
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
6th Edition
ISBN: 8220102801448
Author: Alexander
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 27P
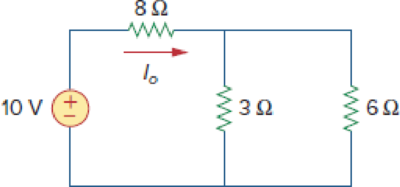
Calculate Io in the circuit of Fig. 2.91.
Figure 2.91
For Prob. 2.27.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
V₁(t)
ww
ZRI
ZLI
Z12
Zci
Zcz
Figure 4. Notch filter circuit topology
ши
Consider the second order resonant circuit shown in Figure 4. Impedances ZLIZ C1. ZL2. Z c2 combine together forming a two-stage "band-
reject" filter, so called because it rejects a "band" (aka range) of frequencies. This circuit topology is also commonly referred to as a "band-stop" filter
or "notch" filter.
The output of the DAB receiver block has been approximated via Thevenin's theorem for you as a voltage source Vs (t) and associated series
impedance Z RI
To succeed in our goal, we are going to use an iterative design approach. First we will design the interference rejector, and then repeat the process,
using the output of the interference rejector to check the provided waveform converter works as intended.
1. What is the settling time for your output signal (BRF_OUT)? For this question, We define the settling time as the period of time it has taken for the output to settle into a steady state - ie when your oscillation first decays (aka reduces) to less than approximately 1/20 (5%) of the initial value.
(a) Settling time
2. What is the total impedance Zt of your designed circuit? Represent your result in cartesian form
NOTE: use j to represent sqare root
Zt=
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
Ch. 2.2 - The essential component of a toaster is an...Ch. 2.2 - For the circuit shown in Fig. 2.9, calculate the...Ch. 2.2 - A resistor absorbs an instantaneous power of 30...Ch. 2.3 - How many branches and nodes does the circuit in...Ch. 2.4 - Find v1 and v2 in the circuit of Fig. 2.22. Figure...Ch. 2.4 - Find vx and vo in the circuit of Fig. 2.24. Figure...Ch. 2.4 - Find vo and io in the circuit of Fig. 2.26. Figure...Ch. 2.4 - Find the current and voltages in the circuit shown...Ch. 2.6 - By combining the resistors in Fig.2.36, find Req....Ch. 2.6 - Find Rab for the circuit in Fig.2.39. Figure 2.39...
Ch. 2.6 - Calculate Geq in the circuit of Fig.2.41. Figure...Ch. 2.6 - Find v1 and v2 in the circuit shown in Fig. 2.43....Ch. 2.7 - Transform the wye network in Fig. 2.51 to a delta...Ch. 2.7 - For the bridge network in Fig. 2.54, find Rab and...Ch. 2.8 - Refer to Fig. 2.55 and assume there are six light...Ch. 2.8 - Following the ammeter setup of Fig. 2.61. design...Ch. 2 - The reciprocal of resistance is: (a) voltage (b)...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2RQCh. 2 - Prob. 3RQCh. 2 - The maximum current that a 2W, 80 k resistor can...Ch. 2 - Prob. 5RQCh. 2 - The current I in the circuit of Fig. 2.63 is: (a)...Ch. 2 - The current I0 of Fig. 2.64 is: (a) 4 A (b) 2 A...Ch. 2 - In the circuit in Fig. 2.65, V is: (a) 30 V (b) 14...Ch. 2 - Which of the circuit in Fig. 2.66 will give you...Ch. 2 - In the circuit of Fig. 2.67, a decrease in R3...Ch. 2 - Design a problem, complete with a solution, to...Ch. 2 - Find the hot resistance of a light bulb rated 60...Ch. 2 - A bar of silicon is 4 cm long with a circular...Ch. 2 - (a) Calculate current i in Fig. 2.68 when the...Ch. 2 - For the network graph in Fig. 2.69. find the...Ch. 2 - In the network graph