
Managerial Accounting: Creating Value in a Dynamic Business Environment
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781259569562
Author: Ronald W Hilton Proffesor Prof, David Platt
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 29E
Alexandria Aluminum Company, a manufacturer of recyclable soda cans, had the following inventory balances at the beginning and end of 20x1.
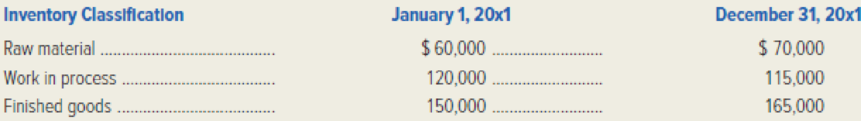
During 20x1, the company purchased $250,000 of raw material and spent $400,000 on direct labor.

Sales revenue was $1,105,000 for the year. Selling and administrative expenses for the year amounted to $110,000. The firm’s tax rate is 40 percent.
Required:
- 1. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured.
- 2. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods sold.
- 3. Prepare an income statement.
- 4. Build a spreadsheet: Construct an Excel spreadsheet to solve all of the preceding requirements. Show how both cost schedules and the income statement will change if the following data change: direct labor is $390,000 and utilities cost $35,000.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Question 25
expert of general accounting
Please give me answer and accounting
Chapter 2 Solutions
Managerial Accounting: Creating Value in a Dynamic Business Environment
Ch. 2 - Distinguish between product costs and period...Ch. 2 - Why are product costs also called inventoriable...Ch. 2 - What is the most important difference between a...Ch. 2 - List several product costs incurred in the...Ch. 2 - Prob. 5RQCh. 2 - Why is the cost of idle time treated as...Ch. 2 - Explain why an overtime premium is included in...Ch. 2 - Prob. 8RQCh. 2 - Give examples to illustrate how the city of Tampa...Ch. 2 - Distinguish between fixed costs and variable...
Ch. 2 - How does the fixed cost per unit change as the...Ch. 2 - Prob. 12RQCh. 2 - Distinguish between volume-based and...Ch. 2 - Would each of the following characteristics be a...Ch. 2 - List three direct costs of the food and beverage...Ch. 2 - List three costs that are likely to be...Ch. 2 - Which of the following costs are likely to be...Ch. 2 - Distinguish between out-of-pocket costs and...Ch. 2 - Define the terms sunk cost and differential cost.Ch. 2 - Distinguish between marginal and average costs.Ch. 2 - Prob. 21RQCh. 2 - Two years ago the manager of a large department...Ch. 2 - Indicate whether each of the following costs is a...Ch. 2 - For each case below, find the missing amount.Ch. 2 - A foundry employee worked a normal 40-hour shift,...Ch. 2 - A loom operator in a textiles factory earns 16 per...Ch. 2 - Consider the following costs that were incurred...Ch. 2 - Alexandria Aluminum Company, a manufacturer of...Ch. 2 - Prob. 30ECh. 2 - A hotel pays the phone company 100 per month plus...Ch. 2 - Prob. 32ECh. 2 - Orbital Communications, Inc. manufactures...Ch. 2 - The state Department of Education owns a computer...Ch. 2 - Prob. 35ECh. 2 - List the costs that would likely be included in...Ch. 2 - Consider the following cost items: 1. Salaries of...Ch. 2 - The following selected information was extracted...Ch. 2 - Prob. 39PCh. 2 - Mason Corporation began operations at the...Ch. 2 - Determine the missing amounts in each of the...Ch. 2 - The following cost data for the year just ended...Ch. 2 - The following data refer to San Fernando Fashions...Ch. 2 - Highlander Cutlery manufactures kitchen knives....Ch. 2 - Cape Cod Shirt Shop manufactures T-shirts and...Ch. 2 - Heartland Airways operates commuter flights in...Ch. 2 - San Diego Sheet Metal, Inc. incurs a variable cost...Ch. 2 - Hightide Upholstery Company manufactures a special...Ch. 2 - For each of the following costs, indicate whether...Ch. 2 - Indicate for each of the following costs whether...Ch. 2 - Water Technology, Inc. incurred the following...Ch. 2 - The following terms are used to describe various...Ch. 2 - Several costs incurred by Bayview Hotel and...Ch. 2 - Refer to Exhibit 23, and answer the following...Ch. 2 - Roberta Coy makes custom mooring covers for boats....Ch. 2 - The Department of Natural Resources is responsible...Ch. 2 - Prob. 57PCh. 2 - Prob. 58PCh. 2 - CompTech, Inc. manufactures printers for use with...Ch. 2 - You just started a summer internship with the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I want Solutionarrow_forwardanswer isarrow_forwardWhat role should the precautionary principle play in the development and application A of accounting standards? Discuss the potential tensions that may arise between the need for financial transparency and the desire to mitigate against excessive risk- taking or overly optimistic reporting.arrow_forward
- general accountingarrow_forwardThe industrial enterprise "HUANG S.A." purchased a sorting and packaging machine from a foreign company on 1/4/2017 at a cost of €500,000. The useful life of the machine was estimated by the Management at ten (10) years, while the residual value was estimated at zero. For the transportation of the machine from abroad to the company's factory, the amount of €20,000 was paid on 15/4/2017. As the insurance coverage of the machine during transportation was the responsibility of the selling company, HUANG S.A. proceeded to insure the machine from 16/4/2017 to 15/4/2018, paying the amount of €1,200. The delivery took place on 15/4/2017. As adequate ventilation of the multifunction device is essential for its proper operation, the company fitted an air duct on the multifunction device. The cost of the air duct amounted to €2,000 and was paid on 20/4/2017. On 25/4/2017, an external electrician was paid €5,000 for the electrical connection of the device. The company also paid €5,000 to an…arrow_forwardNO AI ANSWERarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Job Costing and Spoilage | Topic 2 | Spoilage, Re-work, and Scrap; Author: Samantha Taylor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VP55_W2oXic;License: CC-BY