
a)
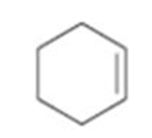
Interpretation:
How to prepare cyclohexene from 2-cyclohexenone is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Wolf-Kishner reduction rection can be used to prepare cyclohexene from 2-cyclohexenone.
To state:
How to prepare cyclohexene from 2-cyclohexenone.
b)
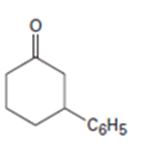
Interpretation:
How to prepare 3-phenylcyclohexanone from 2-cyclohexenone is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
By treating 2-cyclohexenone with lithiumdiphenylcopper and acidifying the product formed 3-phenylcyclohexanone can be prepared, as the organolithiumcopper reagents are good reagents for the conjugate addition to α,β- unsaturated
To state:
How to prepare 3-phenylcyclohexanone from 2-cyclohexenone.
c)
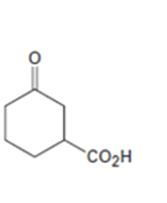
Interpretation:
How to prepare the ketoacid shown from 2-cyclohexenone is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
An easily oxidizable group is introduced to C3 of 2-cyclohexenone by a conjugate addition using lithiumdialkylcopper reagent. The resulting product can then be oxidized to a
To state:
How to prepare the keto acid shown from 2-cyclohexenone.
d)
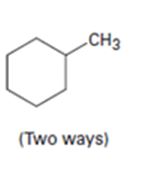
Interpretation:
How to prepare methylcyclohexane from 2-cyclohexenone (two ways) is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
An alkyl group can be introduced into 2-cyclohexenone by treating it with lithiumdialkyl reagent(conjugate addition takes place). The keto group can be reduced to CH2 by Wolff-Kishner reduction.
Another way is to replace the C =O in 2-cyclohexenone by C =CH2 by a Wittig reaction first and then reducing it to C-CH3 by H2, Pd/C.
To state:
How to prepare methylcyclohexane from 2-cyclohexenone.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 19 Solutions
Study Guide with Student Solutions Manual for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- (a) Draw the structures of A and B in the following reaction. (i) NaNH2, NH3(1) A + B (ii) H3O+arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forwardConsider the following decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): For the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 → NO2 + NO3 (K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5 → NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: d[N2O5] = -k₁[N₂O₂] + K¸₁[NO₂][NO3] - K¸[NO₂]³ dtarrow_forward
- In a reaction of A + B to give C, another compound other than A, B or C may appear in the kinetic equation.arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forwardGiven the reaction R + Q → P, indicate the rate law with respect to R, with respect to P and with respect to P.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

