
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 24, Problem 17P
GO In Fig.24-33, what is the net electric potential at point P due to the four particles if V = 0 at infinity, q = 5.00 fC, and d = 4.00 cm?
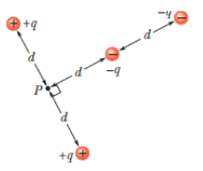
Figure 24-38 Problem 17.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls
Consider the situation in the figure below; a neutral conducting ball hangs from the ceiling by an insulating string, and a charged insulating rod is going to be placed nearby.
A. First, if the rod was not there, what statement best describes the charge distribution of the ball?
1) Since it is a conductor, all the charges are on the outside of the ball. 2) The ball is neutral, so it has no positive or negative charges anywhere. 3) The positive and negative charges are separated from each other, but we don't know what direction the ball is polarized. 4) The positive and negative charges are evenly distributed everywhere in the ball.
B. Now, when the rod is moved close to the ball, what happens to the charges on the ball?
1) There is a separation of charges in the ball; the side closer to the rod becomes positively charged, and the opposite side becomes negatively charged. 2) Negative charge is drawn from the ground (via the string), so the ball acquires a net negative charge. 3)…
answer question 5-9
Chapter 24 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 24 - Figure 24-24 shows eight particles that form a...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-25 shows three sets of cross sections of...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-26 shows four pairs of charged...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-27 gives the electric potential V as a...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-28 shows three paths along which we can...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-29 shows four arrangement? of charged...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-30 shows a system of three charged...Ch. 24 - In the situation of Question 7, is the work done...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-26 shows four pairs of charged particles...Ch. 24 - a In Fig. 24-31a, what is the potential at point P...
Ch. 24 - Figure 24-32 shows a thin, uniformly charged rod...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-33, a particle is to be released at...Ch. 24 - SSM A particular 12 V car battery can send a total...Ch. 24 - The electric potential difference between the...Ch. 24 - Suppose that in a lightning flash the potential...Ch. 24 - Two large, parallel, conducting plates are 12 cm...Ch. 24 - SSM An infinite nonconducting sheet has a surface...Ch. 24 - When an electron moves from A to B along an...Ch. 24 - The electric field in a region of space has the...Ch. 24 - A graph of the x component of the electric field...Ch. 24 - An infinite nonconducting sheet has a surface...Ch. 24 - GO Two uniformly charged, infinite, nonconducting...Ch. 24 - A nonconducting sphere has radius R = 2.31 cm and...Ch. 24 - As a space shuttle moves through the dilute...Ch. 24 - What are a the change and b the charge density on...Ch. 24 - Consider a particle with charge q = 1.0 C, point A...Ch. 24 - SSM ILW A spherical drop of water carrying a...Ch. 24 - GO Figure 24-37 shows a rectangular array of...Ch. 24 - GO In Fig.24-33, what is the net electric...Ch. 24 - GO Two charged particles are shown in Fig. 24-39a....Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-40, particles with the charges q1 = 5e...Ch. 24 - Two particles, of charges q1 and q2, are separated...Ch. 24 - ILW The ammonia molecule NH3 has a permanent...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-41a, a particle of elementary charge e...Ch. 24 - a Figure 24-42a shows a nonconducting rod of...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 21-43, a plastic rod having a uniformly...Ch. 24 - A plastic rod has been bent into a circle of...Ch. 24 - GO Figure 24-45 shows a thin rod with a uniform...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-46, three thin plastic rods form...Ch. 24 - GO Figure 24-47 shows a thin plastic rod of length...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-48, what is the net electric potential...Ch. 24 - GO The smiling face of Fig. 24-49 consists of...Ch. 24 - SSM WWW A plastic disk of radius R = 64.0 cm is...Ch. 24 - GO A non uniform linear charge distribution given...Ch. 24 - GO The thin plastic rod shown in Fig. 24-47 has...Ch. 24 - Two large parallel metal plates are 1.5 cm apart...Ch. 24 - The electric potential al points in an xy plane is...Ch. 24 - The electric potential V in the space between two...Ch. 24 - SSM What is the magnitude of the electric field at...