
(a)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with dilute
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product
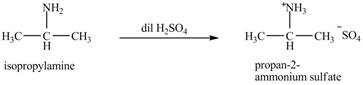
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of amines with dilute

Figure 1
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with dilute
(b)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with a dilute
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and it also has the ability to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The reaction does not form any product. The reaction is shown below.
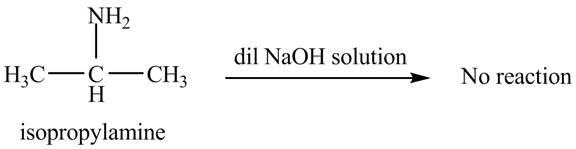
Explanation of Solution
When isopropylamine reacts with a dilute
Figure 2
No product is obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with a dilute
(c)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with butyllithium in
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and it also has the ability to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product lithium isopropylamide is obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with butyllithium in
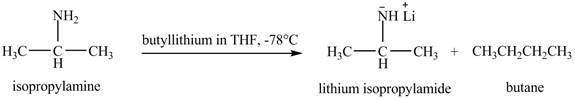
Explanation of Solution
The organolithium base butyllithium in

Figure 3
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with butyllithium in
(d)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with acetyl chloride and pyridine is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and it also has the ability to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product,
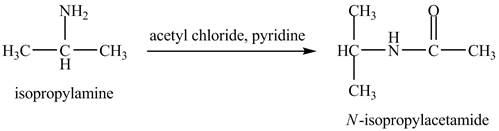
Explanation of Solution
The acid chloride is a very reactive compound. When it reacts with amines it forms amides. The reaction of isopropylamine with acetyl chloride in pyridine results in the formation of
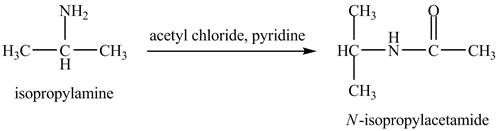
Figure 4
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with acetyl chloride and pyridine is
(e)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. The formation of diazonium salt from
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product,
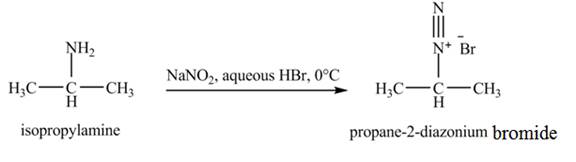
Explanation of Solution
The reaction is an example of a diazotization reaction. When isopropylamine reacts with

Figure 5
The product that obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with
(f)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with acetone and
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and it also has the ability to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
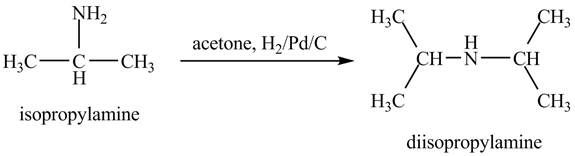
Explanation of Solution
When acetone reacts with isopropylamine, it forms enamine, with double bonds. It is then hydrogenated by

Figure 6
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with acetone and
(g)
Interpretation:
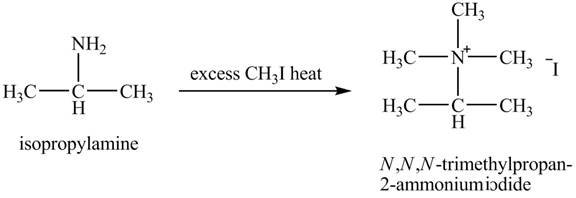
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with excess
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Hofmann elimination reaction occurs as an anti-elimination reaction. In this reaction, the starting material is quaternary ammonium hydroxide. When quaternary ammonium hydroxide is heated,
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product,
Explanation of Solution
Hofmann elimination reaction occurs as an anti-elimination reaction. In this reaction, the starting material is isopropylamine. When it reacts with an excess of

Figure 7
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with excess
(h)
Interpretation:
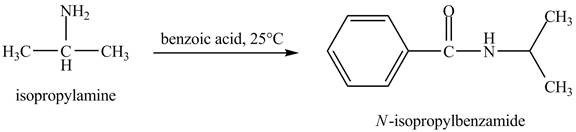
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with benzoic acid at
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and it also has the ability to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product
Explanation of Solution
In this reaction, benzoic acid is a reactive compound. When it reacts with amine it results in the formation of an amide. This reaction is similar to the conversion of carboxylic acid to amides. The reaction is shown below.
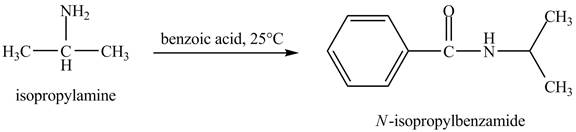
Figure 8
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with benzoic acid at
(i)
Interpretation:
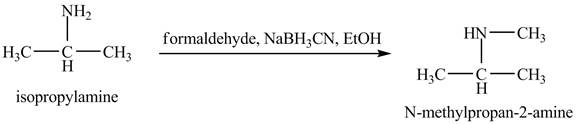
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with formaldehyde,
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and it also has the ability to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product
Explanation of Solution
This reaction is an example of a reductive amination reaction. Reductive amination reaction is the conversion of the carbonyl group to the amine or it converts one amine to newer amine. In this reaction, when isopropylamine reacts formaldehyde,

Figure 9
The product that obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with formaldehyde,
(j)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and it also has the ability to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product
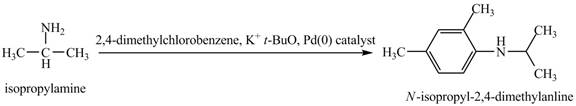
Explanation of Solution
This reaction is an example of a Buchwald-Hartwig reaction. Buchwald Hartwig reaction is used for
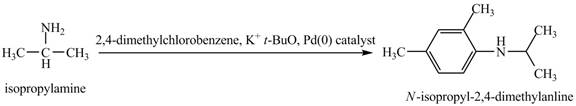
Figure 10
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with
(k)
Interpretation:
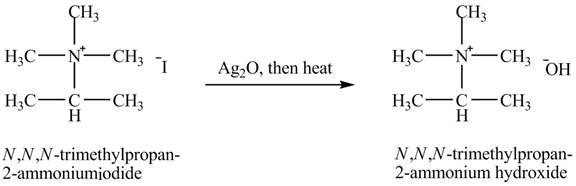
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with a product of part (g) +
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Hofmann elimination reaction occurs as an anti-elimination reaction. In this reaction, the starting material is quaternary ammonium hydroxide. When quaternary ammonium hydroxide is heated,
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product
Explanation of Solution
When isopropylamine undergoes Hofmann elimination reaction with a product of part (g)

Figure 11
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with a product of part (g)
(l)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with a product of part (d) with
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and it also has the ability to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product,
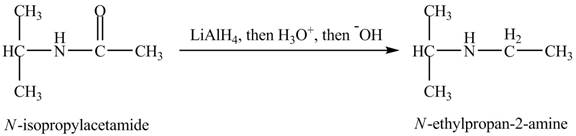
Explanation of Solution
When
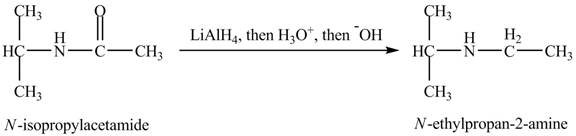
Figure 12
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with a product of part (d) with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Ebook And Single-course Homework Access
- Polymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. Draw three repeat units (trimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. Assume there are hydrogen atoms there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the trimer. Ignore inorganic byproducts.arrow_forwardDraw a tetramer if this alternating copolymer pleasearrow_forwardDraw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer.arrow_forward
- Draw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer.arrow_forward8:44 PM Sun Apr 13 Earn Freecash.com O Measurement and Matter =1 Setting up a unit conversion 110 Eddie says... ✰ www-awu.aleks.com A student sets up the following equation to convert a measurement. (The ? stands for a number the student is going to calculate.) Fill in the missing part of this equation. Note: your answer should be in the form of one or more fractions multiplied together. (- 4 J kJ -7.0 × 10 ☐ = ? mmol.°C mol °C x10 μ Explanation Check □·□ torox.io Grey Hill LLC. All Rightsarrow_forwardPolymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. Draw three repeat units (trimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. Assume there are hydrogen atoms there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the trimer. Ignore inorganic byproducts please.arrow_forward
- i need help on how to complete the followingarrow_forwardno AI walkthrough current image is wrong answerarrow_forwarda. Determine whether each of the Followery Molecules is in the R- On the y- Configuration 1-01"/ 1-6-4 Br 4 I el Br b. Draw The Fisher projection For all the Meso compounds that can exist FOR The Following molenlearrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
