
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
6th Edition
ISBN: 8220102801448
Author: Alexander
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 18P
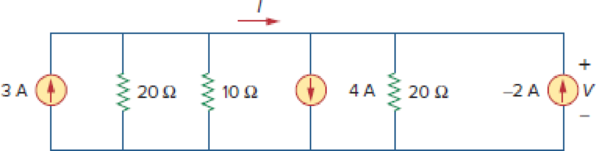
Find I and V in the circuit of Fig. 2.82.
Figure 2.82
For Prob. 2.18.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A3 m long cantilever ABC is built-in at A, partially supported at B, 2 m from A,
with a force of 10 kN and carries a vertical load of 20 kN at C. A uniformly distributed
bad of 5 kN/m is also applied between A and B. Determine
(a) the values of the vertical reaction and built-in moment at A and
(b) the deflection of the free end C of the cantilever,
Develop an expression for the slope of the beam at any position and hence plot a slope diagram.
E = 208GN / (m ^ 2) and 1 = 24 * 10 ^ - 6 * m ^ 4
7. Consider the following feedback system with a proportional controller.
K
G(s)
The plant transfer function is given by
G(s) =
10
(s + 2)(s + 10)
You want the system to have a damping ratio of 0.3 for unit step response. What is the
value of K you need to choose to achieve the desired damping ratio? For that value of
K, find the steady-state error for ramp input and settling time for step input.
Hint: Sketch the root locus and find the point in the root locus that intersects with z =
0.3 line.
Create the PLC ladder logic diagram
for the logic gate circuit displayed in
Figure 7-35. The pilot light red (PLTR)
output section has three inputs: PBR,
PBG, and SW. Pushbutton red (PBR)
and pushbutton green (PBG) are inputs
to an XOR logic gate. The output of the
XOR logic gate and the inverted switch
SW) are inputs to a two-input AND
logic gate. These inputs generate the
pilot light red (PLTR) output.
The two-input AND logic gate output
is also fed into a two-input NAND logic
PBR
PBG
SW
TSW
PLTR
Figure 7-35. Logic gate circuit for Example 7-3.
PLTW
Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
gate. The temperature switch (TSW) is the other input to the NAND logic gate. The output generated from
the NAND logic gate is labeled pilot light white (PLTW).
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
Ch. 2.2 - The essential component of a toaster is an...Ch. 2.2 - For the circuit shown in Fig. 2.9, calculate the...Ch. 2.2 - A resistor absorbs an instantaneous power of 30...Ch. 2.3 - How many branches and nodes does the circuit in...Ch. 2.4 - Find v1 and v2 in the circuit of Fig. 2.22. Figure...Ch. 2.4 - Find vx and vo in the circuit of Fig. 2.24. Figure...Ch. 2.4 - Find vo and io in the circuit of Fig. 2.26. Figure...Ch. 2.4 - Find the current and voltages in the circuit shown...Ch. 2.6 - By combining the resistors in Fig.2.36, find Req....Ch. 2.6 - Find Rab for the circuit in Fig.2.39. Figure 2.39...
Ch. 2.6 - Calculate Geq in the circuit of Fig.2.41. Figure...Ch. 2.6 - Find v1 and v2 in the circuit shown in Fig. 2.43....Ch. 2.7 - Transform the wye network in Fig. 2.51 to a delta...Ch. 2.7 - For the bridge network in Fig. 2.54, find Rab and...Ch. 2.8 - Refer to Fig. 2.55 and assume there are six light...Ch. 2.8 - Following the ammeter setup of Fig. 2.61. design...Ch. 2 - The reciprocal of resistance is: (a) voltage (b)...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2RQCh. 2 - Prob. 3RQCh. 2 - The maximum current that a 2W, 80 k resistor can...Ch. 2 - Prob. 5RQCh. 2 - The current I in the circuit of Fig. 2.63 is: (a)...Ch. 2 - The current I0 of Fig. 2.64 is: (a) 4 A (b) 2 A...Ch. 2 - In the circuit in Fig. 2.65, V is: (a) 30 V (b) 14...Ch. 2 - Which of the circuit in Fig. 2.66 will give you...Ch. 2 - In the circuit of Fig. 2.67, a decrease in R3...Ch. 2 - Design a problem, complete with a solution, to...Ch. 2 - Find the hot resistance of a light bulb rated 60...Ch. 2 - A bar of silicon is 4 cm long with a circular...Ch. 2 - (a) Calculate current i in Fig. 2.68 when the...Ch. 2 - For the network graph in Fig. 2.69. find the...Ch. 2 - In the network graph shown in Fig. 2.70, determine...Ch. 2 - Determine the number of branches and nodes in the...Ch. 2 - Design a problem, complete with a solution, to...Ch. 2 - Find i1, i2, and i3 in Fig. 2.73. Figure 2.73 For...Ch. 2 - Determine i1 and i2 in the circuit of Fig. 2.74....Ch. 2 - In the circuit of Fig. 2.75, calculate V1 and V2....Ch. 2 - In the circuit in Fig. 2.76, obtain v1, v2, and...Ch. 2 - For the circuit in Fig. 2.77, use KCL to find the...Ch. 2 - Given the circuit in Fig. 2.78, use KVL to find...Ch. 2 - Calculate v and ix in the circuit of Fig. 2.79....Ch. 2 - Determine Vo in the circuit in Fig. 2.80. Figure...Ch. 2 - Obtain v1 through v3 in the circuit of Fig. 2.81....Ch. 2 - Find I and V in the circuit of Fig. 2.82. Figure...Ch. 2 - From the circuit in Fig. 2.83, find I, the power...Ch. 2 - Determine io in the circuit of Fig. 2.84. Figure...Ch. 2 - Find Vx in the circuit of Fig. 2.85. Figure 2.85...Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. 2.86 and the power...Ch. 2 - In the circuit shown in Fig. 2.87, determine Vx...Ch. 2 - For the circuit in Fig. 2.88, find Vo/Vs in terms...Ch. 2 - For the network in Fig. 2.89, find the current,...Ch. 2 - For the circuit in Fig. 2.90, io = 3 A. Calculate...Ch. 2 - Calculate Io in the circuit of Fig. 2.91. Figure...Ch. 2 - Design a problem, using Fig. 2.92, to help other...Ch. 2 - All resistors (R) in Fig. 2.93 are 10 each. Find...Ch. 2 - For the circuit in Fig. 2.95, determine i1 to i5....Ch. 2 - Find i1 through i4 in the circuit in Fig. 2.96....Ch. 2 - Obtain v and i in the circuit of Fig. 2.97. Figure...Ch. 2 - Using series/parallel resistance combination, find...Ch. 2 - Calculate Vo and Io in the circuit of Fig. 2.99....Ch. 2 - Find i and Vo in the circuit of Fig. 2.100. Figure...Ch. 2 - Given the circuit in Fig. 2.101 and that the...Ch. 2 - Find Req and io in the circuit of Fig. 2.102....Ch. 2 - Evaluate Req looking into each set of terminals...Ch. 2 - For the ladder network in Fig. 2.104, find I and...Ch. 2 - If Req = 50 in the circuit of Fig. 2.105, find R....Ch. 2 - Reduce each of the circuits in Fig. 2.106 to a...Ch. 2 - Calculate the equivalent resistance Rab at...Ch. 2 - For the circuits in Fig. 2.108, obtain the...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance at terminals a-b of...Ch. 2 - Find I in the circuit of Fig. 2.110. Figure 2.110Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance Rab in the circuit...Ch. 2 - Convert the circuits in Fig. 2.112 from Y to ....Ch. 2 - Transform the circuits in Fig. 2.113 from to Y....Ch. 2 - Design a problem to help other students better...Ch. 2 - Obtain the equivalent resistance at the terminals...Ch. 2 - For the circuit shown in Fig. 2.116, find the...Ch. 2 - Obtain the equivalent resistance Rab in each of...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit in Fig. 2.118. Find the...Ch. 2 - Calculate I0 in the circuit of Fig. 2.119. Figure...Ch. 2 - Determine V in the circuit of Fig. 2.120. Figure...Ch. 2 - Find Req and I in the circuit of Fig. 2.121....Ch. 2 - The 150 W tight bulb in Fig. 2.122 is rated at 110...Ch. 2 - If the three bulbs of Prob. 2.59 are connected in...Ch. 2 - As a design engineer, you are asked to design a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 62PCh. 2 - If an ammeter with an internal resistance of 100 ...Ch. 2 - The potentiometer (adjustable resistor) Rx in Fig....Ch. 2 - Design a circuit that uses a dArsonval meter (with...Ch. 2 - A 20-k/V voltmeter reads 10 V full scale. (a) What...Ch. 2 - (a) Obtain the voltage Vo in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 2 - (a) Find the current I in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 2 - A voltmeter used to measure Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 2 - (a) Consider the Wheatstone bridge shown in Fig....Ch. 2 - Figure 2.131 represents a model of a solar...Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the two-way power divider circuit in...Ch. 2 - An ammeter model consists of an ideal ammeter in...Ch. 2 - The circuit in Fig. 2.134 is to control the speed...Ch. 2 - Find Rab in the four-way power divider circuit in...Ch. 2 - Repeat Prob. 2.75 for the eight-way divider shown...Ch. 2 - Suppose your circuit laboratory has the following...Ch. 2 - In the circuit in Fig. 2.137, the wiper divides...Ch. 2 - Prob. 79CPCh. 2 - A loudspeaker is connected to an amplifier as...Ch. 2 - For a specific application, the circuit shown in...Ch. 2 - The pin diagram of a resistance array is shown in...Ch. 2 - Two delicate devices are rated as shown in Fig....
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
3.3 It is known that a vertical force of 200 lb is required to remove the nail at C from the board. As the nail...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
1.2 Explain the difference between geodetic and plane
surveys,
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
This optional Google account security feature sends you a message with a code that you must enter, in addition ...
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Imaginary Axis (seconds) 1 6. Root locus for a closed-loop system with L(s) = is shown below. s(s+4)(s+6) 15 10- 0.89 0.95 0.988 0.988 -10 0.95 -15 -25 0.89 20 Root Locus 0.81 0.7 0.56 0.38 0.2 5 10 15 System: sys Gain: 239 Pole: -0.00417 +4.89 Damping: 0.000854 Overshoot (%): 99.7 Frequency (rad/s): 4.89 System: sys Gain: 16.9 Pole: -1.57 Damping: 1 Overshoot (%): 0 Frequency (rad/s): 1.57 0.81 0.7 0.56 0.38 0.2 -20 -15 -10 -5 5 10 Real Axis (seconds) From the values shown in the figure, compute the following. a) Range of K for which the closed-loop system is stable. b) Range of K for which the closed-loop step response will not have any overshoot. Note that when all poles are real, the step response has no overshoot. c) Smallest possible peak time of the system. Note that peak time is the smallest when wa is the largest for the dominant pole. d) Smallest possible settling time of the system. Note that peak time is the smallest when σ is the largest for the dominant pole.arrow_forwardFor a band-rejection filter, the response drops below this half power point at two locations as visualised in Figure 7, we need to find these frequencies. Let's call the lower frequency-3dB point as fr and the higher frequency -3dB point fH. We can then find out the bandwidth as f=fHfL, as illustrated in Figure 7. 0dB Af -3 dB Figure 7. Band reject filter response diagram Considering your AC simulation frequency response and referring to Figure 7, measure the following from your AC simulation. 1% accuracy: (a) Upper-3db Frequency (fH) = Hz (b) Lower-3db Frequency (fL) = Hz (c) Bandwidth (Aƒ) = Hz (d) Quality Factor (Q) =arrow_forwardP 4.4-21 Determine the values of the node voltages V1, V2, and v3 for the circuit shown in Figure P 4.4-21. 29 ww 12 V +51 Aia ww 22. +21 ΖΩ www ΖΩ w +371 ①1 1 Aarrow_forward
- 1. What is the theoretical attenuation of the output voltage at the resonant frequency? Answer to within 1%, or enter 0, or infinity (as “inf”) Attenuation =arrow_forwardWhat is the settling time for your output signal (BRF_OUT)? For this question, We define the settling time as the period of time it has taken for the output to settle into a steady state - ie when your oscillation first decays (aka reduces) to less than approximately 1/20 (5%) of the initial value. (a) Settling time = 22 μs Your last answer was interpreted as follows: Incorrect answer. Check 22 222 What is the peak to peak output voltage (BRF_OUT pp) at the steady state condition? You may need to use the zoom function to perform this calculation. Select a time point that is two times the settling time you answered in the question above. Answer to within 10% accuracy. (a) BRF_OUT pp= mVpp As you may have noticed, the output voltage amplitude is a tiny fraction of the input voltage, i.e. it has been significantly attenuated. Calculate the attenuation (decibels = dB) in the output signal as compared to the input based on the formula given below. Answer to within 1% accuracy.…arrow_forwardmy previous answers for a,b,d were wrong a = 1050 b = 950 d=9.99 c was the only correct value i got previously c = 100hz is correctarrow_forward
- V₁(t) ww ZRI ZLI ZL2 ZTH Zci VTH Zc21 Figure 8. Circuit diagram showing calculation approach for VTH and Z TH we want to create a blackbox for the red region, we want to use the same input signal conditions as previously the design of your interference ector circuit: Sine wave with a 1 Vpp, with a frequency of 100 kHz (interference) Square wave with 2.4Vpp, with a frequency of 10 kHz (signal) member an AC Thevenin equivalent is only valid at one frequency. We have chosen to calculate the Thevenin equivalent circuit (and therefore the ackbox) at the interference frequency (i.e. 100 kHz), and the signal frequency (i.e. 10 kHz) as these are the key frequencies to analyse. Your boss is assured you that the waveform converter module has been pre-optimised to the DAB Receiver if you use the recommended circuit topology.arrow_forwardVs(t) + v(t) + vi(t) ZR ZL Figure 1: Second order RLC circuit Zc + ve(t) You are requested to design the circuit shown in Figure 1. The circuit is assumed to be operating at its resonant frequency when it is fed by a sinusoidal voltage source Vs (t) = 2sin(le6t). To help design your circuit you have been given the value of inductive reactance ZL = j1000. Assume that the amplitude of the current at resonance is Is (t) = 2 mA. Based on this information, answer the following to help design your circuit. Use cartesian notation for your answers, where required.arrow_forwardWhat is the attenuation at the resonant frequency? You should use the LTSpice cursors for your measurement. Answer to within 1% accuracy, or enter 0, or infinity (as "inf") (a) Attenuation (dB) = dB Check You may have noticed that it was significantly easier to use frequency-domain "AC" simulation to measure the attenuation, compared to the steps we performed in the last few questions. (i.e. via a time-domain "transient" simulation). AC analysis allows us to observe and quantify large scale positive or negative changes in a signal of interest across a wide range of different frequencies. From the response you will notice that only frequencies that are relatively close to 100 kHz have been attenuated. This is the result of the Band-reject filter you have designed, and shows the 'rejection' (aka attenuation) of any frequencies that lie in a given band. The obvious follow-up question is how do we define this band? We use a quantity known as the bandwidth. A commonly used measurement for…arrow_forward
- V₁(t) ww ZRI ZLI ZL2 ZTH Zci VTH Zc21 Figure 8. Circuit diagram showing calculation approach for VTH and Z TH we want to create a blackbox for the red region, we want to use the same input signal conditions as previously the design of your interference ector circuit: Sine wave with a 1 Vpp, with a frequency of 100 kHz (interference) Square wave with 2.4Vpp, with a frequency of 10 kHz (signal) member an AC Thevenin equivalent is only valid at one frequency. We have chosen to calculate the Thevenin equivalent circuit (and therefore the ackbox) at the interference frequency (i.e. 100 kHz), and the signal frequency (i.e. 10 kHz) as these are the key frequencies to analyse. Your boss is assured you that the waveform converter module has been pre-optimised to the DAB Receiver if you use the recommended circuit topology.arrow_forwardVs(t) + v(t) + vi(t) ZR ZL Figure 1: Second order RLC circuit Zc + ve(t) You are requested to design the circuit shown in Figure 1. The circuit is assumed to be operating at its resonant frequency when it is fed by a sinusoidal voltage source Vs (t) = 2sin(le6t). To help design your circuit you have been given the value of inductive reactance ZL = j1000. Assume that the amplitude of the current at resonance is Is (t) = 2 mA. Based on this information, answer the following to help design your circuit. Use cartesian notation for your answers, where required.arrow_forwardFor a band-rejection filter, the response drops below this half power point at two locations as visualised in Figure 7, we need to find these frequencies. Let's call the lower frequency-3dB point as fr and the higher frequency -3dB point fH. We can then find out the bandwidth as f=fHfL, as illustrated in Figure 7. 0dB Af -3 dB Figure 7. Band reject filter response diagram Considering your AC simulation frequency response and referring to Figure 7, measure the following from your AC simulation. 1% accuracy: (a) Upper-3db Frequency (fH) = Hz (b) Lower-3db Frequency (fL) = Hz (c) Bandwidth (Aƒ) = Hz (d) Quality Factor (Q) =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Superposition Theorem; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EX52BuZxpQM;License: Standard Youtube License