
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The enantiomer of the given monosaccharide has to be drawn and D or L-sugar has to be identified from the pair.
Concept introduction:
The pair of Enantiomers is non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
The stereo-descriptor used for carbohydrates is D or L. it is based on the dextrorotatory or levorotatory of smallest carbohydrate glyceraldehyde (1 chiral center).
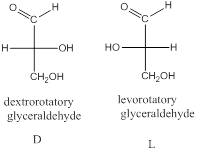
The stereo-descriptor for other carbohydrates of having more than one chiral center will be evaluated by the location of –OH group (right or left) of farthest chiral carbon (bottom) from the carbonyl group. Such as,
If the –OH group is located in right side then, the carbohydrate is a D-sugar.
If the –OH group is located in left side then, the carbohydrate is an L-sugar.
(b)
Interpretation:
The enantiomer of the given monosaccharide has to be drawn and D or L-sugar has to be identified from the pair.
Concept introduction:
The pair of Enantiomers is non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
The stereo-descriptor used for carbohydrates is D or L. it is based on the dextrorotatory or levorotatory of smallest carbohydrate glyceraldehyde (1 chiral center).

The stereo-descriptor for other carbohydrates of having more than one chiral center will be evaluated by the location of –OH group (right or left) of farthest chiral carbon (bottom) from the carbonyl group. Such as,
If the –OH group is located in right side then, the carbohydrate is a D-sugar.
If the –OH group is located in left side then, the carbohydrate is an L-sugar.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 20 Solutions
FUND.OF GEN CHEM CHAP 1-13 W/ACCESS
- Label the following polysaccharide derivatives as reducing or nonreducing. a. C. b. HO CH₂OH CH2OH OH OH OH OH OH HOCH₂ OH OH OH HOCH₂ HO HO HO OH OH ΙΟ CH₂OH OH OH "OH OHarrow_forwardFor a red blood cell (erythrocyte) undergoing active glycolysis, briefly explain how increases in concentration of the following factors are likely to affect glycolytic flux. a. ATP b. AMP c. F-1,6-BP d. F-2,6-BP e. Citrate f. Glucose-6-phosphatearrow_forwardThe ∆G°’ for hydrolysis of phosphoenol pyruvate is -62.2 kJ/mol. The standard freeenergy of ATP hydrolysis is -30.5 kJ/mol. A. What is the standard free energy and K eq of the spontaneous reaction betweenADP/ATP and phosphoenol pyruvate. B. Repeat A for F-1,6-BP (∆G°’=-16.7 kJ/mol) and 1,3-BPG (∆G°’=-49.6 kJ/mol)hydrolysis. C. If the ATP and ADP concentrations are 8mM and 1mM respectively, what would bethe ratio of pyruvate/phosphoenolpyruvate at equilibrium?arrow_forward
- Answerarrow_forward13. Which one is the major organic product of the following sequence of reactions? A OH (CH3)2CHCH2COOH SOCI2 CH3OH 1. CH3MgBr 2. H₂O, H+ B C D OH E OHarrow_forward14. Which one is the major organic product of the following sequence of reactions? (CH3)2CH-COCI CH3OH 1. DIBALH, -78°C 1. PhCH2MgBr ? 2. H2O, HCI 2. H2O, HCI OH OMe A Ph B Ph OH Ph C OMe Ph D E OH .Pharrow_forward
- 6. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction? CO₂Me 1. LiAlH4 2. H₂O CH₂OH CH₂OCH3 5555 HO A B HO C HO D CH₂OH E ?arrow_forward1. (10 points) Pulverized coal pellets, which may be ° approximated as carbon spheres of radius r = 1 mm, are burned in a pure oxygen atmosphere at 1450 K and 1 atm. Oxygen is transferred to the particle surface by diffusion, where it is consumed in the reaction C + O₂ →> CO₂. The reaction rate is first order and of the form No2 = k₁C₁₂(r), where k₁ = 0.1 m/s. Neglecting changes in r, determine the steady-state O₂ molar consumption rate in kmol/s. At 1450 K, the binary diffusion coefficient for O2 and CO2 is 1.71 x 10ª m²/s.arrow_forward2. (20 points) Consider combustion of hydrogen gas in a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen adjacent to the metal wall of a combustion chamber. Combustion occurs at constant temperature and pressure according to the chemical reaction 2H₂+ O₂→ 2H₂O. Measurements under steady-state conditions at 10 mm from the wall indicate that the molar concentrations of hydrogen, oxygen, and water vapor are 0.10, 0.10, and 0.20 kmol/m³, respectively. The generation rate of water vapor is 0.96x102 kmol/m³s throughout the region of interest. The binary diffusion coefficient for each of the species (H, O̟, and H₂O) in the remaining species is 0.6 X 10-5 m²/s. (a) Determine an expression for and make a qualitative plot of C as a function of distance from the wall. H2 (b) Determine the value of C2 at the wall. H2 (c) On the same coordinates used in part (a), sketch curves for the concentrations of oxygen and water vapor. This will require you to calculate Co, and C. 02 H20 (d) What is the molar flux of water…arrow_forward
- 4. (15 points) Consider a spherical organism of radius ro within which respiration occurs at a uniform volumetric rate of That is, oxygen (species A) consumption is governed by a first- order reaction, homogeneous chemical reaction. a. If a molar concentration of CA(ro) = CA,o is maintained at the surface of the organism, obtain an expression for the radial distribution of oxygen, CA(r), within the organism. Hint: To simplify solution of the species diffusion equation, invoke the transformation y = rCA. b. Obtain an expression for the rate of oxygen consumption within the organism. c. Consider an organism of radius ro = 0.10 mm and a diffusion coefficient of DAB = 108 m2/s. If CA, o = 5 x105 kmol/m3 and k1 20 s1, estimate the corresponding value of the molar concentration at the center of the organism. What is the rate of oxygen consumption by the organism?arrow_forward3. (15 points) Living cells homogeneously distributed (immobilized) with an agarose gel require glucose to survive. An important aspect of the biochemical system design is the effective diffusion coefficient of glucose (A) into the cell- immobilized gel. Consider the experiment shows below where a slab of the cell-immobilized gel of 1.0cm thickness is placed within a well-mixed aqueous solution of glucose maintained at a concentration of 50 mmol/L. The glucose consumption within the cell-immobilized gel proceeds by a zero-order process given by R₁ = -0.05 mmol/(L min). The solubilities of glucose in both the water and the gel are the same; that is, the concentration of the glucose on the water side of the water-gel interface is equal to the concentration of the glucose on the gel side of the water gel interface. A syringe is mounted at the center of the gel carefully excises a tiny sample of the gel for glucose analysis. A Well mixed solution Constant concentration 50nmol/L Living…arrow_forwardTwo tetrapeptides were isolated from a possum's sweat glands. These peptides were sequenced using Edman degradation and the following 2 sequences were obtained: Gly-Asp-Ala-Leu Gly-Asp-Asp-Leu Can you please help show the titration curve for both of these peptides and calculate the PI?arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning





