
Concept explainers
. Give the systematic name for each of the following alcohols. Indicate whether the alcohol is primary, secondary, or tertiary.
a. 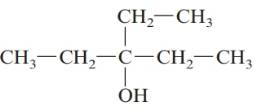
b. 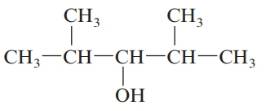
c. 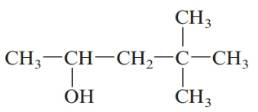
d. 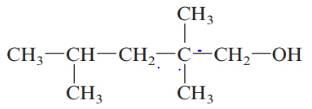
Interpretation:
The systematic names of the given alcohol and whether it is primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
An organic compound in which hydroxyl functional group that is -OH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be an alcohol. The general formula for alcohol is Cn H2 n + 1 OH. Based on the attachment to the carbon the alcohols are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a primary carbon atom (carbon atom to which one carbon atom is attached) then such alcohol is said to be a primary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a secondary carbon atom (carbon atom to which two carbon atoms are attached) then such alcohol is said to be a secondary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a tertiary carbon atom (carbon atom to which three carbon atoms are attached) then such alcohol is said to be a tertiary alcohol.
In order to give the name to the alcohol following steps are followed:
1. The parent (longest) continuous carbon chain containing hydroxyl group (-OH) is selected.
2. While writing the name of alcohol, the suffix "e" of the corresponding alkane is replaced by "-ol".
3. Name should be written in alphabetical order and numbering should be done in such a way that the multiple bond and substituent group gets lowest number.
4. Hyphen is used to connect the number to the name.
For number of carbons atoms in alkane chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec.
Answer to Problem 61QAP
3-ethylpentan-3-ol; tertiary alcohol.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is:
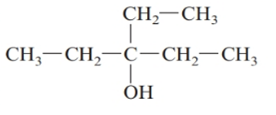
The parent chain in the given structure is of 5-carbon atoms so, prefix will be pent. Numbering is done in such a way that the hydroxyl group gets lower number that is 3 and the ethyl substituent also get 3.
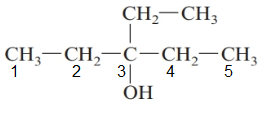
So, the IUPAC name will be: 3-ethylpentan-3-ol.
Since, -OH group is attached to tertiary carbon so, it is tertiary alcohol.
Interpretation:
The systematic names of the given alcohol and whether it is primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
An organic compound in which hydroxyl functional group that is -OH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be an alcohol. The general formula for alcohol is Cn H2 n + 1 OH. Based on the attachment to the carbon the alcohols are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a primary carbon atom (carbon atom to which one carbon atom is attached) then such alcohol is said to be a primary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a secondary carbon atom (carbon atom to which two carbon atoms are attached) then such alcohol is said to be a secondary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a tertiary carbon atom (carbon atom to which three carbon atoms are attached) then such alcohol is said to be a tertiary alcohol.
In order to give the name to the alcohol following steps are followed:
1. The parent (longest) continuous carbon chain containing hydroxyl group (-OH) is selected.
2. While writing the name of alcohol, the suffix "e" of the corresponding alkane is replaced by "-ol".
3. Name should be written in alphabetical order and numbering should be done in such a way that the multiple bond and substituent group gets lowest number.
4. Hyphen is used to connect the number to the name.
For number of carbons atoms in alkane chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec.
Answer to Problem 61QAP
2, 4-dimethylpentan-3-ol; secondary alcohol.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is:
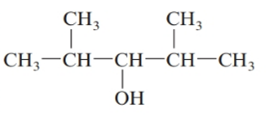
The parent chain in the given structure is of 5-carbon atoms so, prefix will be pent. Numbering is done in such a way that the hydroxyl group gets lower number that is 3 and the methyl substituent on 2 and 5.
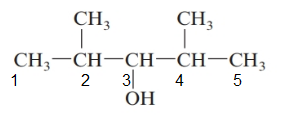
So, the IUPAC name will be: 2, 4-dimethylpentan-3-ol.
Since, -OH group is attached to secondary carbon so, it is secondary alcohol.
Interpretation:
The systematic names of the given alcohol and whether it is primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
An organic compound in which hydroxyl functional group that is -OH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be an alcohol. The general formula for alcohol is Cn H2 n + 1 OH. Based on the attachment to the carbon the alcohols are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a primary carbon atom (carbon atom to which one carbon atom is attached) then such alcohol is said to be a primary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a secondary carbon atom (carbon atom to which two carbon atoms are attached) then such alcohol is said to be a secondary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a tertiary carbon atom (carbon atom to which three carbon atoms are attached) then such alcohol is said to be a tertiary alcohol.
In order to give the name to the alcohol following steps are followed:
1. The parent (longest) continuous carbon chain containing hydroxyl group (-OH) is selected.
2. While writing the name of alcohol, the suffix "e" of the corresponding alkane is replaced by "-ol".
3. Name should be written in alphabetical order and numbering should be done in such a way that the multiple bond and substituent group gets lowest number.
4. Hyphen is used to connect the number to the name.
For number of carbons atoms in alkane chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec.
Answer to Problem 61QAP
4, 4-dimethylpentan-2-ol; secondary alcohol.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is:
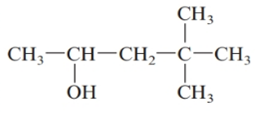
The parent chain in the given structure is of 5-carbon atoms so, prefix will be pent. Numbering is done in such a way that the hydroxyl group gets lower number that is 2 and the methyl substituent on carbon number 4.
