
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The types of models shown in the given figure needs to be identified.
Concept introduction:
A scale model which represents the arrangement of atoms in the molecule is said to be molecular model.
(a)
Answer to Problem 46A
The model on the left-hand side is structural formula and the model on right hand side is space-filling model.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Two models of urea are:
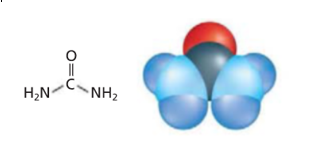
The four molecular models are:
- Molecular formula: It represents
chemical symbols of the elements in the molecule and the number of atoms of each element is represented by subscript. - Structural formula: It consists of symbols of the elements and lines for the
chemical bonds . - Ball-and-stick model: It displays the three-dimensional position of the atoms and the chemical bonds present in a molecule. Differently colored spheres are used to represent atoms and are connected by rods that represents chemical bonds.
- Space-filling model: The relative space that each atom exerts it self in is represented by space-filling model.
As per the definitions, the given models are identified as:
The model on the left-hand side is structural formula as it contains symbols of the elements and lines for the chemical bonds. The model on right hand side is space-filling model as relative space of each atom is shown in this model.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether urea is an organic or inorganic compound needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A class of chemical compounds where one or more carbon atoms are bonded with other or to atoms of other elements, most commonly
(b)
Answer to Problem 46A
Urea is an organic compound.
Explanation of Solution
In urea, the main base element is carbon so, it is classified as an organic compound. The total elements present in urea are:
The molecule of urea has a carbonyl group,
In 1828, Friedrich Wohler synthesize urea (compound found in animal urine) from ammonium cyanate, a mineral as:
Chapter 21 Solutions
Glencoe Chemistry: Matter and Change, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
- We discussed the solid phase resin using in peptide synthesis. Provide a mechanism, for its formation. DRAW THE MECHANISM.arrow_forwardPlease help. Every time I've asked an expert in the past, it's been wrong :(arrow_forwardPlease help everysingle time ive asked in the past, the solution has been wrongarrow_forward
- Please helparrow_forward(a) 21.8 Name the following compounds. & (b) Br (e) O₂N. (h) H (c) Br (d) NH2 ☑N Br H ہیں Ph (g) OMe бл .0-0.e 21.9 Draw a structural formula for each compound. (a) 2,3-Dinitrotoluene (c) Diphenylmethanol (e) p-Nitroaniline (b) 3-Propylanisole (d) m-Propylphenol (f) Pentabromobenzenearrow_forwardIs this the major product of this reaction?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





