
Concept explainers
(a)
To identify: Whether there is any instant at which the two bicycles have the same velocity.
(a)
Answer to Problem 85GP
Yes, there is one point where the two bicycles have the same velocity. It is when the slopes of both the functions are parallel.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
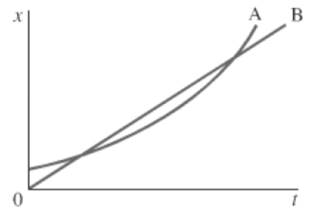
The given position-time for two bicycles is shown below.
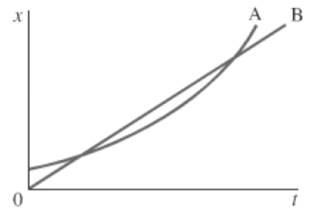
Formula used:
The slope of a function in a position time graph provides the velocity of the moving object.
Calculation:
Consider the given graph. Slopes of parallel lines are equal. B is a straight line, so it will have a constant slope. A is a curve, hence its slope varies while moving from bottom to top. At the point of maximum curvature, A’s slope is the same as B. At this instant, both A and B have the same velocity.
Conclusion:
Therefore, for the given graph there is a point when velocity of both the bicycles is same.
(b)
The bicycle that will have larger acceleration.
(b)
Answer to Problem 85GP
Bicycle A has a larger acceleration.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given position-time for two bicycles is shown below.
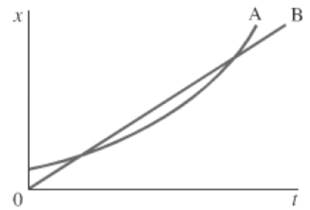
Formula used:
The slope of a function in a position time graph is the velocity of the moving object.
Calculation:
Bicycle B depicts a straight line in the position time graph. Hence its slope is constant. Since the slope is constant, the acceleration is 0. Bicycle A is represented by a curve, which means that its slope, and hence its velocity changes. From the graph, it is evident that the slope keeps increasing.
Conclusion:
Therefore, bicycle A has a larger acceleration
(c)
The instants at which the bicycles passing each other. Also, the bicycle that will pass the another bicycle.
(c)
Answer to Problem 85GP
At the points of intersections in the graph, the bicycles pass each other. First bicycle B will pass bicycle A and then bicycle A will pass bicycle B.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given position-time for two bicycles is shown below.
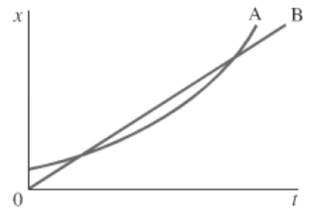
Calculation:
The graph plots position against time. Thus, it shows the position of an object at different instances of time. If the functions for A and B intersect, then, it means that both A and B are at the same position at that particular instant. Therefore, the bicycles have to pass each other at points of intersections.
From the given graph, it is observed that at the first intersection point bicycle B will pass bicycle but later on at the second point of intersection, bicycle A will pass bicycle B.
Conclusion:
Therefore, both bicycles will meet at point of intersection and will pass each other.
(d)
The bicycle that will have the highest instantaneous velocity.
(d)
Answer to Problem 85GP
Before the instant of time where their velocities are equal, bicycle B has the higher instantaneous velocity after which Bicycle A has the higher velocity.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given position-time for two bicycles is shown below.
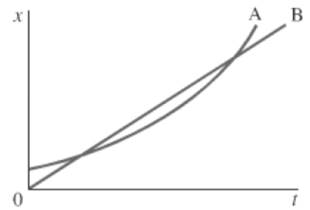
Formula used:
The slope at particular point of position time graph defines the instantaneous velocity of a moving object.
Calculation:
The slope at a point in the position-time graph gives the velocity of the bicycle at that instant. bicycle B has constant slope since it is a straight line. The slope of the curve representing bicycle A shows an increase from bottom to top. Thus, till the instant where the slopes are equal, bicycle B has a higher instantaneous velocity. After this point, bicycle A, whose slope keeps increasing will have a higher instantaneous velocity.
Conclusion:
Therefore, bicycle B will have greatest instantaneous velocity and then later on A will have greatest velocity.
(e)
The bicycle that will have higher average velocity.
(e)
Answer to Problem 85GP
Both the bicycles must havethe same average velocity.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given position-time for two bicycles is shown below.
Formula used:
The slope of a function in a position time graph is the velocity of the moving object. The average velocity is the ratio of total displacement and total time taken
Calculation:
Bicycle B is depicted by a straight line. Its velocity is constant. For A, the displacement is lesser but the total time taken is also lesser. So, the average velocity for both the bicycles A and B should have almost the same value.
Conclusion:
Therefore, both bicycles will have same average velocity.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Physics: Principles with Applications
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- The cylindrical beam of a 12.7-mW laser is 0.920 cm in diameter. What is the rms value of the electric field? V/marrow_forwardConsider a rubber rod that has been rubbed with fur to give the rod a net negative charge, and a glass rod that has been rubbed with silk to give it a net positive charge. After being charged by contact by the fur and silk...? a. Both rods have less mass b. the rubber rod has more mass and the glass rod has less mass c. both rods have more mass d. the masses of both rods are unchanged e. the rubber rod has less mass and the glass rod has mroe massarrow_forward8) 9)arrow_forward
- Lab 8 Part 3 PHET Wave Interface simulation. I am having trouble with this part of the lab.arrow_forwardMick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forwardHi, I have canceled, why did you charge me again?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





