
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The empirical formula of the given acid has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Maleic acid is prepared by the catalytic oxidation of benzene.It is a dicarboxylic acid ,that is, it has two
It is cis– isomer of butenedioic acid.Molecular formula is
The structure of maleic acid is as shown below.

Empirical formula of a compound is the smallest integer ratio of numbers of each element presented in that compound.
Molecular formula of a compound is integer multiple of empirical formula, the integer is depend upon the mass of empirical formula and the molecular mass of the compound.
The number of moles of any substance can be determined using the equation,
(a)
Answer to Problem 113SCQ
Empirical formula of the acid is
Explanation of Solution
Assuming the molecular formula of the compound is
It dissociates into carbondioxide and water. The equation is as follows.
Let’s calculate the moles of C in
Let’s calculate the moles of
Weight of Hydrogen =
Let’s calculate the weight of Oxygen:
Let’s calculate the mole of Oxygen:
Let’s calculate the mole ratio of each element:
Therefore, the empirical formula of the given compound is
(b)
Interpretation:
The molecular formula of the given acid has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Maleic acid is prepared by the catalytic oxidation of benzene.It is a dicarboxylic acid ,that is, it has two carboxylic acid groups.
It is cis– isomer of butenedioic acid.Molecular formula is
The structure of maleic acid is as shown below.

Empirical formula of a compound is the smallest integer ratio of numbers of each element presented in that compound.
Molecular formula of a compound is integer multiple of empirical formula, the integer is depend upon the mass of empirical formula and the molecular mass of the compound.
The number of moles of any substance can be determined using the equation,
(b)
Answer to Problem 113SCQ
Molecular formula of the acid is
Explanation of Solution
According to the law of gram equivalents, equivalent acid is equal to the equivalents of base.
Let’s calculate the molecular formula:
Substitute the ‘n’ value we get molecular formula of acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the given acid has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Maleic acid is prepared by the catalytic oxidation of benzene.It is a dicarboxylic acid ,that is, it has two carboxylic acid groups.
It is cis– isomer of butenedioic acid.Molecular formula is
The structure of maleic acid is as shown below.

Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represent the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure indicates the all unpaired electrons present in the atom in the molecules.
The Lewis structure of Maleic is as follows.
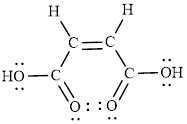
(d)
Interpretation:
The hybridization used by the carbon atom in the given acid compound has to be described.
Concept introduction:
Maleic acid is prepared by the catalytic oxidation of benzene.It is a dicarboxylic acid ,that is, it has two carboxylic acid groups.
It is cis– isomer of butenedioic acid.Molecular formula is
The structure of maleic acid is as shown below.

Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure indicates the all unpaired electrons present in the atom in the molecules.
The Lewis structure of Maleic is as follows.

The geometry around the entire carbon atoms in the molecule is trigonal planar, which means these carbon atoms used
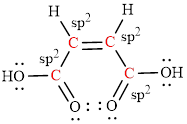
(e)
Interpretation:
The bond angles around each C-atom in the given molecule has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Maleic acid is prepared by the catalytic oxidation of benzene.It is a dicarboxylic acid ,that is, it has two carboxylic acid groups.
It is cis– isomer of butenedioic acid.Molecular formula is
The structure of maleic acid is as shown below.

Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure of Maleic is as follows.

The geometry around the entire carbon atoms in the molecule is trigonal planar, which means these carbon atoms used

The geometry around each carbon atom in the given compound is trigonal planar and so the bond angle is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
CHEMISTRY+CHEM...HYBRID ED.(LL)>CUSTOM<
- 10. Write out the mechanism (intermediate/transition state) for this reaction; indicate stereochemistry in product. H3C CH₂OH CH3 SN1 Harrow_forwardWrite "most" under the member of each trio which is most stable. Write "least under the member of each trio which is least stable. b) Draw a Fischer projection of a pair of enantiomers with three chiral carbons. Which of these two would you expect to be more soluble in water? Why? 1-butanol 1-heptanol Which of these two would you expect to have the higher boiling point? Why? hexyl methyl ether 1-heptanolarrow_forwardWrite "most" under the most acidic compound. Write "least" under the least acidic compound. OH NO₂ OCH3 Br 9. Compound X, C50H84F2, reacts with excess H2/Pd to give a C50H88F2 compound. How many rings are in X? How many double bonds are in X? Show your work.arrow_forward
- 4. State whether these two are: a) the same molecule b) c) d) different compounds that are not isomers constitutional isomers diastereomers e) enantiomers CH3 CH₁₂ H OH HO H H OH HO H CH, CH₂ 5. a) How many stereocenters does this compound have? b) How many stereoisomers are possible for this compound? CH₂ OH CHCHarrow_forwardCalculating the pH at equivalence of a titration A chemist titrates 210.0 mL of a 0.1003 M hydrobromic acid (HBr) solution with 0.7550M KOH solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of KOH solution added. pH = ] ☑ o0o 18 Ararrow_forwardDo you do chemistry assignmentsarrow_forward
- Using the conditions of spontaneity to deduce the signs of AH and AS Use the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A This reaction is always spontaneous, but proceeds slower at temperatures above 120. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except above 117. °C. AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) This reaction is slower below 20. °C than C above. AS is |(pick one) ? 18 Ar 1arrow_forwardCalculating the pH at equivalence of a titration Try Again Your answer is incorrect. 0/5 a A chemist titrates 70.0 mL of a 0.7089 M hydrocyanic acid (HCN) solution with 0.4574M KOH solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The pK of hydrocyanic acid is 9.21. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of KOH solution added. pH = 11.43] G 00. 18 Ar B•arrow_forwardBiological Macromolecules Naming and drawing the products of aldose oxidation and reduction aw a Fischer projection of the molecule that would produce L-ribonic acid if it were subjected to mildly oxidizing reaction conditions. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X AP ‡ 1/5 Naor Explanation Check McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibilarrow_forward
- ● Biological Macromolecules Identifying the parts of a disaccharide Take a look at this molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. CH2OH O H H H OH OH OH H H CH2OH H O OH H OH H H H H OH Is this a reducing sugar? Does this molecule contain a glycosidic bond? If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the symbol describing it. If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the common names (including anomer and enantiomer labels) of the molecules that would be released if that bond were hydrolyzed. If there's more than one molecule, separate each name with a comma. Explanation Check O yes X O no ○ yes O no Uarrow_forwardThe aim of the lab is to measure the sodium content from tomato sauce using the Mohr titration method. There are two groups being: Regular Tomato sauce & Salt Reduced tomato sauce QUESTION: State how you would prepare both Regular & Salt reduced tomato sauce samples for chemical analysis using the Mohr titration methodarrow_forwardUsing the conditions of spontaneity to deduce the signs of AH and AS Use the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous but proceeds faster at temperatures above -48. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) ✓ AS is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except below 114. °C but proceeds at a slower rate below 135. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is C This reaction is exothermic and proceeds faster at temperatures above -43. °C. (pick one) AS is (pick one) v Х 5 ? 18 Ararrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning



