
Concept explainers
a)
To compute: The labor productivity and multifactor productivity for each unit.
Introduction: Labor productivity is the measure of productivity of a worker during a period of time. It the ratio of total output to the total productivity hours.
a)
Answer to Problem 7P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Unit | Employees | Customer processed/day |
| A | 4 | 36 |
| B | 5 | 40 |
| C | 8 | 60 |
| D | 3 | 20 |
Hourly wage=$25Overhead=1.0×Labor costMaterial cost=$5 per customer
Formula:
Multifactor Productivity=OutputTotal costLabor Productivity=Customersper dayEmployeesTotal cost=Labor cost+Overhead cost+Material cost
Laborcost=Number of workers ×8 hours×$25/hourOverhead cost=Labor cost×1.00Material cost=Customers×$5/customer
Calculation of multifactor productivity:
| Unit | Employees | Customer processed/day | Labor cost | Overhead cost | Material cost | Total cost | Labor productivity | MFP (2decimal) | MFP (3decimal) |
| A | 4 | 36 | 800 | 800 | 180 | 1780 | 9 | 0.02 | 0.020 |
| B | 5 | 40 | 1000 | 1000 | 200 | 2200 | 8 | 0.02 | 0.018 |
| C | 8 | 60 | 1600 | 1600 | 300 | 3500 | 7.5 | 0.02 | 0.017 |
| D | 3 | 20 | 600 | 600 | 100 | 1300 | 6.6666667 | 0.02 | 0.015 |
Table 1
Excel Worksheet:
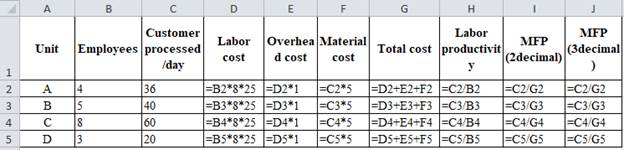
Calculation of multifactor productivity:
Unit A:
Labor cost is calculated by multiplying number of workers (4) with 8working hours and 25 hourly wages which gives 800.
Overhead cost is calculated by multiplying Labor cost of 800 with 1.0 which gives 800.
Material cost is calculated by multiplying 36 with 5 which gives 180.
Total cost is calculated by adding labor cost of 800, overhead cost of 800 and material cost of 180 which yields 1780.
Labor productivity is calculated by dividing 36 with 4 which yields 9.
Multifactor productivity is calculated by dividing 36 with the total cost of 1,780 which yields 0.02 (2-decimal) and 0.020 (3 decimal).
Same procedure is followed for unit B, C and D the result is shown in table 1.
Hence, multifactor productivity has dropped from 0.020 to 0.015.
b)
To compute: The labor productivity and multifactor productivity for each unit.
Introduction: Multifactor productivity is also referred as total factor productivity. It is the measure of economic performance by comparing the amount of goods and services produced to the total input used to produce the output.
b)
Answer to Problem 7P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Every employee process on additional customers.
| Unit | Employees | Customer processed/day |
| A | 4 | 40 |
| B | 5 | 45 |
| C | 8 | 68 |
| D | 3 | 23 |
Hourly wage=$25Overhead=1.0×Labor costMaterial cost=$5 per customer
Formula:
Multifactor Productivity=OutputTotal costLabor Productivity=Customersper dayEmployeesTotal cost=Labor cost+Overhead cost+Material cost
Laborcost=Number of workers ×8 hours×$25/hourOverhead cost=Labor cost×1.00Material cost=Customers×$5/customer
Calculation of multifactor productivity:
| Unit | Employees | Customer processed/day | Labor cost | Overhead cost | Material cost | Total cost | Labor productivity | MFP (2decimal) | MFP (3decimal) |
| A | 4 | 40 | 800 | 800 | 200 | 1800 | 10 | 0.02 | 0.022 |
| B | 5 | 45 | 1000 | 1000 | 225 | 2225 | 9 | 0.02 | 0.020 |
| C | 8 | 68 | 1600 | 1600 | 340 | 3540 | 8.5 | 0.02 | 0.019 |
| D | 3 | 23 | 600 | 600 | 115 | 1315 | 7.6666667 | 0.02 | 0.017 |
Table 2
Excel Worksheet:
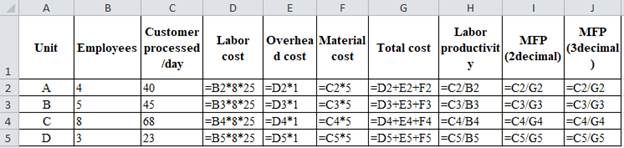
Calculation of multifactor productivity:
Unit A:
Labor cost is calculated by multiplying number of workers (4) with 8 working hours and 25 hourly wages which gives 800.
Overhead cost is calculated by multiplying Labor cost of 800 with 1.0 which gives 800.
Material cost is calculated by multiplying 40 with 5 which gives 200.
Total cost is calculated by adding labor cost of 800, overhead cost of 800 and material cost of 200 which yields 1800.
Labor productivity is calculated by dividing 40 with 4 which yields 10.
Multifactor productivity is calculated by dividing 40 with the total cost of 1,800 which yields 0.02 (2-decimal) and 0.022 (3 decimal).
Same procedure is followed for unit B, C and D the result is shown in table 2.
Hence, multifactor productivity has dropped from 0.022to 0.017.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Loose-leaf for Operations Management (The Mcgraw-hill Series in Operations and Decision Sciences)
- The Donald Fertilizer Company produces industrial chemical fertilizers. The projected manufacturing requirements (in gallons) for the next four quarters are 90,000, 90,000, 60,000, and 140,000 respectively. A level workforce is desired, relying only on anticipation inventory as a supply option. Stockouts and backorders are to be avoided, as are overtime and undertime. a. Determine the quarterly production rate required to meet total demand for the year, and minimize the anticipation inventory that would be left over at the end of the year. Beginning inventory is 0. The quarterly production rate is 95000 gallons. (Enter your response as an integer.) b. Specify the anticipation inventory that will be produced. (Enter your responses as an integers.) Quarter Anticipation inventory (gallons) 1 5000 2 10000 3 4 45000 c. Suppose that the requirements (in gallons) for the next four quarters are revised to 140,000, 60,000, 90,000, and 90,000 respectively. If total demand is the same, what level…arrow_forwardPlease help with the attached Capstone proposal Requirements:arrow_forwardLong term capacity plans and how to properly make decisions regarding long-term planning Long-term capacity plans cover periods longer periods of time. These plans are suitable for large businesses that want to scale their operations with a proven strategy for achieving production targets and meeting customer demands. Long-term capacity plans consider other factors apart from the productive requirements of the company. How important is it, in your mind, to properly make decisions regarding long-term capacity planning? How does this decision impact the present and future profitability of an organization? Be specific and give examples.arrow_forward
- In addition to the Amazon case study you provided, I'm curious if you've encountered other examples of companies successfully applying Little's Law to enhance their supply chain risk management practices. For instance, have you seen organizations use queuing theory to assess the potential ripple effects of disruptions, stress-test their contingency plans, or identify critical control points that require heightened monitoring and agility? Please provide a referencearrow_forwardSam's Pet Hotel operates 48 weeks per year, 6 days per week, and uses a continuous review inventory system. It purchases kitty litter for $13.00 per bag The following information is available about these bags: > Demand 85 bags/week >Order cost $60.00/order > Annual holding cost = 35 percent of cost > Desired cycle-service level 80 percent > Lead time = 4 weeks (24 working days) > Standard deviation of weekly demand = 15 bags > Current on-hand inventory is 320 bags, with no open orders or backorders. a. Suppose that the weekly demand forecast of 85 bags is incorrect and actual demand averages only 65 bags per week. How much higher will total costs be, owing to the distorted EOQ caused by this forecast error? The costs will be $higher owing to the error in EOQ. (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardOsprey Sports stocks everything that a musky fisherman could want in the Great North Woods. A particular musky lure has been very popular with local fishermen as well as those who buy lures on the Internet from Osprey Sports. The cost to place orders with the supplier is $3030/order; the demand averages 55 lures per day, with a standard deviation of 11 lure; and the inventory holding cost is $1.001.00/lure/year. The lead time form the supplier is 1010 days, with a standard deviation of 33 days. It is important to maintain a 9898 percent cycle-service level to properly balance service with inventory holding costs. Osprey Sports is open 350 days a year to allow the owners the opportunity to fish for muskies during the prime season. The owners want to use a continuous review inventory system for this item. Refer to the standard normal table LOADING... for z-values. Part 2 a. What order quantity should be used? enter your response here lures. (Enter your response rounded to the…arrow_forward
- 9. Research Methodology Fully explain the Quantitative research methodology that and add in the following sub-sections: . Data Collection • Data Analysisarrow_forwardRuby-Star Incorporated is considering two different vendors for one of its top-selling products which has an average weekly demand of 40 units and is valued at $80 per unit. Inbound shipments from vendor 1 will average 340 units with an average lead time (including ordering delays and transit time) of 2 weeks. Inbound shipments from vendor 2 will average 550 units with an average lead time of 1 week. Ruby-Star operates 52 weeks per year; it carries a 2-week supply of inventory as safety stock and no anticipation inventory. a. The average aggregate inventory value of the product if Ruby-Star used vendor 1 exclusively is $ (Enter your response as a whole number.)arrow_forwardThe Carbondale Hospital is considering the purchase of a new ambulance. The decision will rest partly on the anticipated mileage to be driven next year. The miles driven during the past 5 years are as follows: Year Mileage 1 3,000 2 3 4 4,000 3,450 3,850 5 3,800 a) Using a 2-year moving average, the forecast for year 6 = miles (round your response to the nearest whole number). b) If a 2-year moving average is used to make the forecast, the MAD based on this = miles (round your response to one decimal place). (Hint: You will have only 3 years of matched data.) c) The forecast for year 6 using a weighted 2-year moving average with weights of 0.40 and 0.60 (the weight of 0.60 is for the most recent period) = ☐ miles (round your response to the nearest whole number). miles (round your response to one decimal place). (Hint: You will have only 3 years of The MAD for the forecast developed using a weighted 2-year moving average with weights of 0.40 and 0.60 = matched data.) d) Using…arrow_forward
- Task time estimates for the modification of an assembly line at Jim Goodale's Carbondale, Illinois, factory are as follows: B D G Time Activity (in hours) Immediate Predecessor(s) A 5.0 B 7.5 C 5.0 A DEFC 8.0 B, C 4.5 Figure 2 A B, C 7.7 D G 5.0 E, F This exercise contains only part a. a) The correct precedence diagram for the project is shown in 目 F B Figure 3 A E B E ☑ D Farrow_forwardDave Fletcher was able to determine the activity times for constructing his laser scanning machine. Fletcher would like to determine ES, EF, LS, LF, and slack for each activity. The total project completion time and the critical path should also be determined. Here are the activity times: Activity Time (weeks) Immediate Predecessor(s) Activity Time (weeks) Immediate Predecessor(s) A 6 E 3 B B 8 F 6 B C 3 A G 11 C, E D 1 A H 7 D, F Dave's earliest start (ES) and earliest finish (EF) are: Activity ES .EF A 0 6 B 0 8 C 3 9 D 6 E F 8 G 22 H 21 Dave's latest start (LS) and latest finish (LF) are: Activity LS LF H 15 G 11 F 9arrow_forwardThere are multiple ways a company can enter a foreign market. Explore two possibilities such as exporting, foreign direct investment, and collaborations (joint ventures, alliances, licensing, franchising), and evaluate the pros and cons of each method. Which types of products and services would be appropriate for each market entry method?arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub Understanding Management (MindTap Course List)ManagementISBN:9781305502215Author:Richard L. Daft, Dorothy MarcicPublisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Management (MindTap Course List)ManagementISBN:9781305502215Author:Richard L. Daft, Dorothy MarcicPublisher:Cengage Learning Foundations of Business (MindTap Course List)MarketingISBN:9781337386920Author:William M. Pride, Robert J. Hughes, Jack R. KapoorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Business (MindTap Course List)MarketingISBN:9781337386920Author:William M. Pride, Robert J. Hughes, Jack R. KapoorPublisher:Cengage Learning




