
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction of
Concept introduction: The bimolecular elimination reaction that favours the removal of a HX substituent from an
Answer to Problem 23.13P
The product that is formed by the reaction of
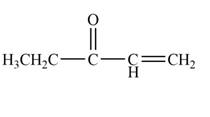
Explanation of Solution
The product that is formed by the reaction of
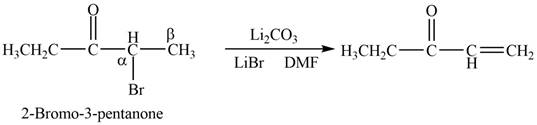
Figure 1
In this reaction, the given
The product that is formed by the reaction of
(b)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction of
Concept introduction: The substitution reaction involves the replacement of one
The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Answer to Problem 23.13P
The product that is formed by the reaction of
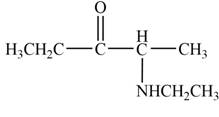
Explanation of Solution
The product that is formed by the reaction of
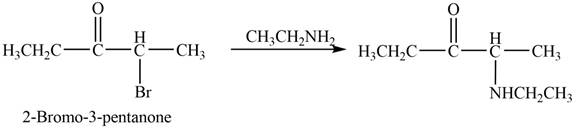
Figure 2
In this reaction, the given ketone,
The product that is formed by the reaction of
(c)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction of
Concept introduction: The substitution reaction involves the replacement of one functional group by other functional group. In nucleophilic substitution an electron rich species attack the species that is deficient in electrons. The electrophile and the leaving group together form a substrate. The nucleophile attacks over the substrate and there occurs the removal of leaving group from the substrate.
The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Answer to Problem 23.13P
The product that is formed by the reaction of
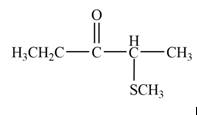
Explanation of Solution
The product that is formed by the reaction of
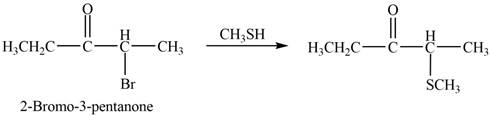
Figure 3
In this reaction, the given ketone,
The product that is formed by the reaction of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Is the structural form shown possible given the pKa constraints of the side chains?arrow_forwardon x Fina X Sign X Sign x lab X Intro X Cop X chat X My x Grac x Laur x Laur x ashes x S Shox S SHE x a eve.macmillanlearning.com/ihub/assessment/f188d950-dd73-11e0-9572-0800200c9a66/d591b3f2-d5f7-4983-843c-0d00c1c0340b/f2b47861-07c4-4d1b-a1ee-e7db27d6b4ee?actualCourseld=d591b3f2-c stions estion. ct each urces. +95 Macmillan Learning Draw the product formed by the reaction of potassium t-butoxide with (15,25)-1-bromo-2-methyl-1-phenylbutane (shown). Clearly show the stereochemistry of the product. H BH (CH3)3CO-K+ +100 H3CW (CH3)3COH +85 H3CH2C +95 ossible ↓ Q Search Select Draw Templates More C H 0 bp A Erase 2Q 112 Resouarrow_forwardIdentify the structure of the PTH derivative generated after two rounds of Edman degradation.arrow_forward
- Use the data below from an electron impact mass spectrum of a pure compound to deduce its structure. Draw your structure in the drawing window. Data selected from the NIST WebBook, https://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/ m/z Relative intensity 31 0.5 30 26 29 22 28 100 27 33 26 23 15 4 • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. 妊 n ? Previous Nextarrow_forwardfor this question. Write the molecular formula for a compound with the possible elements C, H, N and O that exhibits a molecular ion at M+ = 98.1106. Exact Masses of the Most Abundant Isotope of Selected Elements Isotope Natural abundance (%) Exact mass 1H 99.985 1.008 12C 98.90 12.000 14N 99.63 14.003 160 99.76 15.995 Molecular formula (In the order CHNO, with no subscripts)arrow_forwardPLEASE READ!!! I DONT WANT EXAMPLES, I DONT WANT WORDS OR PARAGRAPHS!!! PLEASE I UNDERSTAND THE BASICS BUT THIS IS AN EXCEPTION THAT EVEN THE INTERNET CANT HELP!!!! THIS IS THE THIRD TIME I'VE SENT THOSE QUESTIONS SO PLEASE DONT RESEND THE SAME STUFF, ITS NOT HELPING ME!!! I ALSO ALREADY TRIED TO DRAW THE MECHANISM MYSELF, SO IF ITS RIGHT PLEASE TELL ME OR TELL ME WHAT I HAVE TO CHANGE!!! First image: I have to SHOW (DRAWING) the mechanism (with arows and structures of molecules) NOT WORDS PLEASE! of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primary Second image: I have to show the mechanism (IMAGE) (with arrows and structures of the molecules) NOT WORDS PLEASE !! for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion HOMEWORK, NOT EXAM!! ALL DETAILS ARE IN THE IMAGES PLEASE LOOK AT THE IMAGES, DONT LOOK AT THE AI GENERATED TEXT!!!arrow_forward
- Write the molecular formula for a compound with the possible elements C, H, N and O that exhibits a molecular ion at M+ = 85.0899. Exact Masses of the Most Abundant Isotope of Selected Elements Isotope Natural abundance (%) Exact mass 1H 99.985 1.008 12C 98.90 12.000 14N 99.63 14.003 160 99.76 15.995 Molecular formula (In the order CHNO, with no subscripts)arrow_forwardUse the data below from an electron impact mass spectrum of a pure compound to deduce its structure. Draw your structure in the drawing window. Data selected from the NIST WebBook, https://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/ m/z Relative intensity 59 3.0 58 64 43 100 15 23 • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. •You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. + n[] 85 // ? CH4 Previous Nextarrow_forwardWrite the molecular formula for a compound with the possible elements C, H, N and O that exhibits a molecular ion at M* = 128.0632. Exact Masses of the Most Abundant Isotope of Selected Elements Isotope Natural abundance (%) Exact mass 1H 99.985 12C 98.90 14N 99.63 160 99.76 Molecular formula 1.008 12.000 14.003 15.995 (In the order CHNO, with no subscripts)arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this? And can I please the lowest possible significant number?arrow_forwardWhat is the molar mass of a gas that takes three times longer to effuse than helium?arrow_forwardFirst image: I have to show the mecanism (with arows and structures) of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primary Second image: I have to show the mecanism (with arrows and structures) for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion its not an examarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
