
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 24, Problem 44P
In Fig. 24-53, seven charged particles are fixed in place to form a square with an edge length of 4.0 cm. How much work must we do to bring a particle of charge +6e initially at rest from an infinite distance to the center of the square?
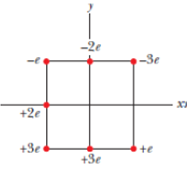
Figure 24-53 Problem 44.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls
The position of a coffee cup on a table as referenced by the corner of the room in which it sits is r=0.5mi +1.5mj +2.0mk . How far is the cup from the corner? What is the unit vector pointing from the corner to the cup?
No chatgpt pls
Chapter 24 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 24 - Figure 24-24 shows eight particles that form a...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-25 shows three sets of cross sections of...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-26 shows four pairs of charged...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-27 gives the electric potential V as a...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-28 shows three paths along which we can...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-29 shows four arrangement? of charged...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-30 shows a system of three charged...Ch. 24 - In the situation of Question 7, is the work done...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-26 shows four pairs of charged particles...Ch. 24 - a In Fig. 24-31a, what is the potential at point P...
Ch. 24 - Figure 24-32 shows a thin, uniformly charged rod...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-33, a particle is to be released at...Ch. 24 - SSM A particular 12 V car battery can send a total...Ch. 24 - The electric potential difference between the...Ch. 24 - Suppose that in a lightning flash the potential...Ch. 24 - Two large, parallel, conducting plates are 12 cm...Ch. 24 - SSM An infinite nonconducting sheet has a surface...Ch. 24 - When an electron moves from A to B along an...Ch. 24 - The electric field in a region of space has the...Ch. 24 - A graph of the x component of the electric field...Ch. 24 - An infinite nonconducting sheet has a surface...Ch. 24 - GO Two uniformly charged, infinite, nonconducting...Ch. 24 - A nonconducting sphere has radius R = 2.31 cm and...Ch. 24 - As a space shuttle moves through the dilute...Ch. 24 - What are a the change and b the charge density on...Ch. 24 - Consider a particle with charge q = 1.0 C, point A...Ch. 24 - SSM ILW A spherical drop of water carrying a...Ch. 24 - GO Figure 24-37 shows a rectangular array of...Ch. 24 - GO In Fig.24-33, what is the net electric...Ch. 24 - GO Two charged particles are shown in Fig. 24-39a....Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-40, particles with the charges q1 = 5e...Ch. 24 - Two particles, of charges q1 and q2, are separated...Ch. 24 - ILW The ammonia molecule NH3 has a permanent...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-41a, a particle of elementary charge e...Ch. 24 - a Figure 24-42a shows a nonconducting rod of...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 21-43, a plastic rod having a uniformly...Ch. 24 - A plastic rod has been bent into a circle of...Ch. 24 - GO Figure 24-45 shows a thin rod with a uniform...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-46, three thin plastic rods form...Ch. 24 - GO Figure 24-47 shows a thin plastic rod of length...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-48, what is the net electric potential...Ch. 24 - GO The smiling face of Fig. 24-49 consists of...Ch. 24 - SSM WWW A plastic disk of radius R = 64.0 cm is...Ch. 24 - GO A non uniform linear charge distribution given...Ch. 24 - GO The thin plastic rod shown in Fig. 24-47 has...Ch. 24 - Two large parallel metal plates are 1.5 cm apart...Ch. 24 - The electric potential al points in an xy plane is...Ch. 24 - The electric potential V in the space between two...Ch. 24 - SSM What is the magnitude of the electric field at...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-47 shows a thin plastic rod of length L...Ch. 24 - An electron is placed in an xy plane where I he...Ch. 24 - GO The thin plastic rod of length L = 10.0 cm in...Ch. 24 - A particle of charge 7.5 C is released from rest...Ch. 24 - a What is the electric potential energy of two...Ch. 24 - How much work is required to set up the...