
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To indicate whether the statement “pyruvate is the final product for glycolysis” concerning glucose
Concept introduction: Pyruvate
A product is defined as the substance that is formed after the completion of a
(b)
Interpretation: To indicate whether the statement “lactate is the final product for gluconeogenesis” concerning glucose metabolic pathways is true or false.
Concept introduction: Lactate is the conjugate base of lactic acid. The structure of lactate is as follows:
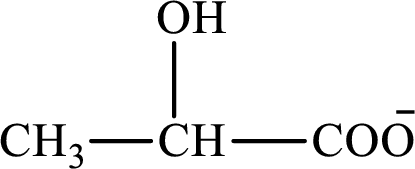
A product is defined as the substance that is formed after the completion of a chemical reaction.
(c)
Interpretation: To indicate whether the statement “glycogen is the final product for glycogenolysis” concerning glucose metabolic pathways is true or false.
Concept introduction: Glucose is a monosaccharide with the molecular formula
A product is defined as the substance that is formed after the completion of a chemical reaction.
(d)
Interpretation: To indicate whether the statement “
Concept introduction: Glucose is a monosaccharide with the molecular formula
A product is defined as the substance that is formed after the completion of a chemical reaction.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 24 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Seventh Edition
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning




