
Interpretation:
Two different optical isomers needs to be drawn by attaching the following atoms or groups to the carbon atom:
Concept introduction:
Two mirror image representations are possible for a molecule having chiral center in its structure. If the mirror images are non-superimposable to each other then, they are said to be optical isomers.
Explanation of Solution
A molecule is said to be chiral molecule when all the attached groups to central carbon atom are different and lacks in plane of symmetry in the molecule. The molecules having chiral centres show optical isomerism as there are two mirror image representations possible for a molecule having chiral center in its structure and if the mirror images are non-superimposable to each other then, they are said to be optical isomers.
Now, starting from a single carbon atom, two different optical isomers can be drawn by attaching
The single compound formed will be:
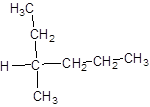
Since the central carbon atom is attached to four different atoms and groups so, it is chiral in nature shown by * as:
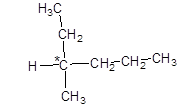
Now, drawing the optical isomers using mirror as:
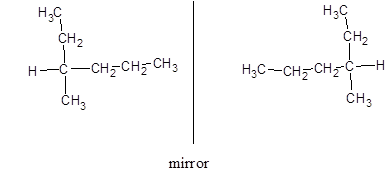
Since, the mirror image is not superimposable to each other so, they are optical isomers of each other.
Chapter 21 Solutions
Glencoe Chemistry: Matter and Change, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
- We discussed the solid phase resin using in peptide synthesis. Provide a mechanism, for its formation. DRAW THE MECHANISM.arrow_forwardPlease help. Every time I've asked an expert in the past, it's been wrong :(arrow_forwardPlease help everysingle time ive asked in the past, the solution has been wrongarrow_forward
- Please helparrow_forward(a) 21.8 Name the following compounds. & (b) Br (e) O₂N. (h) H (c) Br (d) NH2 ☑N Br H ہیں Ph (g) OMe бл .0-0.e 21.9 Draw a structural formula for each compound. (a) 2,3-Dinitrotoluene (c) Diphenylmethanol (e) p-Nitroaniline (b) 3-Propylanisole (d) m-Propylphenol (f) Pentabromobenzenearrow_forwardIs this the major product of this reaction?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