shown in Fig. 2.70, determine...Ch. 2 - Determine the number of branches and nodes in the...Ch. 2 - Design a problem, complete with a solution, to...Ch. 2 - Find i1, i2, and i3 in Fig. 2.73. Figure 2.73 For...Ch. 2 - Determine i1 and i2 in the circuit of Fig. 2.74....Ch. 2 - In the circuit of Fig. 2.75, calculate V1 and V2....Ch. 2 - In the circuit in Fig. 2.76, obtain v1, v2, and...Ch. 2 - For the circuit in Fig. 2.77, use KCL to find the...Ch. 2 - Given the circuit in Fig. 2.78, use KVL to find...Ch. 2 - Calculate v and ix in the circuit of Fig. 2.79....Ch. 2 - Determine Vo in the circuit in Fig. 2.80. Figure...Ch. 2 - Obtain v1 through v3 in the circuit of Fig. 2.81....Ch. 2 - Find I and V in the circuit of Fig. 2.82. Figure...Ch. 2 - From the circuit in Fig. 2.83, find I, the power...Ch. 2 - Determine io in the circuit of Fig. 2.84. Figure...Ch. 2 - Find Vx in the circuit of Fig. 2.85. Figure 2.85...Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. 2.86 and the power...Ch. 2 - In the circuit shown in Fig. 2.87, determine Vx...Ch. 2 - For the circuit in Fig. 2.88, find Vo/Vs in terms...Ch. 2 - For the network in Fig. 2.89, find the current,...Ch. 2 - For the circuit in Fig. 2.90, io = 3 A. Calculate...Ch. 2 - Calculate Io in the circuit of Fig. 2.91. Figure...Ch. 2 - Design a problem, using Fig. 2.92, to help other...Ch. 2 - All resistors (R) in Fig. 2.93 are 10 each. Find...Ch. 2 - For the circuit in Fig. 2.95, determine i1 to i5....Ch. 2 - Find i1 through i4 in the circuit in Fig. 2.96....Ch. 2 - Obtain v and i in the circuit of Fig. 2.97. Figure...Ch. 2 - Using series/parallel resistance combination, find...Ch. 2 - Calculate Vo and Io in the circuit of Fig. 2.99....Ch. 2 - Find i and Vo in the circuit of Fig. 2.100. Figure...Ch. 2 - Given the circuit in Fig. 2.101 and that the...Ch. 2 - Find Req and io in the circuit of Fig. 2.102....Ch. 2 - Evaluate Req looking into each set of terminals...Ch. 2 - For the ladder network in Fig. 2.104, find I and...Ch. 2 - If Req = 50 in the circuit of Fig. 2.105, find R....Ch. 2 - Reduce each of the circuits in Fig. 2.106 to a...Ch. 2 - Calculate the equivalent resistance Rab at...Ch. 2 - For the circuits in Fig. 2.108, obtain the...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance at terminals a-b of...Ch. 2 - Find I in the circuit of Fig. 2.110. Figure 2.110Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance Rab in the circuit...Ch. 2 - Convert the circuits in Fig. 2.112 from Y to ....Ch. 2 - Transform the circuits in Fig. 2.113 from to Y....Ch. 2 - Design a problem to help other students better...Ch. 2 - Obtain the equivalent resistance at the terminals...Ch. 2 - For the circuit shown in Fig. 2.116, find the...Ch. 2 - Obtain the equivalent resistance Rab in each of...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit in Fig. 2.118. Find the...Ch. 2 - Calculate I0 in the circuit of Fig. 2.119. Figure...Ch. 2 - Determine V in the circuit of Fig. 2.120. Figure...Ch. 2 - Find Req and I in the circuit of Fig. 2.121....Ch. 2 - The 150 W tight bulb in Fig. 2.122 is rated at 110...Ch. 2 - If the three bulbs of Prob. 2.59 are connected in...Ch. 2 - As a design engineer, you are asked to design a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 62PCh. 2 - If an ammeter with an internal resistance of 100 ...Ch. 2 - The potentiometer (adjustable resistor) Rx in Fig....Ch. 2 - Design a circuit that uses a dArsonval meter (with...Ch. 2 - A 20-k/V voltmeter reads 10 V full scale. (a) What...Ch. 2 - (a) Obtain the voltage Vo in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 2 - (a) Find the current I in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 2 - A voltmeter used to measure Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 2 - (a) Consider the Wheatstone bridge shown in Fig....Ch. 2 - Figure 2.131 represents a model of a solar...Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the two-way power divider circuit in...Ch. 2 - An ammeter model consists of an ideal ammeter in...Ch. 2 - The circuit in Fig. 2.134 is to control the speed...Ch. 2 - Find Rab in the four-way power divider circuit in...Ch. 2 - Repeat Prob. 2.75 for the eight-way divider shown...Ch. 2 - Suppose your circuit laboratory has the following...Ch. 2 - In the circuit in Fig. 2.137, the wiper divides...Ch. 2 - Prob. 79CPCh. 2 - A loudspeaker is connected to an amplifier as...Ch. 2 - For a specific application, the circuit shown in...Ch. 2 - The pin diagram of a resistance array is shown in...Ch. 2 - Two delicate devices are rated as shown in Fig....
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An electric resistance space heater is designed such that it resembles a rectangular box 55 cm high, 75 cm long, and 20 cm wide filled with 45 kg of oil. The heater is to be placed against a wall, and thus heat transfer from its back surface is negligible. The surface temperature of the heater is not to exceed 75°C in a room at 25°C for safety considerations. The emissivity of the outer surface of the heater is 0.8 and the average temperature of the ceiling and wall surfaces is the same as the room air temperature. The properties of air at 1 atm and the film temperature are: k = 0.02753 W/m-°C, v=1.798 x 10-5 m²/s, Pr = 0.7228, and ẞ= 0.003096K-1 Wall T₁ =75°C Oil € = 0.8 Electric heater Heating element Disregarding heat transfer from the bottom and top surfaces of the heater in anticipation that the top surface will be used as a shelf, determine the power rating of the heater in W. The power rating of the heater is W.arrow_forwardcircuit 2arrow_forwardSuppose you have 8 LED's connected to port-B (Bo-B7) of PIC16F877A and one switch connected to port-D (Do) as shown in figure below. Write a program code that performs a nibble (4-bits) toggling: if the switch is released then LED's (Bo to B3) are OFF and LED's (B4 to B7) are ON, while if the switch is pressed then LED's (Bo to B3) are ON and LED's (B4 to B7) are OFF. Use 300ms delay for each case with 4MHz frequency. 13 14 22 NATHON 20 U1 OSC1/CLKIN U2 33 REOINT 20 34 OSC2/CLKOUT 19 RB1 35 3 18 RB2 RADIANO debt0RB3PGM 30 4 17 37 5 10 RA1/AN1 RB4 38 RA2/ANZ/VREF-/CVREF 15 RB5 39097 RA3/AN3VREF RB6/PGC 7 14 40 RA4/TOCK/C1OUT 13 RB7/PGO RAS/ANA/SS/CZOUT 15 RCO/T1OSO/TICKI 10 11 REQIANS/RD 18 RC1/T10S/CCP2 17 10 RE1/AN/WR REZ/ANTICS MCLR/Vpp/THV RC2/CCP1 LED-BARGRAPH-RED RC3/SCK/SCL RC4/SDUSDA RC5/SDO Eng of ROSTX/CX RC7/RX/DT RDO/PSPO RD1/PSP1 RD2PSP2 RO3/PSP3 RD4/PSP4 ROS/PSP5 RD6/PSP6 RD7/PSP7 PIC16F877A +5V R1 100Rarrow_forward
- Write a PIC16F877A program that flash ON the 8-LED's connected to port-B by using two switches connected to port-D (Do & D₁) as shown in figure below, according to the following scenarios: (Hint: Use 500ms delay for each case with 4MHz frequency) 1. When Do=1 then B₁,B3,B, are ON. 2. When Do 0 then Bo,B2,B4, B5, B6 are ON. 3. When D₁=1 then B4,B,,B6,B7 are ON. 4. When D₁-0 then Bo,B1,B2,B3 are ON. U1 5 33 OSC/CLION OSC2/CLKOUT ROOINT RB1 35 RB2 20 17 RACIANO RESPOM RATANT RAZIANZ/VREF-CVREF RBS RA3/AN3/VREF+ REPOC 39 14 40 RA4/TOCK C1OUT 13 RB7/PGO 12 RASIAN/SCOUT 15 ROOT1050/TICK +5V REGIANERD REVANDVIR REZANTICS RCMT10SUCCP2 17 RC2/CCP1 LED-BARGRAPH-RED RC3SCHISCL 23 --- MCUANTV RC4/SOSDA 24 RCS/SDO RCB/TICK RC7/RXDT 25 ROOPSPO RDMPSP1 RD2PSF2 RO3PSP3 RD4PSP4 RDSPSPS PIC16F877A ROOPSP RO7/PSP7 R2 R1 100R 100Rarrow_forwardQuestion 5 The following data were obtained from testing a 48-kVA 240/4800 V step up transformer. Open-circuit test Short-circuit test Voltage (V) 240 150 Current (I) 2 10 Power (W) 120 600 Determine the equivalent circuit of the transformer as viewed from the primary side. Ans: Rc = 480 ohm, Xm = 123.94 ohm, Reqp = 0.015 ohm, Xeqp = 0.034 ohmarrow_forwardFrom the following mass-spring system, obtain its transfer function and pole-zero wwwwwwww wwww diagram in MATLAB. Analyze how stability varies when entering values. wwwww (4)x1 ▷ x(t) M f(t) B f(t) is the input variable and x(t) is the controlled variable.arrow_forward
- R2 L3 C5 BRF_OUT HH Sine_OUT 100 1m 100n C3 C4 100n 100n Figure 9. Square to sine waveform converter circuit How do we make sense of this? First, we note that R2 and C3 form a first order low pass filter and L3 and C4 form another low pass filter. Both low pass filters have been set at the same cutoff frequency. The combination of both form a two stage filter to remove the high frequency content present in the DAB signal. Capacitor C5 is used to remove any residual DC offset in the signal. But let's just deal with the AC steady state response, which means that you don't need to know any of these details, and then can conveniently treat this circuit as a blackbox. What is the theoretical cutoff frequency for the RC and LC filters shown in Figure 9? Answer to within 1% accuracy. (a) RC Filter cutoff frequency (f 1) = kHzarrow_forwardFor the following steady-state AC circuit, find the complex output voltage, VO, shown in the diagram. Write the answer in polar form (angles in degrees), accurate within 1%. L1=0.7H, L2=5H, C=14F, R=0.60, and w=0.7 rad/s L1 m Vo R Vs 5/30°V Answer: ய ww L2 23arrow_forwardPlease draw logic circuitarrow_forward
- A 220-volt, 20-horsepower compound motor (long shunt, Figure 21–16A) has an armature resistance of 0.25 ohm, series field resistance of 0.19 ohm, and shunt field resistance of 33 ohms. a. Calculate the current taken by the motor at the instant of starting if it is con-nected directly to the 220-volt line. b. Calculate the current when the motor is running if the armature is developing 184 volts counter-emf.arrow_forwardDesign a modulo-11 ripple (asynchronous) up-counter with negative edge-triggered T flip-flops and draw the corresponding logic circuit. (I)Build the state diagram and extract the state table (II)Draw the logic circuit (III)What is the maximum modulus of the counter?arrow_forwardthe diagram show 4 motor connected to a k-35 controller. I would like detail explanation to know how the circuit work. Is the controller compatible with the motor? The motor shown is series, parallel or both?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Z Parameters - Impedance Parameters; Author: Electrical Engineering Authority;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qoD4AoNmySA;License: Standard Youtube License