
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of benzoic anhydride
Concept introduction: Anhydrides involve two carbonyl groups. The nucleophilic substitution reaction of anhydride involves the attack of nucleophilic at one carbonyl group, which causes the second carbonyl group to be the part of leaving group.
Answer to Problem 22.14P
The products formed by the treatment of benzoic anhydride
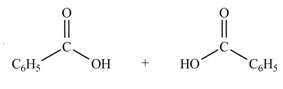
Explanation of Solution
The given treatment involves reaction of benzoic anhydride
Anhydrides involve two carbonyl groups. The nucleophilic substitution reaction of anhydride involves the attack of nucleophilic at one carbonyl group, which causes the second carbonyl group to be the part of leaving group.
Anhydrides yield two equivalents of carboxylic acids, when they are treated with
The products formed by the treatment of benzoic anhydride
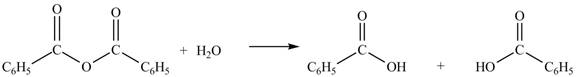
Figure 1
The products formed by the treatment of benzoic anhydride
(b)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of benzoic anhydride
Concept introduction: Anhydrides involve two carbonyl groups. The nucleophilic substitution reaction of anhydride involves the attack of nucleophilic at one carbonyl group, which causes the second carbonyl group to be the part of leaving group.
Answer to Problem 22.14P
The products formed by the treatment of benzoic anhydride
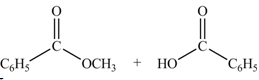
Explanation of Solution
The given treatment involves reaction of benzoic anhydride
Anhydrides involve two carbonyl groups. The nucleophilic substitution reaction of anhydride involves the attack of nucleophilic at one carbonyl group, which causes the second carbonyl group to be the part of leaving group.
Anhydrides yield esters, and carboxylic acids, when they are treated with
The products formed by the treatment of benzoic anhydride
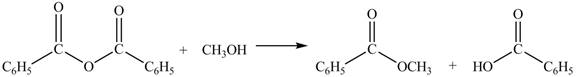
Figure 2
The products formed by the treatment of benzoic anhydride
(c)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of benzoic anhydride
Concept introduction: Anhydrides involve two carbonyl groups. The nucleophilic substitution reaction of anhydride involves the attack of nucleophilic at one carbonyl group, which causes the second carbonyl group to be the part of leaving group.
Answer to Problem 22.14P
The products formed by the treatment of benzoic anhydride
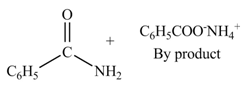
Explanation of Solution
The given treatment involves reaction of benzoic anhydride
Anhydrides involve two carbonyl groups. The nucleophilic substitution reaction of anhydride involves the attack of nucleophilic at one carbonyl group, which causes the second carbonyl group to be the part of leaving group.
Anhydrides yield amide and an ammonium salt of
The products formed by the treatment of benzoic anhydride
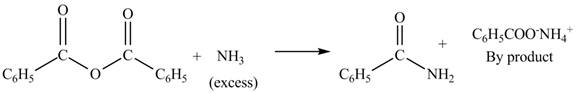
Figure 3
The products formed by the treatment of benzoic anhydride
(d)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of benzoic anhydride
Concept introduction: Anhydrides involve two carbonyl groups. The nucleophilic substitution reaction of anhydride involves the attack of nucleophilic at one carbonyl group, which causes the second carbonyl group to be the part of leaving group.
Answer to Problem 22.14P
The products formed by the treatment of benzoic anhydride
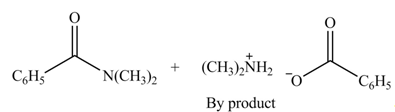
Explanation of Solution
The given treatment involves reaction of benzoic anhydride
Anhydrides involve two carbonyl groups. The nucleophilic substitution reaction of anhydride involves the attack of nucleophilic at one carbonyl group, which causes the second carbonyl group to be the part of leaving group.
Anhydrides yield amide and an ammonium salt of carboxylic acid, when they are treated with
The products formed by the treatment of benzoic anhydride
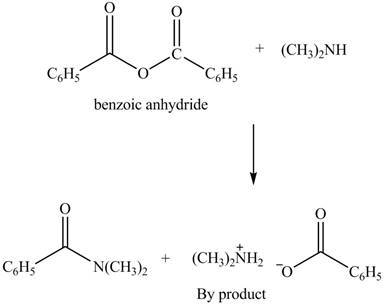
Figure 4
The products formed by the treatment of benzoic anhydride
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- For the decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 NO2 + NO3 (K1) | NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) | NO2 + NO3 NO2 + O2 + NO (k2) | NO + N2O51 NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) → Give the expression for the acceptable rate. → → (A). d[N205] dt == 2k,k₂[N₂O₂] k₁+k₁₂ (B). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k₁[NO₂] [NO3] - k₂[NO₂]³ dt (C). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k [NO] - k₂[NO] [NO] d[N2O5] (D). = dt = -k₁[N2O5] - k¸[NO][N₂05] dt Do not apply the calculations, based on the approximation of the stationary state, to make them perform correctly. Basta discard the 3 responses that you encounter that are obviously erroneous if you apply the formula to determine the speed of a reaction.arrow_forwardR lactam or lactone considering as weak acid or weak base and whyarrow_forward81. a. Propose a mechanism for the following reaction: OH CH2=CHCHC=N b. What is the product of the following reaction? HO H₂O N=CCH2CH2CH OH HO CH3CCH=CH2 H₂O C=N 82. Unlike a phosphonium ylide that reacts with an aldehyde or a ketone to form an alkene a sulfonium uliaarrow_forward
- For each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new CC bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. ? NH2 MgBr Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? ○ Yes ○ No MgBr ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? O Yes O No Click and drag to start drawing a structure. :☐ G x c olo Ar HEarrow_forwardPredicting As the lead product manager at OrganometALEKS Industries, you are trying to decide if the following reaction will make a molecule with a new C - C bond as its major product: H₂N O H 1. ? 2. H3O+ If this reaction will work, draw the major organic product or products you would expect in the drawing area below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. 0 If the major products of this reaction won't have a new CC bond, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. فا Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardHighlight the chirality (or stereogenic) center(s) in the given compound. A compound may have one or more stereogenic centers. OH OH OH OH OH OHarrow_forward
- Using wedge-and-dash bonds, modify the bonds on the chiral carbon in the molecule below so the molecule has R stereochemical configuration. NH H Br X टेarrow_forwardProvide photos of models of the following molecules. (Include a key for identification of the atoms) 1,2-dichloropropane 2,3,3-trimethylhexane 2-bromo-3-methybutanearrow_forwardPlease draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forward
- A 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardFirefly luciferin exhibits three rings. Identify which of the rings are aromatic. Identify which lone pairs are involved in establishing aromaticity. The lone pairs are labeled A-D below.arrow_forwardA 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