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-53, seven charged particles are fixed...Ch. 24 - ILW A particle of charge q is fixed at point P,...Ch. 24 - A charge of 9.0 nC is uniformly distributed around...Ch. 24 - GO What is the escape speed for an electron...Ch. 24 - A thin, spherical conducting shell of radius R is...Ch. 24 - GO Two electrons are fixed 2.0 cm apart. Another...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-54, how much work must we do to bring a...Ch. 24 - GO In the rectangle of Fig. 24-55, the sides have...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-56a shows an electron moving along an...Ch. 24 - Two tiny metal sphere? A and B, mass mA = 5.00 g...Ch. 24 - GO A positron charge e, mass equal to the electron...Ch. 24 - An electron is projected with an initial speed of...Ch. 24 - Particle 1 with a charge of 5.0 C and particle 2...Ch. 24 - SSM Identical 50 C charges are fixed or an x axis...Ch. 24 - GO Proton in a well. Figure 24-59 shows electric...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-60, a charged particle either an...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-61a, we move an electron from an...Ch. 24 - Suppose N electrons can be placed in either of two...Ch. 24 - Sphere 1 with radius R1 has positive charge q....Ch. 24 - SSM WWW Two metal spheres, each of radius 3.0 cm,...Ch. 24 - A hollow metal sphere has a potential of 400 V...Ch. 24 - SSM What is the excess charge on a conducting...Ch. 24 - Two isolated, concentric, conducting spherical...Ch. 24 - A metal sphere of radius 15 cm has a net charge of...Ch. 24 - Here are the charges and coordinates of two...Ch. 24 - SSM A long, solid, conducting cylinder has a...Ch. 24 - The chocolate crumb mystery. This story begins...Ch. 24 - SSM Starting from Eq. 24-30, derive an expression...Ch. 24 - The magnitude E of an electric field depends on...Ch. 24 - a If an isolated conducting sphere 10 cm in radius...Ch. 24 - Three particles, charge q1 = 10 C, q2 = 20 C, and...Ch. 24 - An electric field of approximately 100 V/m is...Ch. 24 - A Gaussian sphere of radius 4.00 cm is centered or...Ch. 24 - In a Millikan oil-drop experiment Module 22-6, a...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-63 shows three circular, nonconducting...Ch. 24 - An electron is released from rest on the axis of...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-64 shows a ring of outer radius R = 13.0...Ch. 24 - GO Electron in a well. Figure 24-65 shows electric...Ch. 24 - a If Earth had a uniform surface charge density of...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-66, point P is at distance d1 = 4.00 m...Ch. 24 - A solid conducting sphere of radius 3.0 cm has a...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-67, we move a particle of charge 2e in...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-68 shows a hemisphere with a charge of...Ch. 24 - SSM Three 0.12 C charges form an equilateral...Ch. 24 - Two charges q = 2.0 C are fixed a distance d = 2.0...Ch. 24 - Initially two electrons are fixed in place with a...Ch. 24 - A particle of positive charge Q is fixed at point...Ch. 24 - Two charged, parallel, flat conducting surfaces...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-70, point P is at the center of the...Ch. 24 - SSM A uniform charge of 16.0 C is on a thin...Ch. 24 - Consider a particle with charge q = 150 108 C,...Ch. 24 - SSM A thick spherical shell of charge Q and...Ch. 24 - A charge q is distributed uniformly throughout a...Ch. 24 - SSM A solid copper sphere whose radius is 1.0 cm...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-71, a metal sphere with charge q = 5.00...Ch. 24 - a Using Eq. 24-32, show that the electric...Ch. 24 - An alpha particle which has two protons is seat...Ch. 24 - In the quark model of fundamental particles, a...Ch. 24 - A charge of 1.50 108 C lies on an isolated metal...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-72, two particles of charges q1 and q2...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Oceanic crust and the underlying rocks to a depth of about 100 kilometers have a basaltic composition Does the ...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
21.49 The atomic masses of hydrogen-2 (deuterium), helium-4, and lithium-6 are 2.014102 amu, 4.002602 amu, 6.01...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
With the initial appearance of the feature we call Now Solve This, a short introduction is in order. The featur...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
56. Global Positioning System. Learn more about the global positioning system and its uses. Write a short repo...
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
Why are the top predators in food chains most severely affected by pesticides such as DDT?
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
explain the function of fermentation and the conditions under which it occurs?
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Find the total capacitance in micro farads of the combination of capacitors shown in the figure below. HF 5.0 µF 3.5 µF №8.0 μLE 1.5 µF Ι 0.75 μF 15 μFarrow_forwardthe answer is not 0.39 or 0.386arrow_forwardFind the total capacitance in micro farads of the combination of capacitors shown in the figure below. 2.01 0.30 µF 2.5 µF 10 μF × HFarrow_forward
- I do not understand the process to answer the second part of question b. Please help me understand how to get there!arrow_forwardRank the six combinations of electric charges on the basis of the electric force acting on 91. Define forces pointing to the right as positive and forces pointing to the left as negative. Rank in increasing order by placing the most negative on the left and the most positive on the right. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. ▸ View Available Hint(s) [most negative 91 = +1nC 92 = +1nC 91 = -1nC 93 = +1nC 92- +1nC 93 = +1nC -1nC 92- -1nC 93- -1nC 91= +1nC 92 = +1nC 93=-1nC 91 +1nC 92=-1nC 93=-1nC 91 = +1nC 2 = −1nC 93 = +1nC The correct ranking cannot be determined. Reset Help most positivearrow_forwardPart A Find the x-component of the electric field at the origin, point O. Express your answer in newtons per coulomb to three significant figures, keeping in mind that an x component that points to the right is positive. ▸ View Available Hint(s) Eoz = Η ΑΣΦ ? N/C Submit Part B Now, assume that charge q2 is negative; q2 = -6 nC, as shown in (Figure 2). What is the x-component of the net electric field at the origin, point O? Express your answer in newtons per coulomb to three significant figures, keeping in mind that an x component that points to the right is positive. ▸ View Available Hint(s) Eoz= Η ΑΣΦ ? N/Carrow_forward
- 1. A charge of -25 μC is distributed uniformly throughout a spherical volume of radius 11.5 cm. Determine the electric field due to this charge at a distance of (a) 2 cm, (b) 4.6 cm, and (c) 25 cm from the center of the sphere. (a) = = (b) E = (c)Ẻ = = NC NC NCarrow_forward1. A long silver rod of radius 3.5 cm has a charge of -3.9 ис on its surface. Here ŕ is a unit vector ст directed perpendicularly away from the axis of the rod as shown in the figure. (a) Find the electric field at a point 5 cm from the center of the rod (an outside point). E = N C (b) Find the electric field at a point 1.8 cm from the center of the rod (an inside point) E=0 Think & Prepare N C 1. Is there a symmetry in the charge distribution? What kind of symmetry? 2. The problem gives the charge per unit length 1. How do you figure out the surface charge density σ from a?arrow_forward1. Determine the electric flux through each surface whose cross-section is shown below. 55 S₂ -29 S5 SA S3 + 9 Enter your answer in terms of q and ε Φ (a) s₁ (b) s₂ = -29 (C) Φ զ Ερ (d) SA = (e) $5 (f) Sa $6 = II ✓ -29 S6 +39arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardthe cable may break and cause severe injury. cable is more likely to break as compared to the [1] ds, inclined at angles of 30° and 50° to the vertical rings by way of a scaled diagram. [4] I 30° T₁ 3cm 3.8T2 cm 200 N 50° at it is headed due North and its airspeed indicat 240 km/h. If there is a wind of 100 km/h from We e relative to the Earth? [3]arrow_forwardCan you explain this using nodal analysis With the nodes I have present And then show me how many KCL equations I need to write, I’m thinking 2 since we have 2 dependent sourcesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics Capacitor & Capacitance part 7 (Parallel Plate capacitor) CBSE class 12; Author: LearnoHub - Class 11, 12;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JoW6UstbZ7Y;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY