
FUND.OF GEN CHEM CHAP 1-13 W/ACCESS
16th Edition
ISBN: 9781323406038
Author: McMurry
Publisher: PEARSON C
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 20.7, Problem 20.18P
(a)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The structural difference between glucose and
Concept introduction:
The structure of
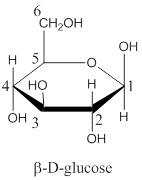
(b)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The structural difference between glucose and
Concept introduction:
The structure of

(c)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The structural difference between glucose and
Concept introduction:
The structure of

Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Two tetrapeptides were isolated from a possum's sweat glands. These peptides were sequenced using Edman degradation and the following 2 sequences were obtained:
Gly-Asp-Ala-Leu
Gly-Asp-Asp-Leu
Can you please help show the titration curve for both of these peptides and calculate the PI?
Two tetrapeptides were isolated from a possum's sweat glands. These peptides were sequenced using Edman degradation and the following 2 sequences were obtained:
Gly-Asp-Ala-Leu
Gly-Asp-Asp-Leu
What is the structure of the PTH derivative produced during the last round of amino acid sequencing?
What is the primary sequence of this undecapeptide? Also, if x-ray crystallography shows a highly stable hairpin turn within the polypeptide, what about the primary sequence explains this structural feature?
Chapter 20 Solutions
FUND.OF GEN CHEM CHAP 1-13 W/ACCESS
Ch. 20.1 - Classify the following monosaccharides as an...Ch. 20.1 - Prob. 20.2PCh. 20.2 - Prob. 20.3PCh. 20.2 - Prob. 20.4PCh. 20.2 - Prob. 20.6PCh. 20.3 - D-Talose, a constituent of certain antibiotics,...Ch. 20.3 - Prob. 20.8PCh. 20.3 - Draw the structure that completes the mutarotation...Ch. 20.4 - Prob. 20.10KCPCh. 20.4 - Prob. 20.11P
Ch. 20.4 - Prob. 20.12PCh. 20.4 - Prob. 20.13PCh. 20.4 - Prob. 20.1CIAPCh. 20.4 - Prob. 20.2CIAPCh. 20.4 - All cells in your body contain glycoproteins...Ch. 20.5 - Draw the structure of the and anomers that...Ch. 20.6 - Prob. 20.15PCh. 20.6 - Prob. 20.16PCh. 20.6 - Prob. 20.17KCPCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.4CIAPCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.5CIAPCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.6CIAPCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.7CIAPCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.18PCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.19PCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.8CIAPCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.9CIAPCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.10CIAPCh. 20 - During the digestion of starch from potatoes, the...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.21UKCCh. 20 - Consider the trisaccharide A, B, C shown in...Ch. 20 - Hydrolysis of both glycosidic bonds in the...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.24UKCCh. 20 - Are one or more of the disaccharides maltose,...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.26UKCCh. 20 - Prob. 20.27UKCCh. 20 - Prob. 20.28APCh. 20 - What is the family-name ending for a sugar?Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.30APCh. 20 - Classify the four carbohydrates (a)(d) by...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.32APCh. 20 - How many chiral carbon atoms are there in each of...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.34APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.35APCh. 20 - Name four important monosaccharides and tell where...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.37APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.38APCh. 20 - What is the structural relationship between...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.40APCh. 20 - In Section 15.6, you saw that aldehydes react with...Ch. 20 - Sucrose and D-glucose rotate plane-polarized light...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.43APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.44APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.45APCh. 20 - What is mutarotation? Do all chiral molecules do...Ch. 20 - What are anomers, and how do the anomers of a...Ch. 20 - What is the structural difference between the ...Ch. 20 - D-Gulose, an aldohexose isomer of glucose, has the...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.50APCh. 20 - In its open-chain form, D-altrose has the...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.52APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.53APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.54APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.55APCh. 20 - What is the structural difference between a...Ch. 20 - What are glycosides, and how can they be formed?Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.58APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.59APCh. 20 - Give the names of three important disaccharides....Ch. 20 - Lactose and maltose are reducing disaccharides,...Ch. 20 - Amylose (a form of starch) and cellulose are both...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.63APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.64APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.65APCh. 20 - Gentiobiose, a rare disaccharide found in saffron,...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.67APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.68APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.69APCh. 20 - Amylopectin (a form of starch) and glycogen are...Ch. 20 - What is the physiological purpose of starch in a...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.72APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.73APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.74CPCh. 20 - Prob. 20.75CPCh. 20 - Prob. 20.76CPCh. 20 - Prob. 20.77CPCh. 20 - Prob. 20.78CPCh. 20 - Write the open-chain structure of the only...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.80CPCh. 20 - Prob. 20.81CPCh. 20 - When a person cannot digest galactose, its reduced...Ch. 20 - Describe the differences between mono-, di-, and...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.84CPCh. 20 - Prob. 20.85CPCh. 20 - Many people who are lactose intolerant can eat...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.87GPCh. 20 - Prob. 20.88GPCh. 20 - Prob. 20.89GP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H H ⚫OH HO- -H H- -OH H- -OH CH2OH Ag*, NH4OH, H2O Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H₂O -OH H ⚫OH HO H HO- CH2OH Cu2+ Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H、 H -OH H ⚫OH H -OH CH2OH Fehlings' solution ⑤ Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forward
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO C=0 H ⚫OH H ⚫OH HO- H HO H CH2OH Tollens' solution Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H-C=O HO H HO H H- ⚫OH HO H CH2OH HNO3, H2O Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO HO- HO H HO ∙H HO CH2OH NaBH4, CH3OH Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forward
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Но сво HO H HO H H OH H -OH CH2OH H2 Pd Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the Haworth projection for Gulose-ẞ-1,6-sorbose and answer the following questions. (Gulose will be in the pyranose form and Sorbose will be in the furanose form) a. Label the reducing and nonreducing ends of the disaccharide b. Label the glycosidic bond c. Circle the anomeric carbons and label them as hemiacetals or acetals. d. Can this disaccharide undergo mutarotation?arrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H OH HO HO HO ·H H OH H OH excess CH3CH2I KOHarrow_forward
- Draw the Haworth structures for the following: a. α-D-Gulopyranose b. ẞ-D-Sorbofuranose c. The two possible isomers of a-D-altrose (furanose and pyranose forms)arrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO H ⚫OH HO- ∙H H- -OH H ⚫OH CH2OH HNO3, H2Oarrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO CH2OH OH OH OH excess CHзI Ag2Oarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning



Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College


Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax
Metabolic Pathways; Author: Wisc-Online;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m61bQYio9ys;License: Standard Youtube License