
(a)
Interpretation:
The equation for its formation from vinyl acetate has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Polyvinyl acetate is
It is resistant to oil, grease and solvent. And it is fully degradable and a quick dissolver.
Used in water transfer printing process.
The structure of polyvinyl acetate as shown below.
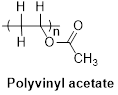
(b)
Interpretation:
Three monomer units has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Polyvinyl acetate is polymer of vinyl acetate. It is used a emulsifying and adhesive properties.
It is resistant to oil, grease and solvent. And it is fully degradable and a quick dissolver.
Used in water transfer printing process.
The structure of polyvinyl acetate as shown below.
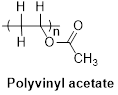
(c)
Interpretation:
The formation polyvinyl alcohol from polyvinyl acetate has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Polyvinyl acetate is polymer of vinyl acetate. It is used as emulsifying and adhesive properties.
It is resistant to oil, grease and solvent. And it is fully degradable and a quick dissolver.
Used in water transfer printing process.
The structure of polyvinyl acetate as shown below.
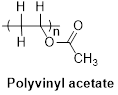
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- 2CIO2 + 20H-1 CIO31 + CIO2 + H2O Experiment [CIO2], M [OH-1], M 1 0.0500 0.100 23 2 0.100 0.100 3 0.100 0.0500 Initial Rate, M/s 0.0575 0.230 0.115 ... Given this date, calculate the overall order of this reaction.arrow_forward2 3 .(be)_[Ɔ+(be)_OI ← (b²)_IƆO+ (be)_I Experiment [1-] M 0.005 [OCI-] 0.005 Initial Rate M/min 0.000275 0.0025 0.005 0.000138 0.0025 0.0025 0.000069 4 0.0025 0.0025 0.000140 Calculate the rate constant of this reaction using the table data.arrow_forward1 2 3 4 I(aq) +OCl(aq) → IO¯¯(aq) + Cl¯(aq) Experiment [I-] M 0.005 [OCI-] 0.005 Initial Rate M/min 0.000275 0.0025 0.005 0.000138 0.0025 0.0025 Calculate the overall order of this reaction using the table data. 0.0025 0.000069 0.0025 0.000140arrow_forward
- H2O2(aq) +3 I¯(aq) +2 H+(aq) → 13(aq) +2 H₂O(l)· ••• Experiment [H2 O2]o (M) [I]o (M) [H+]。 (M) Initial rate (M/s) 1 0.15 0.15 0.05 0.00012 234 0.15 0.3 0.05 0.00024 0.3 0.15 0.05 0.00024 0.15 0.15 0.1 0.00048 Calculate the overall order of this reaction using the table data.arrow_forwardThe U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets limits on healthful levels of air pollutants. The maximum level that the EPA considers safe for lead air pollution is 1.5 μg/m³ Part A If your lungs were filled with air containing this level of lead, how many lead atoms would be in your lungs? (Assume a total lung volume of 5.40 L.) ΜΕ ΑΣΦ = 2.35 1013 ? atoms ! Check your rounding. Your final answer should be rounded to 2 significant figures in the last step. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forwardY= - 0.039 (14.01) + 0.7949arrow_forward
- Suppose 1.76 g of magnesium acetate (Mg (CH3CO2)2) are dissolved in 140. mL of water. Find the composition of the resulting electrolyte solution. In particular, list the chemical symbols (including any charge) of each dissolved ion in the table below. List only one ion per row. mEq Then, calculate the concentration of each ion in dwrite the concentration in the second column of each row. Be sure you round your answers to the L correct number of significant digits. ion Add Row mEq L x 5arrow_forwardA pdf file of your hand drawn, stepwise mechanisms for the reactions. For each reaction in the assignment, you must write each mechanism three times (there are 10 reactions, so 30 mechanisms). (A) do the work on a tablet and save as a pdf., it is expected to write each mechanism out and NOT copy and paste the mechanism after writing it just once. Everything should be drawn out stepwise and every bond that is formed and broken in the process of the reaction, and is expected to see all relevant lone pair electrons and curved arrows.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning