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-47 shows a thin plastic rod of length L...Ch. 24 - An electron is placed in an xy plane where I he...Ch. 24 - GO The thin plastic rod of length L = 10.0 cm in...Ch. 24 - A particle of charge 7.5 C is released from rest...Ch. 24 - a What is the electric potential energy of two...Ch. 24 - How much work is required to set up the...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-53, seven charged particles are fixed...Ch. 24 - ILW A particle of charge q is fixed at point P,...Ch. 24 - A charge of 9.0 nC is uniformly distributed around...Ch. 24 - GO What is the escape speed for an electron...Ch. 24 - A thin, spherical conducting shell of radius R is...Ch. 24 - GO Two electrons are fixed 2.0 cm apart. Another...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-54, how much work must we do to bring a...Ch. 24 - GO In the rectangle of Fig. 24-55, the sides have...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-56a shows an electron moving along an...Ch. 24 - Two tiny metal sphere? A and B, mass mA = 5.00 g...Ch. 24 - GO A positron charge e, mass equal to the electron...Ch. 24 - An electron is projected with an initial speed of...Ch. 24 - Particle 1 with a charge of 5.0 C and particle 2...Ch. 24 - SSM Identical 50 C charges are fixed or an x axis...Ch. 24 - GO Proton in a well. Figure 24-59 shows electric...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-60, a charged particle either an...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-61a, we move an electron from an...Ch. 24 - Suppose N electrons can be placed in either of two...Ch. 24 - Sphere 1 with radius R1 has positive charge q....Ch. 24 - SSM WWW Two metal spheres, each of radius 3.0 cm,...Ch. 24 - A hollow metal sphere has a potential of 400 V...Ch. 24 - SSM What is the excess charge on a conducting...Ch. 24 - Two isolated, concentric, conducting spherical...Ch. 24 - A metal sphere of radius 15 cm has a net charge of...Ch. 24 - Here are the charges and coordinates of two...Ch. 24 - SSM A long, solid, conducting cylinder has a...Ch. 24 - The chocolate crumb mystery. This story begins...Ch. 24 - SSM Starting from Eq. 24-30, derive an expression...Ch. 24 - The magnitude E of an electric field depends on...Ch. 24 - a If an isolated conducting sphere 10 cm in radius...Ch. 24 - Three particles, charge q1 = 10 C, q2 = 20 C, and...Ch. 24 - An electric field of approximately 100 V/m is...Ch. 24 - A Gaussian sphere of radius 4.00 cm is centered or...Ch. 24 - In a Millikan oil-drop experiment Module 22-6, a...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-63 shows three circular, nonconducting...Ch. 24 - An electron is released from rest on the axis of...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-64 shows a ring of outer radius R = 13.0...Ch. 24 - GO Electron in a well. Figure 24-65 shows electric...Ch. 24 - a If Earth had a uniform surface charge density of...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-66, point P is at distance d1 = 4.00 m...Ch. 24 - A solid conducting sphere of radius 3.0 cm has a...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-67, we move a particle of charge 2e in...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-68 shows a hemisphere with a charge of...Ch. 24 - SSM Three 0.12 C charges form an equilateral...Ch. 24 - Two charges q = 2.0 C are fixed a distance d = 2.0...Ch. 24 - Initially two electrons are fixed in place with a...Ch. 24 - A particle of positive charge Q is fixed at point...Ch. 24 - Two charged, parallel, flat conducting surfaces...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-70, point P is at the center of the...Ch. 24 - SSM A uniform charge of 16.0 C is on a thin...Ch. 24 - Consider a particle with charge q = 150 108 C,...Ch. 24 - SSM A thick spherical shell of charge Q and...Ch. 24 - A charge q is distributed uniformly throughout a...Ch. 24 - SSM A solid copper sphere whose radius is 1.0 cm...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-71, a metal sphere with charge q = 5.00...Ch. 24 - a Using Eq. 24-32, show that the electric...Ch. 24 - An alpha particle which has two protons is seat...Ch. 24 - In the quark model of fundamental particles, a...Ch. 24 - A charge of 1.50 108 C lies on an isolated metal...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-72, two particles of charges q1 and q2...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
8. What structures pass through the hypoglossal canal?
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
13. A wire is stretched right to its breaking point by a 5000 N force. A longer wire made of the same material ...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Match the following examples of mutagens. Column A Column B ___a. A mutagen that is incorporated into DNA in pl...
Microbiology: An Introduction
All of the following terms can appropriately describe humans except: a. primary consumer b. autotroph c. hetero...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Explain all answers clearly, with complete sentences and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk (*) desi...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
How do food chains and food webs differ? Which is the more accurate representation of feeding relationships in ...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- AMPS VOLTS OHMS 5) 50 A 110 V 6) .08 A 39 V 7) 0.5 A 60 8) 2.5 A 110 Varrow_forwardThe drawing shows an edge-on view of two planar surfaces that intersect and are mutually perpendicular. Surface (1) has an area of 1.90 m², while surface (2) has an area of 3.90 m². The electric field in the drawing is uniform and has a magnitude of 215 N/C. Find the magnitude of the electric flux through surface (1 and 2 combined) if the angle 8 made between the electric field with surface (2) is 30.0°. Solve in Nm²/C 1 Ө Surface 2 Surface 1arrow_forwardPROBLEM 5 What is the magnitude and direction of the resultant force acting on the connection support shown here? F₁ = 700 lbs F2 = 250 lbs 70° 60° F3 = 700 lbs 45° F4 = 300 lbs 40° Fs = 800 lbs 18° Free Body Diagram F₁ = 700 lbs 70° 250 lbs 60° F3= = 700 lbs 45° F₁ = 300 lbs 40° = Fs 800 lbs 18°arrow_forward
- PROBLEM 3 Cables A and B are Supporting a 185-lb wooden crate. What is the magnitude of the tension force in each cable? A 20° 35° 185 lbsarrow_forwardThe determined Wile E. Coyote is out once more to try to capture the elusive Road Runner of Loony Tunes fame. The coyote is strapped to a rocket, which provide a constant horizontal acceleration of 15.0 m/s2. The coyote starts off at rest 79.2 m from the edge of a cliff at the instant the roadrunner zips by in the direction of the cliff. If the roadrunner moves with constant speed, find the minimum velocity the roadrunner must have to reach the cliff before the coyote. (proper sig fig in answer)arrow_forwardPROBLEM 4 What is the resultant of the force system acting on the connection shown? 25 F₁ = 80 lbs IK 65° F2 = 60 lbsarrow_forward
- Three point-like charges in the attached image are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. Each side of the triangle has a length of 38.0 cm, and the point (C) is located half way between q1 and q3 along the side. Find the magnitude of the electric field at point (C). Let q1 = −2.80 µC, q2 = −3.40 µC, and q3 = −4.50 µC. Thank you.arrow_forwardSTRUCTURES I Homework #1: Force Systems Name: TA: PROBLEM 1 Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the force in the cable shown. PROBLEM 2 The horizontal component of force F is 30 lb. What is the magnitude of force F? 6 10 4 4 F = 600lbs F = ?arrow_forwardThe determined Wile E. Coyote is out once more to try to capture the elusive Road Runner of Loony Tunes fame. The coyote is strapped to a rocket, which provide a constant horizontal acceleration of 15.0 m/s2. The coyote starts off at rest 79.2 m from the edge of a cliff at the instant the roadrunner zips by in the direction of the cliff. If the roadrunner moves with constant speed, find the minimum velocity the roadrunner must have to reach the cliff before the coyote. (proper sig fig)arrow_forward
- Hello, I need some help with calculations for a lab, it is Kinematics: Finding Acceleration Due to Gravity. Equations: s=s0+v0t+1/2at2 and a=gsinθ. The hypotenuse,r, is 100cm (given) and a height, y, is 3.5 cm (given). How do I find the Angle θ1? And, for distance traveled, s, would all be 100cm? For my first observations I recorded four trials in seconds: 1 - 2.13s, 2 - 2.60s, 3 - 2.08s, & 4 - 1.95s. This would all go in the coloumn for time right? How do I solve for the experimental approximation of the acceleration? Help with trial 1 would be great so I can use that as a model for the other trials. Thanks!arrow_forwardAfter the countdown at the beginning of a Mario Kart race, Bowser slams on the gas, taking off from rest. Bowser get up to a full speed of 25.5 m/s due to an acceleration of 10.4 m/s2. A)How much time does it take to reach full speed? B) How far does Bowser travel while accelerating?arrow_forwardThe drawing in the image attached shows an edge-on view of two planar surfaces that intersect and are mutually perpendicular. Side 1 has an area of 1.90 m^2, Side 2 has an area of 3.90 m^2, the electric field in magnitude is around 215 N/C. Please find the electric flux magnitude through side 1 and 2 combined if the angle (theta) made between the electric field with side 2 is 30.0 degrees. I believe side 1 is 60 degrees but could be wrong. Thank you.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY