
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 24, Problem 21P
ILW The ammonia molecule NH3 has a permanent electric dipole moment equal to 1.47 D, where 1 D = 1 debye unit = 3.34 × 10−30 C · m. Calculate the electric potential due to an ammonia molecule at a point 52.0 nm away along the axis of the dipole. (Set V = 0 at infinity.)
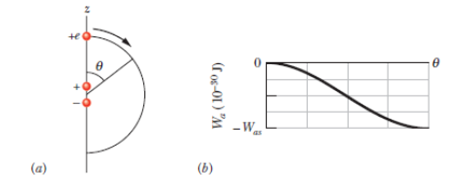
Figure 24-41 Problem 22.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please take your time and solve each part correctly please. Thank you!!
help me answer this with explanations! thanks so much
No chatgpt pls will upvote Already
Chapter 24 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 24 - Figure 24-24 shows eight particles that form a...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-25 shows three sets of cross sections of...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-26 shows four pairs of charged...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-27 gives the electric potential V as a...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-28 shows three paths along which we can...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-29 shows four arrangement? of charged...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-30 shows a system of three charged...Ch. 24 - In the situation of Question 7, is the work done...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-26 shows four pairs of charged particles...Ch. 24 - a In Fig. 24-31a, what is the potential at point P...
Ch. 24 - Figure 24-32 shows a thin, uniformly charged rod...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-33, a particle is to be released at...Ch. 24 - SSM A particular 12 V car battery can send a total...Ch. 24 - The electric potential difference between the...Ch. 24 - Suppose that in a lightning flash the potential...Ch. 24 - Two large, parallel, conducting plates are 12 cm...Ch. 24 - SSM An infinite nonconducting sheet has a surface...Ch. 24 - When an electron moves from A to B along an...Ch. 24 - The electric field in a region of space has the...Ch. 24 - A graph of the x component of the electric field...Ch. 24 - An infinite nonconducting sheet has a surface...Ch. 24 - GO Two uniformly charged, infinite, nonconducting...Ch. 24 - A nonconducting sphere has radius R = 2.31 cm and...Ch. 24 - As a space shuttle moves through the dilute...Ch. 24 - What are a the change and b the charge density on...Ch. 24 - Consider a particle with charge q = 1.0 C, point A...Ch. 24 - SSM ILW A spherical drop of water carrying a...Ch. 24 - GO Figure 24-37 shows a rectangular array of...Ch. 24 - GO In Fig.24-33, what is the net electric...Ch. 24 - GO Two charged particles are shown in Fig. 24-39a....Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-40, particles with the charges q1 = 5e...Ch. 24 - Two particles, of charges q1 and q2, are separated...Ch. 24 - ILW The ammonia molecule NH3 has a permanent...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-41a, a particle of elementary charge e...Ch. 24 - a Figure 24-42a shows a nonconducting rod of...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 21-43, a plastic rod having a uniformly...Ch. 24 - A plastic rod has been bent into a circle of...Ch. 24 - GO Figure 24-45 shows a thin rod with a uniform...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-46, three thin plastic rods form...Ch. 24 - GO Figure 24-47 shows a thin plastic rod of length...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-48, what is the net electric potential...Ch. 24 - GO The smiling face of Fig. 24-49 consists of...Ch. 24 - SSM WWW A plastic disk of radius R = 64.0 cm is...Ch. 24 - GO A non uniform linear charge distribution given...Ch. 24 - GO The thin plastic rod shown in Fig. 24-47 has...Ch. 24 - Two large parallel metal plates are 1.5 cm apart...Ch. 24 - The electric potential al points in an xy plane is...Ch. 24 - The electric potential V in the space between two...Ch. 24 - SSM What is the magnitude of the electric field at...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-47 shows a thin plastic rod of length L...Ch. 24 - An electron is placed in an xy plane where I he...Ch. 24 - GO The thin plastic rod of length L = 10.0 cm in...Ch. 24 - A particle of charge 7.5 C is released from rest...Ch. 24 - a What is the electric potential energy of two...Ch. 24 - How much work is required to set up the...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-53, seven charged particles are fixed...Ch. 24 - ILW A particle of charge q is fixed at point P,...Ch. 24 - A charge of 9.0 nC is uniformly distributed around...Ch. 24 - GO What is the escape speed for an electron...Ch. 24 - A thin, spherical conducting shell of radius R is...Ch. 24 - GO Two electrons are fixed 2.0 cm apart. Another...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-54, how much work must we do to bring a...Ch. 24 - GO In the rectangle of Fig. 24-55, the sides have...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-56a shows an electron moving along an...Ch. 24 - Two tiny metal sphere? A and B, mass mA = 5.00 g...Ch. 24 - GO A positron charge e, mass equal to the electron...Ch. 24 - An electron is projected with an initial speed of...Ch. 24 - Particle 1 with a charge of 5.0 C and particle 2...Ch. 24 - SSM Identical 50 C charges are fixed or an x axis...Ch. 24 - GO Proton in a well. Figure 24-59 shows electric...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-60, a charged particle either an...