
(a)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
1. The hydrocarbon is named after the longest carbon chain.
2. The parent hydrocarbon containing amino group is named as
3. When the nitrogen atom of amine is substituted with alkyl groups, then the amine is named with prefix
Answer to Problem 25.3P
The structure of the given compound is,
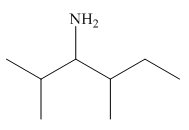
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the compound is

Figure 1
The structure of the given compound is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for hydrocarbon are:
1. The hydrocarbon is named after the longest carbon chain.
2. The parent hydrocarbon containing amino group is named as alkane with suffix amine.
3. When the nitrogen atom of amine is substituted with alkyl groups, then the amine is named with prefix
Answer to Problem 25.3P
The structure of the given compound is,

Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the compound is

Figure 2
The structure of the given compound is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for hydrocarbon are:
1. The hydrocarbon is named after the longest carbon chain.
2. The parent hydrocarbon containing amino group is named as alkane with suffix amine.
3. When the nitrogen atom of amine is substituted with alkyl groups, then the amine is named with prefix
Answer to Problem 25.3P
The structure of the given compound is,
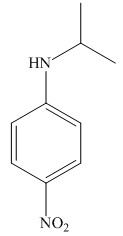
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the compound is

Figure 3
The structure of the given compound is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for hydrocarbon are:
1. The hydrocarbon is named after the longest carbon chain.
2. The parent hydrocarbon containing amino group is named as alkane with suffix amine.
3. When the nitrogen atom of amine is substituted with alkyl groups, then the amine is named with prefix
Answer to Problem 25.3P
The structure of the given compound is,
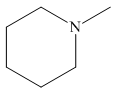
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the compound is

Figure 4
The structure of the given compound is shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for hydrocarbon are:
1. The hydrocarbon is named after the longest carbon chain.
2. The parent hydrocarbon containing amino group is named as alkane with suffix amine.
3. When the nitrogen atom of amine is substituted with alkyl groups, then the amine is named with prefix
Answer to Problem 25.3P
The structure of the given compound is,
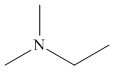
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the compound is

Figure 5
The structure of the given compound is shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for hydrocarbon are:
1. The hydrocarbon is named after the longest carbon chain.
2. The parent hydrocarbon containing amino group is named as alkane with suffix amine.
3. When the nitrogen atom of amine is substituted with alkyl groups, then the amine is named with prefix
Answer to Problem 25.3P
The structure of the given compound is,
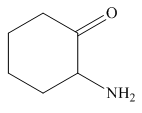
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the compound is

Figure 6
The structure of the given compound is shown in Figure 6.
(g)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for hydrocarbon are:
1. The hydrocarbon is named after the longest carbon chain.
2. The parent hydrocarbon containing amino group is named as alkane with suffix amine.
3. When the nitrogen atom of amine is substituted with alkyl groups, then the amine is named with prefix
Answer to Problem 25.3P
The structure of the given compound is,
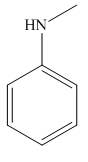
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the compound is

Figure 7
The structure of the given compound is shown in Figure 7.
(h)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for hydrocarbon are:
1. The hydrocarbon is named after the longest carbon chain.
1. The parent hydrocarbon containing amino group is named as alkane with suffix amine.
2. When the nitrogen atom of amine is substituted with alkyl groups, then the amine is named with prefix
Answer to Problem 25.3P
The structure of the given compound is,
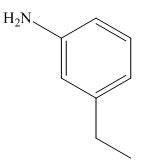
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the compound is

Figure 8
The structure of the given compound is shown in Figure 8.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- what is the skeletal structure of a tertiary alkyl fluoride with six carbon atoms and no rings.arrow_forwardOne step of glycolysis is a retro-aldol reaction (aldolase) to produce ATP.Below is the aldol reaction of the equilibrium. Show the mechanism for the base catalyzed reaction. *see imagearrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardDraw the mechanism (including all curved arrows for electron movement) showing how the maleicanhydride is attacked by the anthracene and formation of the final Diels Alder product.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





