
FUND.OF GEN CHEM CHAP 1-13 W/ACCESS
16th Edition
ISBN: 9781323406038
Author: McMurry
Publisher: PEARSON C
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 20, Problem 20.51AP
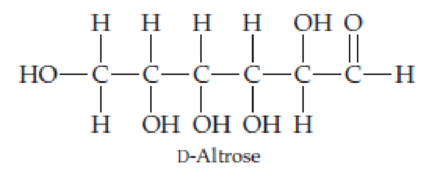
In its open-chain form, D-altrose has the structure shown here. Coil altrose around and draw it in the cyclic hemiacetal α and β forms.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I am a Biochemistry student and I am confused on how to analyze FRAP Analysis using Excel Spread Sheets.
The following spread sheet has my 0 minute data listed at top and the 4 minute data listed on the bottom.
Sheet: https://mnscu-my.sharepoint.com/:x:/g/personal/vi2163ss_go_minnstate_edu/EXjrCizWiXRPmpittqZA12IB8EkB5eE8iaRqj_iun-IAtg?rtime=Wo9zPHFY3Ug
The formula for FRAP Analysis is:
FRAP value = A (4 min sample) - A (0 min sample) over A (4 min 30 uM ascorbic acid) - A (0 min 30 uM ascorbic acid) multiplied by 30 uM and the dilution factor of 1/10
HO
Fill in the missing boxes.
ON
800
NO
NO
Glucose
ATP
NADH
Hexokinase
1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate
Mg2+
ADP
NAD+, Pi
Phosphoglucose
Isomerase
Glucose-6-Phosphate
ON
沁
Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate
HO
حلمة
ADP
ADP Phospho
Mg2+
glycerate
Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate
ATP
kinase
ATP
Phosphoglycerate
3-phosphoglycerate
Mutase
H₁₂O
Fructose-6-Phosphate
ATP
Mg2+
ADP
Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate
2-phosphoglycerate
H₂O
Phosphoenolpyruvate
ADP
Mg2+
ATP
Pyruvate
In a diffraction experiment of a native crystal, intensity of reflection (-1 0 6) is equivalent to the intensity of reflection (1 0 -6).
true or false?
Chapter 20 Solutions
FUND.OF GEN CHEM CHAP 1-13 W/ACCESS
Ch. 20.1 - Classify the following monosaccharides as an...Ch. 20.1 - Prob. 20.2PCh. 20.2 - Prob. 20.3PCh. 20.2 - Prob. 20.4PCh. 20.2 - Prob. 20.6PCh. 20.3 - D-Talose, a constituent of certain antibiotics,...Ch. 20.3 - Prob. 20.8PCh. 20.3 - Draw the structure that completes the mutarotation...Ch. 20.4 - Prob. 20.10KCPCh. 20.4 - Prob. 20.11P
Ch. 20.4 - Prob. 20.12PCh. 20.4 - Prob. 20.13PCh. 20.4 - Prob. 20.1CIAPCh. 20.4 - Prob. 20.2CIAPCh. 20.4 - All cells in your body contain glycoproteins...Ch. 20.5 - Draw the structure of the and anomers that...Ch. 20.6 - Prob. 20.15PCh. 20.6 - Prob. 20.16PCh. 20.6 - Prob. 20.17KCPCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.4CIAPCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.5CIAPCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.6CIAPCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.7CIAPCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.18PCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.19PCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.8CIAPCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.9CIAPCh. 20.7 - Prob. 20.10CIAPCh. 20 - During the digestion of starch from potatoes, the...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.21UKCCh. 20 - Consider the trisaccharide A, B, C shown in...Ch. 20 - Hydrolysis of both glycosidic bonds in the...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.24UKCCh. 20 - Are one or more of the disaccharides maltose,...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.26UKCCh. 20 - Prob. 20.27UKCCh. 20 - Prob. 20.28APCh. 20 - What is the family-name ending for a sugar?Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.30APCh. 20 - Classify the four carbohydrates (a)(d) by...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.32APCh. 20 - How many chiral carbon atoms are there in each of...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.34APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.35APCh. 20 - Name four important monosaccharides and tell where...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.37APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.38APCh. 20 - What is the structural relationship between...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.40APCh. 20 - In Section 15.6, you saw that aldehydes react with...Ch. 20 - Sucrose and D-glucose rotate plane-polarized light...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.43APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.44APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.45APCh. 20 - What is mutarotation? Do all chiral molecules do...Ch. 20 - What are anomers, and how do the anomers of a...Ch. 20 - What is the structural difference between the ...Ch. 20 - D-Gulose, an aldohexose isomer of glucose, has the...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.50APCh. 20 - In its open-chain form, D-altrose has the...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.52APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.53APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.54APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.55APCh. 20 - What is the structural difference between a...Ch. 20 - What are glycosides, and how can they be formed?Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.58APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.59APCh. 20 - Give the names of three important disaccharides....Ch. 20 - Lactose and maltose are reducing disaccharides,...Ch. 20 - Amylose (a form of starch) and cellulose are both...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.63APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.64APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.65APCh. 20 - Gentiobiose, a rare disaccharide found in saffron,...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.67APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.68APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.69APCh. 20 - Amylopectin (a form of starch) and glycogen are...Ch. 20 - What is the physiological purpose of starch in a...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.72APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.73APCh. 20 - Prob. 20.74CPCh. 20 - Prob. 20.75CPCh. 20 - Prob. 20.76CPCh. 20 - Prob. 20.77CPCh. 20 - Prob. 20.78CPCh. 20 - Write the open-chain structure of the only...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.80CPCh. 20 - Prob. 20.81CPCh. 20 - When a person cannot digest galactose, its reduced...Ch. 20 - Describe the differences between mono-, di-, and...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.84CPCh. 20 - Prob. 20.85CPCh. 20 - Many people who are lactose intolerant can eat...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20.87GPCh. 20 - Prob. 20.88GPCh. 20 - Prob. 20.89GP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- in an x-ray diffraction experiment, moving the detector farther away from the crystal will allow collection of reflection of reflections with high Miller indices. true or false?arrow_forwardShow the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed formation of an [α-1,6] glycosidic linkagebetween two molecules of α-D-glucopyranose.arrow_forwardLabel the following polysaccharide derivatives as reducing or nonreducing. a. C. b. HO CH₂OH CH2OH OH OH OH OH OH HOCH₂ OH OH OH HOCH₂ HO HO HO OH OH ΙΟ CH₂OH OH OH "OH OHarrow_forward
- For a red blood cell (erythrocyte) undergoing active glycolysis, briefly explain how increases in concentration of the following factors are likely to affect glycolytic flux. a. ATP b. AMP c. F-1,6-BP d. F-2,6-BP e. Citrate f. Glucose-6-phosphatearrow_forwardThe ∆G°’ for hydrolysis of phosphoenol pyruvate is -62.2 kJ/mol. The standard freeenergy of ATP hydrolysis is -30.5 kJ/mol. A. What is the standard free energy and K eq of the spontaneous reaction betweenADP/ATP and phosphoenol pyruvate. B. Repeat A for F-1,6-BP (∆G°’=-16.7 kJ/mol) and 1,3-BPG (∆G°’=-49.6 kJ/mol)hydrolysis. C. If the ATP and ADP concentrations are 8mM and 1mM respectively, what would bethe ratio of pyruvate/phosphoenolpyruvate at equilibrium?arrow_forwardAnswerarrow_forward
- 13. Which one is the major organic product of the following sequence of reactions? A OH (CH3)2CHCH2COOH SOCI2 CH3OH 1. CH3MgBr 2. H₂O, H+ B C D OH E OHarrow_forward14. Which one is the major organic product of the following sequence of reactions? (CH3)2CH-COCI CH3OH 1. DIBALH, -78°C 1. PhCH2MgBr ? 2. H2O, HCI 2. H2O, HCI OH OMe A Ph B Ph OH Ph C OMe Ph D E OH .Pharrow_forward6. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction? CO₂Me 1. LiAlH4 2. H₂O CH₂OH CH₂OCH3 5555 HO A B HO C HO D CH₂OH E ?arrow_forward
- 1. (10 points) Pulverized coal pellets, which may be ° approximated as carbon spheres of radius r = 1 mm, are burned in a pure oxygen atmosphere at 1450 K and 1 atm. Oxygen is transferred to the particle surface by diffusion, where it is consumed in the reaction C + O₂ →> CO₂. The reaction rate is first order and of the form No2 = k₁C₁₂(r), where k₁ = 0.1 m/s. Neglecting changes in r, determine the steady-state O₂ molar consumption rate in kmol/s. At 1450 K, the binary diffusion coefficient for O2 and CO2 is 1.71 x 10ª m²/s.arrow_forward2. (20 points) Consider combustion of hydrogen gas in a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen adjacent to the metal wall of a combustion chamber. Combustion occurs at constant temperature and pressure according to the chemical reaction 2H₂+ O₂→ 2H₂O. Measurements under steady-state conditions at 10 mm from the wall indicate that the molar concentrations of hydrogen, oxygen, and water vapor are 0.10, 0.10, and 0.20 kmol/m³, respectively. The generation rate of water vapor is 0.96x102 kmol/m³s throughout the region of interest. The binary diffusion coefficient for each of the species (H, O̟, and H₂O) in the remaining species is 0.6 X 10-5 m²/s. (a) Determine an expression for and make a qualitative plot of C as a function of distance from the wall. H2 (b) Determine the value of C2 at the wall. H2 (c) On the same coordinates used in part (a), sketch curves for the concentrations of oxygen and water vapor. This will require you to calculate Co, and C. 02 H20 (d) What is the molar flux of water…arrow_forward4. (15 points) Consider a spherical organism of radius ro within which respiration occurs at a uniform volumetric rate of That is, oxygen (species A) consumption is governed by a first- order reaction, homogeneous chemical reaction. a. If a molar concentration of CA(ro) = CA,o is maintained at the surface of the organism, obtain an expression for the radial distribution of oxygen, CA(r), within the organism. Hint: To simplify solution of the species diffusion equation, invoke the transformation y = rCA. b. Obtain an expression for the rate of oxygen consumption within the organism. c. Consider an organism of radius ro = 0.10 mm and a diffusion coefficient of DAB = 108 m2/s. If CA, o = 5 x105 kmol/m3 and k1 20 s1, estimate the corresponding value of the molar concentration at the center of the organism. What is the rate of oxygen consumption by the organism?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning




Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781337711067
Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna Balac
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Metabolic Pathways; Author: Wisc-Online;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m61bQYio9ys;License: Standard Youtube License