
(a)
Interpretation:
The enol structure of the compound
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 22.7P
The enol structures of the compound
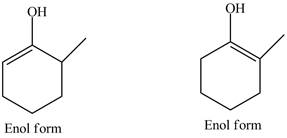
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
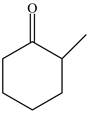
Figure 1
In the compound,
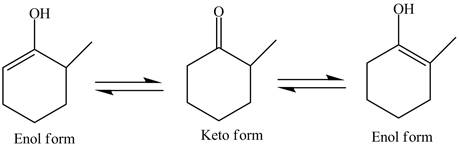
Figure 2
The compound
The enol structures of the compound
(b)
Interpretation:
The enol structure of the compound
Concept introduction:
Ketone also exists in two forms which are commonly known as keto-enol tautomerism. Tautomers are isomers which differ only in the position of the protons and electrons of the double bond of the electronegative atom in the compound. There is no change in the carbon skeleton of the compound. This phenomenon which involves simple proton transfer in an intramolecular fashion is known as tautomerism.
Answer to Problem 22.7P
The enol structure of the compound
Explanation of Solution
The structure of given compound
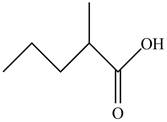
Figure 3
In the compound,
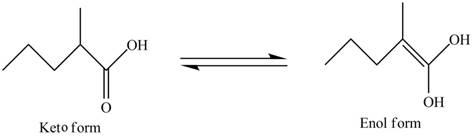
Figure 4
The enol structure of the compound
(c)
Interpretation:
The enol structure of the compound benzaldehyde is to be drawn. The explanation as to why the compound does not form enol structure.
Concept introduction:
The carbonyl compound contains a
Answer to Problem 22.7P
There is no
Explanation of Solution
The given compound benzaldehydeis shown below.
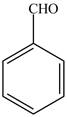
Figure 5
In the compoundbenzaldehydethere is no
In benzaldehyde, due to the absence of
(d)
Interpretation:
The enol structure of the compound
Concept introduction:
Ketone also exists in two forms which are commonly known as keto-enol tautomerism. Tautomers are isomers which differ only in the position of the protons and electrons of the double bond of the electronegative atom in the compound. There is no change in the carbon skeleton of the compound. This phenomenon which involves simple proton transfer in an intramolecular fashion is known as tautomerism.
Answer to Problem 22.7P
The enol structure of the compound
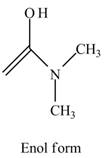
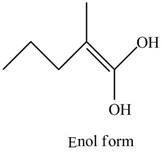
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compound
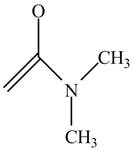
Figure 6
In the compound,
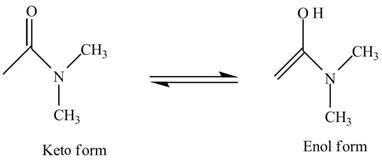
Figure 7
The enol structure of the compound
(e)
Interpretation:
The enol structure of the compound
Concept introduction:
Ketone also exists in two forms which are commonly known as keto-enol tautomerism. Tautomers are isomers which differ only in the position of the protons and electrons of the double bond of the electronegative atom in the compound. There is no change in the carbon skeleton of the compound. This phenomenon which involves simple proton transfer in an intramolecular fashion is known as tautomerism.
Answer to Problem 22.7P
There is no
Explanation of Solution
The given compound
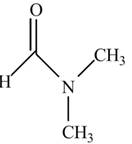
Figure 8
In the compound
In
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY STUDY GUIDE AND S
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are reacted with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward2,2-Dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are reacted with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. Indicate the products obtained.arrow_forward
- Add conditions above and below the arrow that turn the reactant below into the product below in a single transformationADS fint anditions 百 Abl res condinese NC ง Add on condtions 1.0 B H,N.arrow_forward3. Provide all the steps and reagents for this synthesis. OHarrow_forwardSteps and explanationarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





