
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The theoretical yield of
Concept introduction:
Number of moles of a substance,
From its given mass is,
Theoretical yield is the maximum product yield that can be expected based on the masses of the reactants and the reaction stoichiometry.
2-Iodobenzoic acid is a crystaline solid and it can be prepared from 2-aminobenzoic acid treated with
The reaction can be represnted as follows,
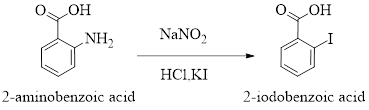
(a)
Answer to Problem 104IL
Theoretical yield of benzoic acid is
Explanation of Solution
From the given data,
Let’s calculate the number of moles of 2-amino benzoic acid:
From the given:
Let’s calculate the number of moles of
From the given:
Let’s calculate the number of moles of
From the equation , we can see that 1 mole of 2- amino benzoic acid gives 1 mole of 1-iodo benzoic acid .
For this conversion required 1 mole of
Theoretically produced
Molar mass of 2-iodobenzoic acid =
Therefore, theoretical yield of 2-iodobenzoic acid is
(b)
Interpretation: To Check the possibilty of isomers for 2-iodobenzoic acid
Concept introduction:
2-Iodobenzoic acid is a crystaline solid and it can be prepared from 2-aminobenzoic acid treated with
The reaction can be represnted as follows,
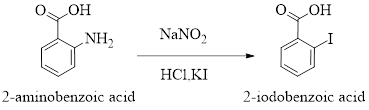
Two compounds that have the same molecular formula, but have different structural formulas are called isomers.
(b)
Answer to Problem 104IL
No other possible isomers for 2-Iodobenzoic acid.
Explanation of Solution
No other isomers of 2-iodo benzoic acid are possible in this reaction because the
(c)
Interpretation: The molar mass of the product formed in the given reaction has to be determined. And check whether the calculated molar mass is in reasonable agreement with the theoretical molar mass or not.
Concept introduction:
2-Iodobenzoic acid is a crystaline solid and it can be prepared from 2-aminobenzoic acid treated with
The reaction can be represnted as follows,
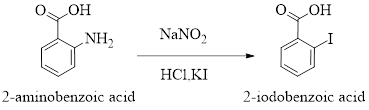
Concentration of solutions can be expressed in various terms; molarity is one such concentration expressing term.
Molarity (M) of a solution is the number of gram moles of a solute present in one liter of the solution.
A solution containing one gram mole or
Amount of substance (mol) can be determined by using the equation,
The molar mass of an element or compound is the mass in grams of 1 mole of that substance, and it is expressed in the unit of grams per mol (g/mol).
Theoretical yield is the maximum product yield that can be expected based on the masses of the reactants and the reaction stoichiometry.
(c)
Answer to Problem 104IL
Molar mass of 2-Iodobenzoic acid
There is only
Explanation of Solution
From the given,
Let’s calculate the number of mole of
Let’s calculate molar mass of 2-iodo benzoic acid.
Theoretical mass 2-Iodobenzoic acid is
Therefore, there is only
We can say that it is in reasonable agreement with theoretical molar mass.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
- 0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward5.arrow_forward9arrow_forward
- alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZS18w-nDB10538ZsAtmorZoFusYj2Xu9b78gZo- O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 3- 200 temperature (K) Explanation Chick Q Sowncharrow_forward0+ aleksog/x/lsl.exe/1ou-lgNgkr7j8P3H-IQs pBaHhviTCeeBZbufuBYTOHz7m7D3ZStEPTBSB3u9bsp3Da pl19qomOXLhvWbH9wmXW5zm O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 Gab The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 0.75 atm and -229. °C is increased until the sample sublimes. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.50 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. F3 pressure (atm) 0- 0 200 Explanation temperature (K) Check F4 F5 ☀+ Q Search Chill Will an 9 ENG F6 F7 F8 F9 8 Delete F10 F11 F12 Insert PrtSc 114 d Ararrow_forwardx + LEKS: Using a phase diagram a X n/alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/10_u-IgNsikr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpw ○ States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the melting point of X when the pressure above the solid is 1.1 atm. pressure (atm) 16 08- solid liquid- 0 200 400 gas 600 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 25 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. × 5arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



