
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 23.44AP
The product obtained in the reaction of
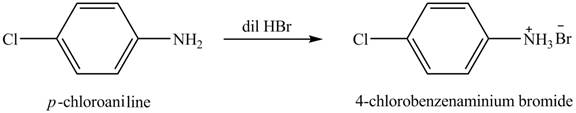
Explanation of Solution
When
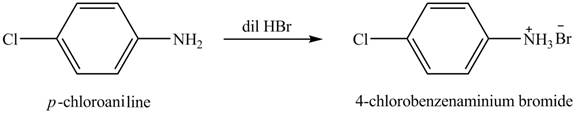
Figure 1
The product obtained in the reaction of
(b)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. When alcohol reacts with hydrogen halide it forms
Answer to Problem 23.44AP
The product obtained in the reaction of
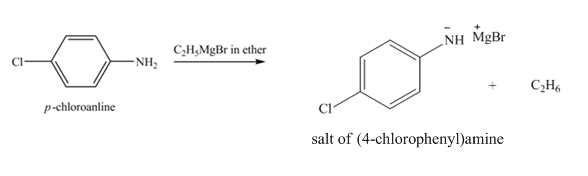
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of

Figure 2
The product obtained in the reaction of
(c)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of
Concept introduction:
The formation of diazonium salt from
Answer to Problem 23.44AP
The product obtained in the reaction of
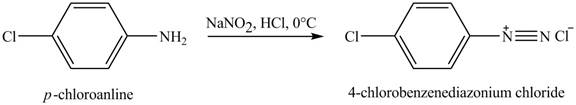
Explanation of Solution
When

Figure 3
The product obtained in the reaction of
(d)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and also the ability of the nitrogen to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.44AP
The product
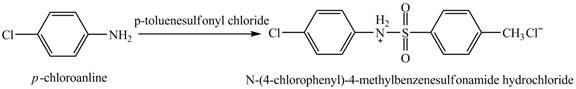
Explanation of Solution
When

Figure 4
The product
(e)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. The formation of diazonium salt from aromatic amines takes place using sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid at low temperatures. Aryl diazonium salts undergo a variety of specific substitution reactions in which the incoming Z group replaces
Answer to Problem 23.44AP
The product
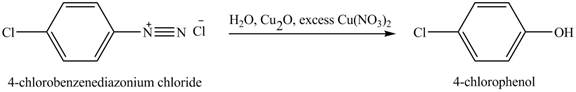
Explanation of Solution
When
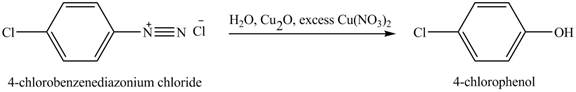
Figure 5
The product obtained in the reaction of
(f)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of
Concept introduction:
The formation of diazonium salt from aromatic amines takes place using sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid at low temperatures. Aryl diazonium salts undergo a variety of specific substitution reactions in which the incoming Z group replaces
Answer to Problem 23.44AP
The product
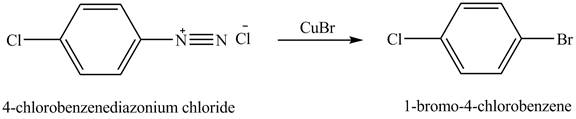
Explanation of Solution
When
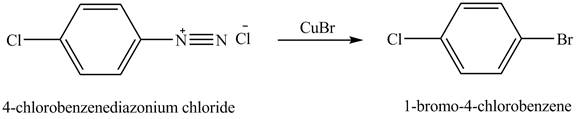
Figure 6
The product
(g)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of
Concept introduction:
The formation of diazonium salt from aromatic amines takes place using sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid at low temperatures. Aryl diazonium salts undergo a variety of specific substitution reactions in which the incoming Z group replaces
Answer to Problem 23.44AP
The product chlorobenzene is obtained in the reaction of the product of part (c) and
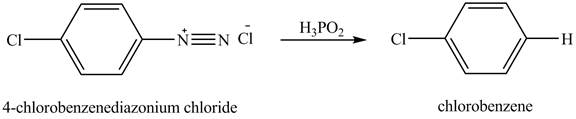
Explanation of Solution
The reduction reaction of
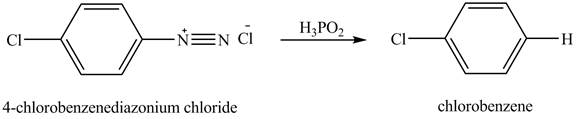
Figure 7
The product chlorobenzene is obtained in the reaction of the product of part (c) and
(h)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of
Concept introduction:
The formation of diazonium salt from aromatic amines takes place using sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid at low temperatures. Aryl diazonium salts undergo a variety of specific substitution reactions in which the incoming Z group replaces
Answer to Problem 23.44AP
The product,
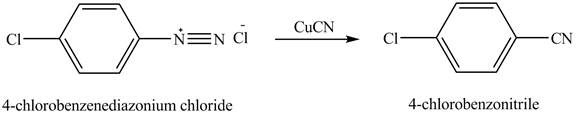
Explanation of Solution
When

Figure 8
The product,
(i)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of
Concept introduction:
The formation of diazonium salt from aromatic amines takes place using sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid at low temperatures. Aryl diazonium salts undergo a variety of specific substitution reactions in which the incoming Z group replaces N2 (a very good leaving group) to form corresponding products.
Answer to Problem 23.44AP
The product
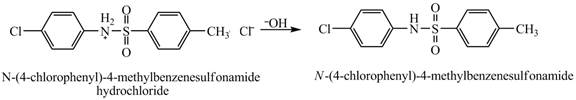
Explanation of Solution
When

Figure 9
The product
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Ebook And Single-course Homework Access
- i need help identifying the four carbon oxygen bonds in the following:arrow_forwardImagine each of the molecules shown below was found in an aqueous solution. Can you tell whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral? molecule HO H3N + The solution is... X O acidic OH O basic H3N-CH-C-O O neutral ○ (unknown) O acidic ○ basic CH2 CH 3-S-CH2 O neutral ○ (unknown) H3N O OH O acidic O basic Oneutral O (unknown) 0 H3N-CH-C-O CH3 CH CH3 O acidic O basic O neutral ○ (unknown) ? olo Ar BHarrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughs need other product (product in picture is wrong dont submit the same thing)arrow_forward
- I have a 2 mil plastic film that degrades after 22 days at 88C and at 61C takes 153 days. What is the failure at 47C in days.arrow_forwardIf a 5 film plastic film degraded in 30 days at 35C and the same film degraded in 10 days at 55 C and 2 days at 65C what would the predicted life time be at 22C for the same film?arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
- I have a aqueous solution (175 ml) of iridium trichloride containing 8,750 ppm Iridium by ICP OES analysis. What is the percent concentration of Iridium trichloride in aquous solution and provide the concentration in moles per liter, percentage by weight.arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


