
EP ENGR.MECH.:DYNAMICS-REV.MOD.MAS.ACC.
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133976588
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON CO
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22.1, Problem 12P
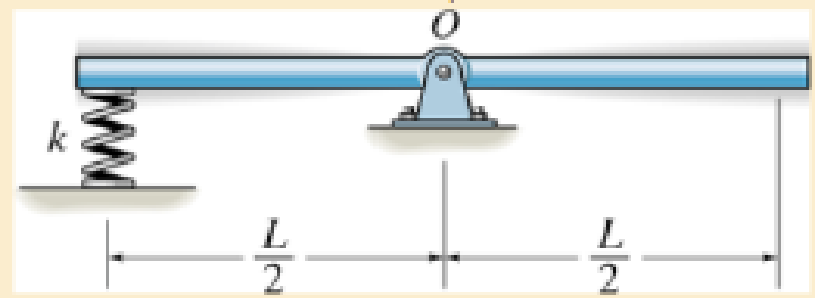
*22-12. Determine the natural period of vibration of the uniform bar of mass m when it is displaced downward slightly and released.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Find the reaction at A and B
The other response I got was not too accurate,I need expert solved answer, don't use Artificial intelligence or screen shot it solving
No chatgpt pls
Solve for the reaction of all the forces
Don't use artificial intelligence or screen shot it, only expert should solve
Chapter 22 Solutions
EP ENGR.MECH.:DYNAMICS-REV.MOD.MAS.ACC.
Ch. 22.1 - A spring is stretched 175 mm by an 8-kg block. If...Ch. 22.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 22.1 - A spring is stretched 200 mm by a 15-kg block. If...Ch. 22.1 - When a 20-lb weight is suspended from a spring,...Ch. 22.1 - Prob. 5PCh. 22.1 - Prob. 6PCh. 22.1 - Prob. 7PCh. 22.1 - Prob. 8PCh. 22.1 - A 3-kg block is suspended from a spring having a...Ch. 22.1 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 22.1 - Prob. 11PCh. 22.1 - 22-12. Determine the natural period of vibration...Ch. 22.1 - The body of arbitrary shape has a mass m, mass...Ch. 22.1 - Determine the torsional stiffness k, measured in...Ch. 22.1 - Prob. 15PCh. 22.1 - Prob. 16PCh. 22.1 - If the natural periods of oscillation of the...Ch. 22.1 - Prob. 18PCh. 22.1 - Prob. 19PCh. 22.1 - A uniform board is supported on two wheels which...Ch. 22.1 - If the wire AB is subjected to a tension of 20 lb,...Ch. 22.1 - The bar has a length l and mass m. It is supported...Ch. 22.1 - The 20-kg disk, is pinned at its mass center O and...Ch. 22.1 - Prob. 24PCh. 22.1 - If the disk in Prob. 22-24 has a mass of 10 kg,...Ch. 22.1 - Prob. 26PCh. 22.1 - Prob. 27PCh. 22.1 - Prob. 28PCh. 22.1 - Prob. 29PCh. 22.2 - Determine the differential equation of motion of...Ch. 22.2 - Determine the natural period of vibration of the...Ch. 22.2 - Determine the natural period of vibration of the...Ch. 22.2 - Prob. 33PCh. 22.2 - Determine the differential equation of motion of...Ch. 22.2 - Prob. 35PCh. 22.2 - Prob. 36PCh. 22.2 - Prob. 37PCh. 22.2 - Prob. 38PCh. 22.2 - Prob. 39PCh. 22.2 - If the slender rod has a weight of 5 lb, determine...Ch. 22.6 - If the block-and-spring model is subjected to the...Ch. 22.6 - Prob. 42PCh. 22.6 - A 4-lb weight is attached to a spring having a...Ch. 22.6 - Prob. 44PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 45PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 46PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 47PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 48PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 49PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 50PCh. 22.6 - The 40-kg block is attached to a spring having a...Ch. 22.6 - The 5kg circular disk is mounted off center on a...Ch. 22.6 - Prob. 53PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 54PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 55PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 56PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 57PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 58PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 59PCh. 22.6 - The 450-kg trailer is pulled with a constant speed...Ch. 22.6 - Prob. 61PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 62PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 63PCh. 22.6 - The spring system is connected to a crosshead that...Ch. 22.6 - Prob. 65PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 66PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 67PCh. 22.6 - The 200-lb electric motor is fastened to the...Ch. 22.6 - Prob. 69PCh. 22.6 - If two of these maximum displacements can be...Ch. 22.6 - Prob. 71PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 72PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 73PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 74PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 75PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 76PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 77PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 78PCh. 22.6 - Prob. 79P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardA six cylinder petrol engine has a compression ratio of 5:1. The clearance volume of each cylinder is 110CC. It operates on the four-stroke constant volume cycle and the indicated efficiency ratio referred to air standard efficiency is 0.56. At the speed of 2400 rpm. 44000KJ/kg. Determine the consumes 10kg of fuel per hour. The calorific value of fuel average indicated mean effective pressure.arrow_forwardThe members of a truss are connected to the gusset plate as shown in (Figure 1). The forces are concurrent at point O. Take = 90° and T₁ = 7.5 kN. Part A Determine the magnitude of F for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. F= 7.03 Submit ? kN Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 21 attempts remaining ▾ Part B Determine the magnitude of T2 for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure T₂ = 7.03 C T2 |? KN Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 23 attempts remaining Provide Feedbackarrow_forward
- Consider the following acid-base reaction: Fe3+(aq) +3H2O -Fe(OH)3 (s) + 3H* ← A. Using thermodynamics, calculate the equilibrium constant K at 25°C (The AG° of formation of Fe(OH)3(s) is -699 kJ/mol). B. Using the value of K you calculated in part a, if a solution contains 10-4 M Fe3+ and has a pH of 7.5, will Fe(OH)3(s) precipitate? Show all calculations necessary to justify your answer. Note that the reaction as written is for precipitation, not dissolution like Ksp-arrow_forwardA vertical force of F = 3.4 kN is applied to the hook at A as shown in. Set d = 1 m. Part A 3 m 3m 0.75 m 1.5 m. Determine the tension in cable AB for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FAB= Value Submit Request Answer Part B Units ? Determine the tension in cable AC for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FAC = Value Submit Request Answer Part C ? Units Determine the tension in cable AD for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardConsider the heat engine operating at steady state between the two thermal reservoirs shown at the right while producing a net power output of 700 kW. If 1000 kW of heat (Q̇H) is transferred to the heat engine from a thermal reservoir at a temperature of TH = 900 K, and heat is rejected to a thermal reservoir at a temperature of TL = 300 K, is this heat engine possible? Can you answer this question for me and show all of the workarrow_forward
- 1.12 A disk of constant radius r is attached to a telescoping rod that is extending at a constant rate as shown in Fig. P1.12. Both the disk and the rod are rotating at a constant rate. Find the inertial velocity and acceleration of point P at the rim of the disk. ท2 L 0 SS P α e 0 O' êL Fig. P1.12 Rotating disk attached to telescoping rod. 60 LLarrow_forwardTwo different options A and B with brake pads for disc brakes are connected to the rope drum. The diameter of the rope drum is 150 mm. What distance must the pads B be at from the center of rotation to cover the same distance as A?A B- Width 50 mm - Width 60 mm- Evidence center 120mm - Construction power 900 N from rotation center.- Maintains a weight of 200 kgwhen the installation force is 1.4kN (μ is missing from the data)M=μF(Ry-Ri)Right answer R=187 mmarrow_forwardAssume the xy plane is level ground, and that the vertical pole shown in the diagram lies along the z-axis with its base at the origin. If the pole is 5 m tall, and a rope is used to pull on the top of the pole with a force of 400 N as shown, determine the magnitudes of the parallel and perpendicular components of the force vector with respect to the axis of the post i.e. with respect to the z-axis.arrow_forward
- 4-1 Q4: Q5: (20 Marks) Find √48 using False Position Method with three iterations. Hint: the root lies between 3 and 4. (20 Marks)arrow_forwardDetermine the angle between vectors FA and FB that is less than 180 degrees. FA is the vector drawn from the origin to point A (-4, 4, 2) while FB is the vector drawn from the origin to point B (3, 1, -3).arrow_forwardFind the resultant force vector from adding F1, F2 and F3, where … F1 = {-8i+10j-32k} N F2 is 40 N in magnitude with coordinate direction angles α, β, and γ, of 45, 120 and 60 degrees, respectively and F3 is 22 N in magnitude with transverse and azimuth angles of 65 and 40 degrees, respectively Express your final answer as a Cartesian vector as well as a magnitude with angles.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Introduction to Undamped Free Vibration of SDOF (1/2) - Structural Dynamics; Author: structurefree;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BkgzEdDlU78;License: Standard Youtube License