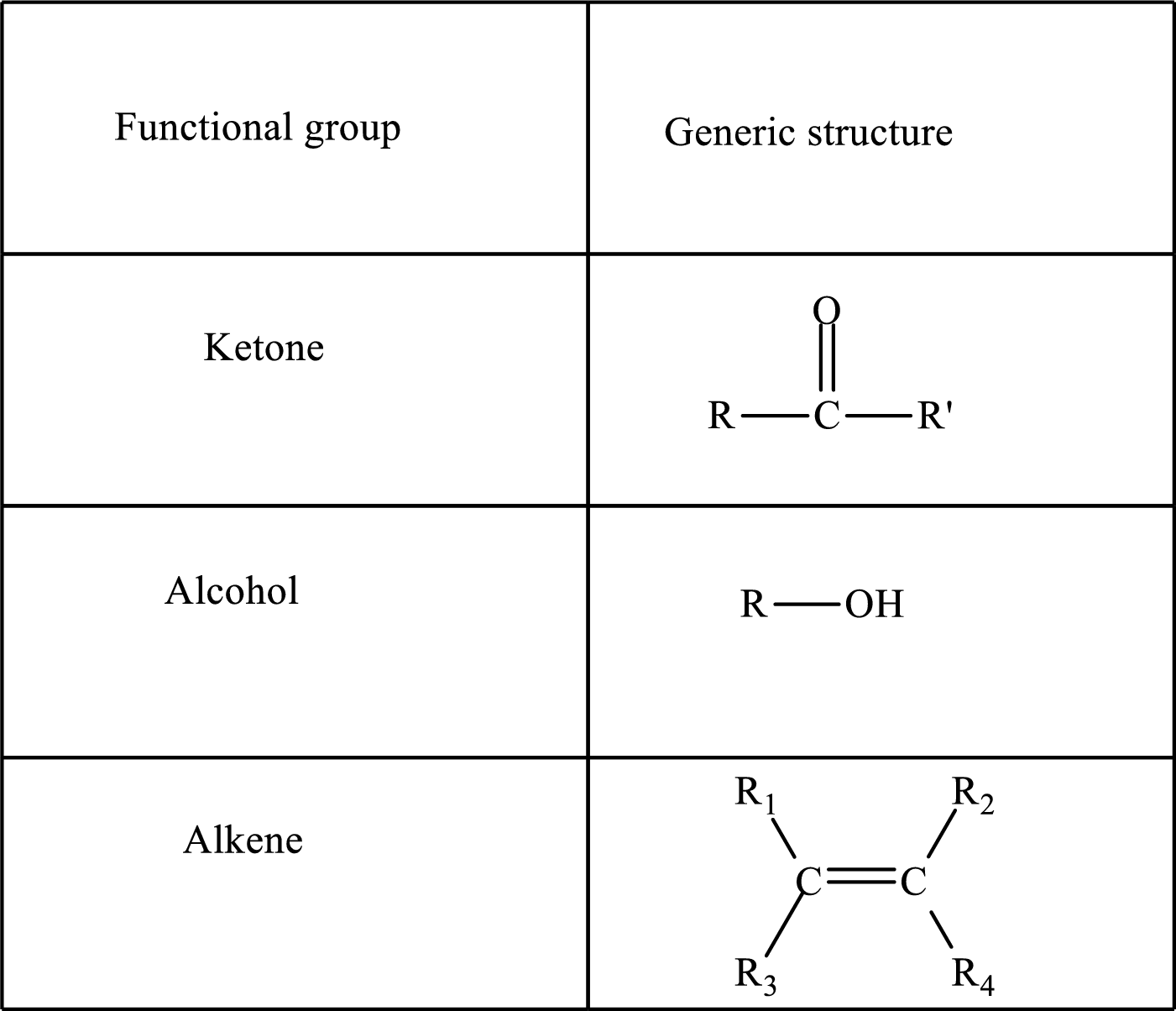
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain covalently bonded hydrogen and carbon atoms. Alkenes have a double bond, hence; they are unsaturated compounds.
Keto acid has a ketone and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Hydroxy acid has a hydroxy (-OH) group and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Saturated acids contain single bonds between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group. Unsaturated acid contains a double or triple bond between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group.
A carboxylate group is formed by the removal of the acidic hydrogen from the carboxylic group. The conjugate base is formed by the removal of acidic hydrogen from the corresponding acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether acetoacetate, a C4 species is a (1) hydroxy acid, (2) keto acid, (3) saturated acid, or (4) unsaturated acid has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional groups are defined as the group of atoms which are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds. These are generally heteroatoms which are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain. Some examples of functional groups are as follows:
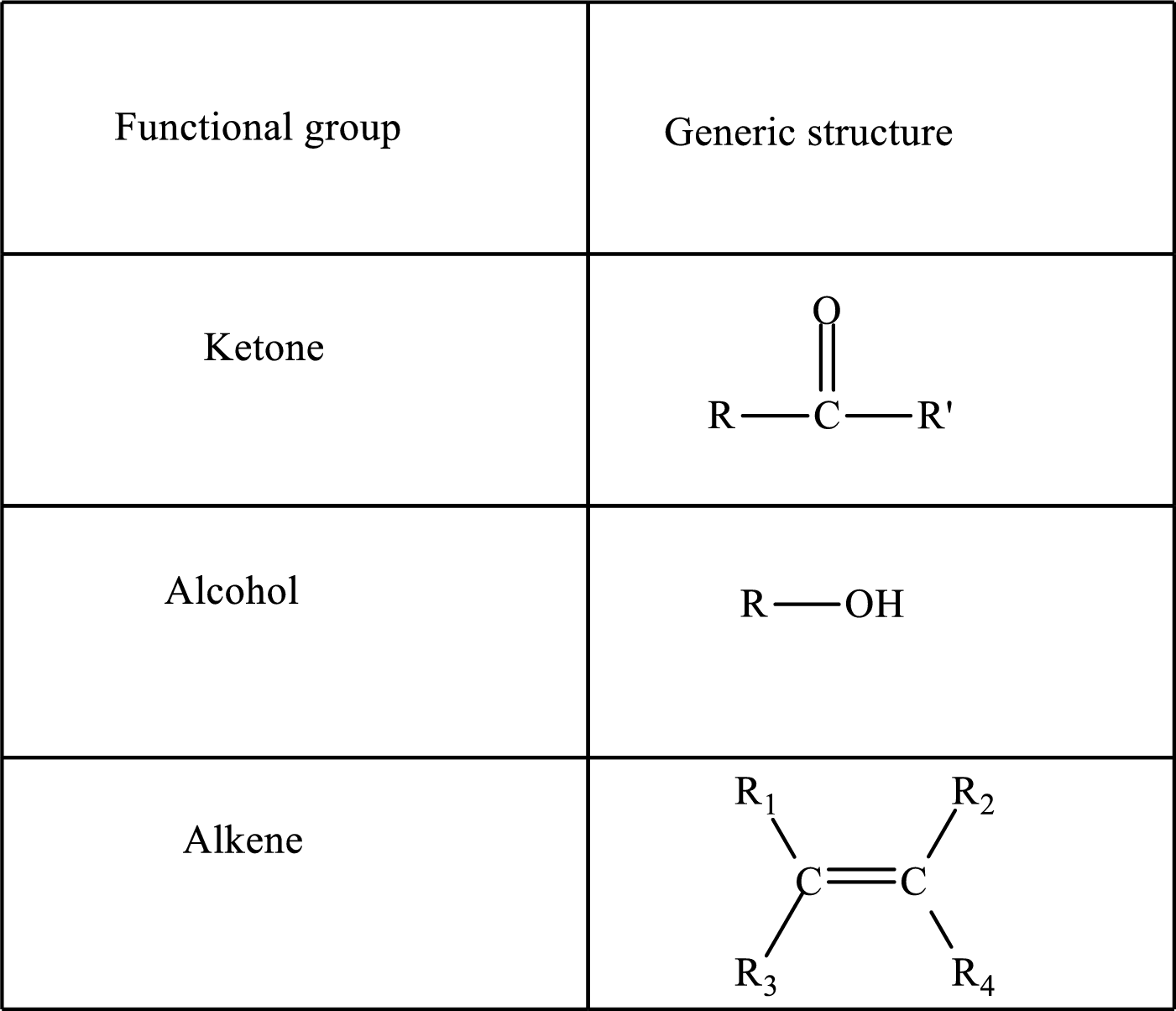
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain covalently bonded hydrogen and carbon atoms. Alkenes have a double bond, hence; they are unsaturated compounds.
Keto acid has a ketone and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Hydroxy acid has a hydroxy (-OH) group and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Saturated acids contain single bonds between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group. Unsaturated acid contains a double or triple bond between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group.
A carboxylate group is formed by the removal of the acidic hydrogen from the carboxylic group. The conjugate base is formed by the removal of acidic hydrogen from the corresponding acid.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether malate, a C4 species is a (1) hydroxy acid, (2) keto acid, (3) saturated acid, or (4) unsaturated acid has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional groups are defined as the group of atoms which are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds. These are generally heteroatoms which are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain. Some examples of functional groups are as follows:
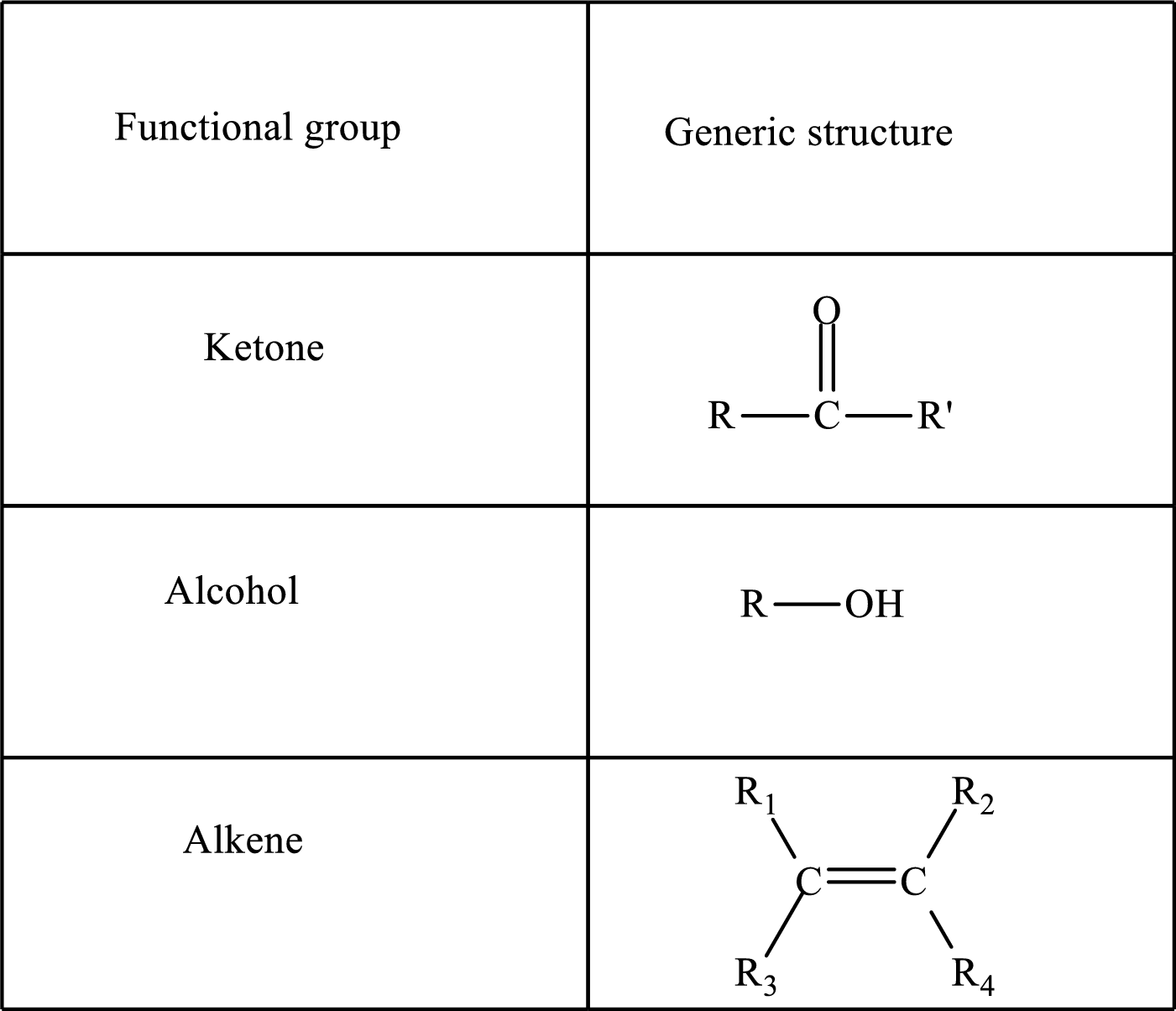
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain covalently bonded hydrogen and carbon atoms. Alkenes have a double bond, hence; they are unsaturated compounds.
Keto acid has a ketone and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Hydroxy acid has a hydroxy (-OH) group and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Saturated acids contain single bonds between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group. Unsaturated acid contains a double or triple bond between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group.
A carboxylate group is formed by the removal of the acidic hydrogen from the carboxylic group. The conjugate base is formed by the removal of acidic hydrogen from the corresponding acid.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 25 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, AND BIOLOGICAL CH
- Noggin mutation: The mouse, one of the phenotypic consequences of Noggin mutationis mispatterning of the spinal cord, in the posterior region of the mouse embryo, suchthat in the hindlimb region the more ventral fates are lost, and the dorsal Pax3 domain isexpanded. (this experiment is not in the lectures).a. Hypothesis for why: What would be your hypothesis for why the ventral fatesare lost and dorsal fates expanded? Include in your answer the words notochord,BMP, SHH and either (or both of) surface ectoderm or lateral plate mesodermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forward
- please helparrow_forwardWhat does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about water reabsorption in this individual at this time? What does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about ADH secretion in this individual at this time?arrow_forwardBiology grade 10 study guidearrow_forward
- Essentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage
 Cardiopulmonary Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781337794909Author:Des Jardins, Terry.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Cardiopulmonary Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781337794909Author:Des Jardins, Terry.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