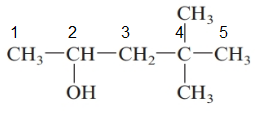
So, the IUPAC name will be: 4, 4-dimethylpentan-2-ol.
Since, -OH group is attached to secondary carbon so, it is secondary alcohol.
Interpretation:
The systematic names of the given alcohol and whether it is primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
An organic compound in which hydroxyl functional group that is -OH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be an alcohol. The general formula for alcohol is Cn H2 n + 1 OH. Based on the attachment to the carbon the alcohols are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a primary carbon atom (carbon atom to which one carbon atom is attached) then such alcohol is said to be a primary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a secondary carbon atom (carbon atom to which two carbon atoms are attached) then such alcohol is said to be a secondary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a tertiary carbon atom (carbon atom to which three carbon atoms are attached) then such alcohol is said to be a tertiary alcohol.
In order to give the name to the alcohol following steps are followed:
1. The parent (longest) continuous carbon chain containing hydroxyl group (-OH) is selected.
2. While writing the name of alcohol, the suffix "e" of the corresponding alkane is replaced by "-ol".
3. Name should be written in alphabetical order and numbering should be done in such a way that the multiple bond and substituent group gets lowest number.
4. Hyphen is used to connect the number to the name.
For number of carbons atoms in alkane chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec.
Answer to Problem 61QAP
2, 2, 4-trimethylpentan-1-ol; primary alcohol.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is:
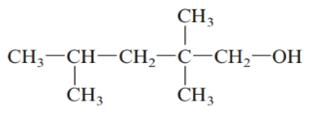
The parent chain in the given structure is of 5-carbon atoms so, prefix will be pent. Numbering is done in such a way that the hydroxyl group gets lower number that is 1 and the methyl substituents on carbon number 2 and 4.
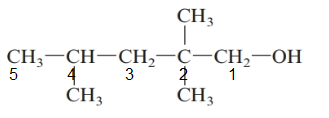
So, the IUPAC name will be: 2, 2, 4-trimethylpentan-1-ol.
Since, -OH group is attached to primary carbon so, it is primary alcohol.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
EBK INTRO.CHEMISTRY (NASTA EDITION)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Loose Leaf For Integrated Principles Of Zoology
Organic Chemistry
Biological Science (6th Edition)
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
- The decimolar calomel electrode has a potential of 0.3335 V at 25°C compared to the standard hydrogen electrode. If the standard reduction potential of Hg22+ is 0.7973 V and the solubility product of Hg2Cl2 is 1.2x 10-18, find the activity of the chlorine ion at this electrode.Data: R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1, F = 96485 C mol-1, T = 298.15 K.arrow_forward2. Add the following group of numbers using the correct number of significant figures for the answer. Show work to earn full credit such as rounding off the answer to the correct number of significant figures. Replace the question marks with the calculated answers or write the calculated answers near the question marks. 10916.345 37.40832 5.4043 3.94 + 0.0426 ? (7 significant figures)arrow_forwardThe emf at 25°C of the cell: Pt l H2(g) l dis X:KCl (sat) l Hg2Cl2(s) l Hg l Pt was 612 mV. When solution X was replaced by normal phosphate buffer solution with a pH of 6.86, the emf was 741 mV. Calculate the pH of solution X.arrow_forward
- Indicate how to calculate the potential E of the reaction Hg2Cl2(s) + 2e ⇄ 2Hg + 2Cl- as a function of the concentration of Cl- ions. Data: the solubility product of Hg2Cl2.arrow_forwardHow can Beer’s Law be used to determine the concentration in a selected food sample. Provide an in-depth discussion and examples of this.arrow_forwardb) H3C- H3C Me CH 3 I HN Me H+arrow_forward
- Using Luther's rule, determine the reference potentials of the electrodes corresponding to the low stability systems Co³+/Co and Cr²+/Cr from the data in the table. Electrodo ΕΝ Co²+/Co Co3+/Co²+ -0,28 +1,808 Cr³+ / Cr -0,508 Cr3+ / Cr²+ -0,41arrow_forwardThe molecule PYRIDINE, 6tt electrons and is there pore aromuntre and is Assigned the Following structure contenus Since aromatk moleculey undergo electrophilic allomatic substitution, Pyridine should undergo The Following reaction + HNO3 12504 a. write all of the possible Mononitration Products that could Result From this roaction Based upon the reaction the reaction mechanism determine which of these producty would be the major Product of the hegetionarrow_forwardUsing Benzene as starting materia Show how each of the Following molecules could Ve synthesked 9. CHI d. 10450 b 0 -50311 ८ City -5034 1-0-650 e NO2arrow_forward
- BA HBr of the fol 1)=MgCI 2) H₂O major NaOEt Ts Cl Py (pyridine) 1) 03 2) Me2S 1arrow_forward4. Provide a clear arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reactions. Do not skip proton transfers, do not combine steps, and make sure your arrows are clear enough to be interpreted without ambiguity. a) NHBoc ⚫OBn HO. H3C CO2CH3 -OBn H3C H3C. H3C. NHBOC CI CO2CH3arrow_forwardDraw structures of the following compounds and identify their role: mCPBA (MCPBA) DMS Py 9-BBN LAH Sia₂BH TsCI PCC t-BuOK LDA MeLi n-BuLi DMSO DMF Sodium Borohydride Lithium DiisopropylAmide 2arrow_forward
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER