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-61a, we move an electron from an...Ch. 24 - Suppose N electrons can be placed in either of two...Ch. 24 - Sphere 1 with radius R1 has positive charge q....Ch. 24 - SSM WWW Two metal spheres, each of radius 3.0 cm,...Ch. 24 - A hollow metal sphere has a potential of 400 V...Ch. 24 - SSM What is the excess charge on a conducting...Ch. 24 - Two isolated, concentric, conducting spherical...Ch. 24 - A metal sphere of radius 15 cm has a net charge of...Ch. 24 - Here are the charges and coordinates of two...Ch. 24 - SSM A long, solid, conducting cylinder has a...Ch. 24 - The chocolate crumb mystery. This story begins...Ch. 24 - SSM Starting from Eq. 24-30, derive an expression...Ch. 24 - The magnitude E of an electric field depends on...Ch. 24 - a If an isolated conducting sphere 10 cm in radius...Ch. 24 - Three particles, charge q1 = 10 C, q2 = 20 C, and...Ch. 24 - An electric field of approximately 100 V/m is...Ch. 24 - A Gaussian sphere of radius 4.00 cm is centered or...Ch. 24 - In a Millikan oil-drop experiment Module 22-6, a...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-63 shows three circular, nonconducting...Ch. 24 - An electron is released from rest on the axis of...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-64 shows a ring of outer radius R = 13.0...Ch. 24 - GO Electron in a well. Figure 24-65 shows electric...Ch. 24 - a If Earth had a uniform surface charge density of...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-66, point P is at distance d1 = 4.00 m...Ch. 24 - A solid conducting sphere of radius 3.0 cm has a...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-67, we move a particle of charge 2e in...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-68 shows a hemisphere with a charge of...Ch. 24 - SSM Three 0.12 C charges form an equilateral...Ch. 24 - Two charges q = 2.0 C are fixed a distance d = 2.0...Ch. 24 - Initially two electrons are fixed in place with a...Ch. 24 - A particle of positive charge Q is fixed at point...Ch. 24 - Two charged, parallel, flat conducting surfaces...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-70, point P is at the center of the...Ch. 24 - SSM A uniform charge of 16.0 C is on a thin...Ch. 24 - Consider a particle with charge q = 150 108 C,...Ch. 24 - SSM A thick spherical shell of charge Q and...Ch. 24 - A charge q is distributed uniformly throughout a...Ch. 24 - SSM A solid copper sphere whose radius is 1.0 cm...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-71, a metal sphere with charge q = 5.00...Ch. 24 - a Using Eq. 24-32, show that the electric...Ch. 24 - An alpha particle which has two protons is seat...Ch. 24 - In the quark model of fundamental particles, a...Ch. 24 - A charge of 1.50 108 C lies on an isolated metal...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-72, two particles of charges q1 and q2...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
How could the metaphyseal area of a bone help determine the age of a skeleton?
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
The following results were obtained from a broth dilution test for microbial susceptibility. Antibiotic Concent...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Plants use the process of photosynthesis to convert the energy in sunlight to chemical energy in the form of su...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
The feature labeled A on the map is a long ridge composed of till. Is this ridge an esker, an end moraine, or a...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
What two components contribute to species diversity? Explain how two communities with the same number of specie...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
4. Three groups of nonvascular plants are _______, ______, and _______. Three groups of seedless vascular plant...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What fuel economy should be expected from a gasoline powered car that encounters a total of 443N of resistive forces while driving down the road? (Those forces are from air drag, rolling resistance and bearing losses.) Assume a 30% thermodynamic efficiency.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward12. What is the angle between two unit vectors if their dot product is 0.5?arrow_forward
- If the car in the previous problem increases its power output by 10% (by pressing the gas pedal farther down), at what rate will the car accelerate? Hint: Consider the net force. In the previous problem the power was 31.8kWarrow_forwardWhat power is required (at the wheels) for a 1400 kg automobile to climb a 4% grade at a constant speed 30 m/s while it is opposed by drag and rolling resistance forces totaling 500 N?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- As a box is lifted against gravity and placed on a shelf, how does the work done by the lifter compare with the work done by gravity? What is the net work done on the box? What does this imply about its change in kinetic energy? Use definitions and mathematics from this chapter to answer these questions.arrow_forwardAs I carry a box up a flight of stairs, am I doing positive work or negative work on the box? Provide a mathematical explanation.arrow_forwardAs a ball falls under the influence of gravity, does gravity do positive work or negative work? Provide a mathematical explanation.arrow_forward
- Under what circumstances is it bad to describe kinetic energy as k = 1/2mv^2arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardAir temperature of 37 °C increases swimming pool temperature of 2.55 °C. What is the fraction of the water in the pool must evaporate during this time to carry enough energy to keep the temperature of the pool constant? 4186 J/(kg°C) = specific heat of water 2,430,000 (2.43 x 106) J/kg = latent heat of vaporization for the water in the pool.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY