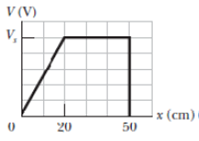
Problem 1Q: Figure 24-24 shows eight particles that form a square, with distance d between adjacent particles.... Problem 2Q: Figure 24-25 shows three sets of cross sections of equipotential surfaces in uniform electric... Problem 3Q: Figure 24-26 shows four pairs of charged particles. For each pair, let V = 0 at infinity and... Problem 4Q: Figure 24-27 gives the electric potential V as a function of x. a Rank the five regions according to... Problem 5Q: Figure 24-28 shows three paths along which we can move the positively charged sphere A closer to... Problem 6Q: Figure 24-29 shows four arrangement? of charged particles, all the same distance from the origin.... Problem 7Q: Figure 24-30 shows a system of three charged particles. If you move the particle of charge q from... Problem 8Q: In the situation of Question 7, is the work done by your force positive, negative, or zero if the... Problem 9Q: Figure 24-26 shows four pairs of charged particles with identical separations. a Rank the pairs... Problem 10Q: a In Fig. 24-31a, what is the potential at point P due to charge Q at distance R from P? Set V = 0... Problem 11Q: Figure 24-32 shows a thin, uniformly charged rod and three points at the same distance d from the... Problem 12Q: In Fig. 24-33, a particle is to be released at rest at point A and then is to be accelerated... Problem 1P: SSM A particular 12 V car battery can send a total charge of 84 A h ampere-hours through a circuit,... Problem 2P: The electric potential difference between the ground and a cloud in a particular thunderstorm is 12 ... Problem 3P: Suppose that in a lightning flash the potential difference between a cloud and the ground is 1.0 ... Problem 4P: Two large, parallel, conducting plates are 12 cm apart and have charges of equal magnitude and... Problem 5P: SSM An infinite nonconducting sheet has a surface charge density = 0.10 C/m2 on one side. How far... Problem 6P: When an electron moves from A to B along an electric field line in Fig. 24-34, the electric field... Problem 7P: The electric field in a region of space has the components Ey = Ez = 0 and Ex = 4.00 N/Cx. Point A... Problem 8P: A graph of the x component of the electric field as a function of x in a region of space is shown in... Problem 9P: An infinite nonconducting sheet has a surface charge density = 5.80 pC/m2. a How much work is done... Problem 10P: GO Two uniformly charged, infinite, nonconducting planes are parallel to a yz plane and positioned... Problem 11P: A nonconducting sphere has radius R = 2.31 cm and uniformly distributed charge q 3.50 fC. Take the... Problem 12P: As a space shuttle moves through the dilute ionized gas of Earths ionosphere, the shuttles potential... Problem 13P: What are a the change and b the charge density on the surface of a conducting sphere of radius 0.15... Problem 14P: Consider a particle with charge q = 1.0 C, point A at distance d1 = 2.0 m from q, and point B at... Problem 15P: SSM ILW A spherical drop of water carrying a charge of 30 pC has a potential of 500 V at its surface... Problem 16P: GO Figure 24-37 shows a rectangular array of charged particles fixed in place, with distance a =... Problem 17P: GO In Fig.24-33, what is the net electric potential at point P due to the four particles if V = 0 at... Problem 18P: GO Two charged particles are shown in Fig. 24-39a. Particle 1. with charge q1, is fixed in place at... Problem 19P: In Fig. 24-40, particles with the charges q1 = 5e and q2 = 15e are fixed in place with a separation... Problem 20P: Two particles, of charges q1 and q2, are separated by distance d in Fig. 24-40. The net electric... Problem 21P: ILW The ammonia molecule NH3 has a permanent electric dipole moment equal to 1.47 D, where 1 D = 1... Problem 22P: In Fig. 24-41a, a particle of elementary charge e is initially at coordinate z = 20 am on the dipole... Problem 23P: a Figure 24-42a shows a nonconducting rod of length L = 6.00 cm and uniform linear charge density =... Problem 24P: In Fig. 21-43, a plastic rod having a uniformly distributed charge Q = 25.6 pC has been bent into a... Problem 25P: A plastic rod has been bent into a circle of radius R = 8.20 cm. It has a charge Q1 = 4.20 pC... Problem 26P: GO Figure 24-45 shows a thin rod with a uniform charge density of 2.00 C/m. Evaluate the electric... Problem 27P: In Fig. 24-46, three thin plastic rods form quarter-circles with a common center of curvature at the... Problem 28P: GO Figure 24-47 shows a thin plastic rod of length L = 12.0 cm and uniform positive charge Q = 56.1... Problem 29P: In Fig. 24-48, what is the net electric potential at the origin due to the circular arc of charge Q1... Problem 30P: GO The smiling face of Fig. 24-49 consists of three items: 1. a thin rod of charge 3.0c that forms... Problem 31P: SSM WWW A plastic disk of radius R = 64.0 cm is charged on one side with a uniform surface charge... Problem 32P: GO A non uniform linear charge distribution given by = bx, where b is a constant, is located along... Problem 33P: GO The thin plastic rod shown in Fig. 24-47 has length L = 12.0 cm and a nonuniform linear charge... Problem 34P: Two large parallel metal plates are 1.5 cm apart and have charges of equal magnitudes but opposite... Problem 35P: The electric potential al points in an xy plane is given by V = 2.0 V/m2x2 3.0 V/m2y2. In... Problem 36P: The electric potential V in the space between two flat parallel plates 1 and 2 is given in volts by... Problem 37P: SSM What is the magnitude of the electric field at the point 3.00 2.00 4.00 k m if the electric... Problem 38P: Figure 24-47 shows a thin plastic rod of length L = 13.5 cm and uniform charge 43.6 fC. a In terms... Problem 39P: An electron is placed in an xy plane where I he electric potential depends on x and y as shown, for... Problem 40P: GO The thin plastic rod of length L = 10.0 cm in Fig. 24-47 has a nonuniform linear charge density ... Problem 41P: A particle of charge 7.5 C is released from rest at the point x = 60 cm on an x axis. The particle... Problem 42P: a What is the electric potential energy of two electrons separated by 2.00 nm? b If the separation... Problem 43P: How much work is required to set up the arrangement of Fig. 24-52 if q = 2.30 pC, a = 64.0 cm, and... Problem 44P: In Fig. 24-53, seven charged particles are fixed in place to form a square with an edge length of... Problem 45P: ILW A particle of charge q is fixed at point P, and a second particle of mass m and the same charge... Problem 46P: A charge of 9.0 nC is uniformly distributed around a thin plastic ring lying in a yz plane with the... Problem 47P: GO What is the escape speed for an electron initially at rest on the surface of a sphere with a... Problem 48P: A thin, spherical conducting shell of radius R is mounted on an isolating support and charged to a... Problem 49P: GO Two electrons are fixed 2.0 cm apart. Another electron is shot from infinity and stops midway... Problem 50P: In Fig. 24-54, how much work must we do to bring a particle, of charge Q = 16e and initially at... Problem 51P: GO In the rectangle of Fig. 24-55, the sides have lengths 5.0 cm and 15 cm. q1 = 5.0 C, and q2 = 2.0... Problem 52P: Figure 24-56a shows an electron moving along an electric dipole axis toward the negative side of the... Problem 53P: Two tiny metal sphere? A and B, mass mA = 5.00 g and mB = 10.0 g, have equal positive charge q =... Problem 54P: GO A positron charge e, mass equal to the electron mass is moving at 1.0 107 m/s in the positive... Problem 55P: An electron is projected with an initial speed of 3.2 105 m/s directly toward a proton that is... Problem 56P: Particle 1 with a charge of 5.0 C and particle 2 with a charge of 3.0 C are fixed in place with... Problem 57P: SSM Identical 50 C charges are fixed or an x axis at x = 3.0 m. A particle of charge q = 15 C is... Problem 58P: GO Proton in a well. Figure 24-59 shows electric potential V along an x axis, The scale of the... Problem 59P: In Fig. 24-60, a charged particle either an electron or a proton is moving rightward between two... Problem 60P: In Fig. 24-61a, we move an electron from an infinite distance to a point at distance R 8.00 cm from... Problem 61P: Suppose N electrons can be placed in either of two configurations. In configuration 1, they are all... Problem 62P: Sphere 1 with radius R1 has positive charge q. Sphere 2 with radius 2.00R1 is far from sphere 1 and... Problem 63P: SSM WWW Two metal spheres, each of radius 3.0 cm, have a center-to-center separation of 2.0 m.... Problem 64P: A hollow metal sphere has a potential of 400 V with respect to ground defined to beat V = 0 and a... Problem 65P: SSM What is the excess charge on a conducting sphere of radius r = 0.15 m if the potential of the... Problem 66P: Two isolated, concentric, conducting spherical shells have radii R1 = 0.500 m and R2 = 1.00 m,... Problem 67P: A metal sphere of radius 15 cm has a net charge of 3.0 108 C. a What is the electric field at the... Problem 68P: Here are the charges and coordinates of two charged particles located in an xy plane: q1 = 3.00 ... Problem 69P: SSM A long, solid, conducting cylinder has a radius of 2.0 cm. The electric field at the surface of... Problem 70P: The chocolate crumb mystery. This story begins with Problem 60 in Chapter 23. a From the answer to... Problem 71P: SSM Starting from Eq. 24-30, derive an expression for the electric field due to a dipole at a point... Problem 72P: The magnitude E of an electric field depends on the radial distance r according to E = A/r4, where A... Problem 73P: a If an isolated conducting sphere 10 cm in radius has a net charge of 4.0 C and if V = 0 at... Problem 74P: Three particles, charge q1 = 10 C, q2 = 20 C, and q3 = 30 C, are positioned at the vertices of an... Problem 75P: An electric field of approximately 100 V/m is often observed near the surface of Earth. If this were... Problem 76P: A Gaussian sphere of radius 4.00 cm is centered or a ball that has a radius of 1.00 cm and a uniform... Problem 77P: In a Millikan oil-drop experiment Module 22-6, a uniform electric field of 1.92 105 N/C is... Problem 78P: Figure 24-63 shows three circular, nonconducting arcs of radius R = 8.50 cm. The charges on the arcs... Problem 79P: An electron is released from rest on the axis of an electric dipole that has charge e and charge... Problem 80P: Figure 24-64 shows a ring of outer radius R = 13.0 cm, inner radius r = 0.200R, and uniform surface... Problem 81P: GO Electron in a well. Figure 24-65 shows electric potential V along an x axis. The scale of the... Problem 82P: a If Earth had a uniform surface charge density of 1.0 electron/m2 a very artificial assumption,... Problem 83P: In Fig. 24-66, point P is at distance d1 = 4.00 m from particle 1 q1 = 2e and distance d2 = 2.00 m... Problem 84P: A solid conducting sphere of radius 3.0 cm has a charge of 30 nC distributed uniformly over its... Problem 85P: In Fig. 24-67, we move a particle of charge 2e in from infinity to the x axis. How much work do we... Problem 86P: Figure 24-68 shows a hemisphere with a charge of 4.00 C distributed uniformly through its volume.... Problem 87P: SSM Three 0.12 C charges form an equilateral triangle 1.7 m on a side. Using energy supplied at the... Problem 88P: Two charges q = 2.0 C are fixed a distance d = 2.0 cm apart Fig. 24-69.a With V = 0 at infinity,... Problem 89P: Initially two electrons are fixed in place with a separation of 2.00 m. How much work must we do to... Problem 90P: A particle of positive charge Q is fixed at point P. A second particle of mass m and negative charge... Problem 91P: Two charged, parallel, flat conducting surfaces are spaced d = 1.00 cm apart and produce a potential... Problem 92P: In Fig. 24-70, point P is at the center of the rectangle. With V = 0 at infinity, q1 = 5.00 fC, q2 =... Problem 93P: SSM A uniform charge of 16.0 C is on a thin circular ring lying in an xy plane and centered on the... Problem 94P: Consider a particle with charge q = 150 108 C, and take V = 0 at infinity, a What are the shape and... Problem 95P: SSM A thick spherical shell of charge Q and uniform volume charge density is bounded by radii r1... Problem 96P: A charge q is distributed uniformly throughout a spherical volume of radius R. Let V = 0 at... Problem 97P: SSM A solid copper sphere whose radius is 1.0 cm has a very thin surface coating of nickel. Some of... Problem 98P: In Fig. 24-71, a metal sphere with charge q = 5.00 C and radius r = 3.00 cm is concentric with a... Problem 99P: a Using Eq. 24-32, show that the electric potential at a point on the central axis of a thin ring of... Problem 100P: An alpha particle which has two protons is seat directly toward a target nucleus containing 92... Problem 101P: In the quark model of fundamental particles, a proton is composed of three quarks: two up quarks,... Problem 102P: A charge of 1.50 108 C lies on an isolated metal sphere of radius 16.0 cm. With V = 0 at infinity,... Problem 103P: In Fig. 24-72, two particles of charges q1 and q2 are fixed to an x axis. If a third particle, of... format_list_bulleted


 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




