
Physics, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134020853
Author: James S. Walker
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 19.5, Problem 5EYU
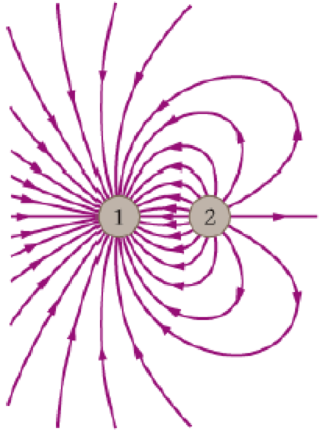
The electric field lines for a system of two charges are shown in Figure 19-23. (a) What is the sign of charge 1? (b) What is the sign of charge 2? (c) Is the magnitude of charge 1 greater than, less than, or equal to the magnitude of charge 2? Explain.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Just 5 and 6 don't mind 7
In an electron gun, electrons are accelerated through a region with an electric field of magnitude 1.5 × 104 N/C for a distance of 2.5 cm. If the electrons start from rest, how fast are they moving after traversing the gun?
Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!
Chapter 19 Solutions
Physics, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Ch. 19.1 - Enhance Your Understanding (Answers given at the...Ch. 19.2 - Enhance Your Understanding (Answers given at the...Ch. 19.3 - Positive and negative charges of equal magnitude...Ch. 19.4 - Enhance Your Understanding (Answers given at the...Ch. 19.5 - The electric field lines for a system of two...Ch. 19.6 - Two conducting spheres of different radii are...Ch. 19.7 - Four Gaussian surfaces (A, B, C, D) are shown in...Ch. 19 - The fact that the electron has a negative charge...Ch. 19 - Explain why a comb that has been rubbed through...Ch. 19 - Small bits of paper are attracted to an...
Ch. 19 - A charged rod is brought near a suspended object,...Ch. 19 - A charged rod is brought near a suspended object,...Ch. 19 - A point charge +Q is fixed at a height H above the...Ch. 19 - A proton moves in a region of constant electric...Ch. 19 - Describe some of the differences between charging...Ch. 19 - A system consists of two charges of equal...Ch. 19 - The force experienced by charge 1 at point A is...Ch. 19 - Can an electric field exist in a vacuum? Explain.Ch. 19 - Gausss law can tell us how much charge is...Ch. 19 - Predict/Explain An electrically neutral object is...Ch. 19 - (a) Based on the materials listed in Table 19-1,...Ch. 19 - This problem refers to the information given in...Ch. 19 - Find the net charge of a system consisting of (a)...Ch. 19 - Find the total electric charge of 2.5 kg of (a)...Ch. 19 - A container holds a gas consisting of 2.85 moles...Ch. 19 - The Charge on Adhesive Tape When adhesive tape is...Ch. 19 - Four pairs of conducting spheres, all with the...Ch. 19 - A system of 1525 particles, each of which is...Ch. 19 - A charge +q and a charge q are placed at opposite...Ch. 19 - Consider the three electric charges, A, B, and C,...Ch. 19 - Predict/Explain Suppose the charged sphere in...Ch. 19 - At what separation is the electrostatic force...Ch. 19 - How much equal charge should be placed on the...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Two point charges, the first...Ch. 19 - When two identical ions are separated by a...Ch. 19 - Given that q = +18 C and d = 21 cm, find the...Ch. 19 - Five point charges, q1 = +q, q2 = +2q q3 = 3q, q4...Ch. 19 - Three charges, q1 = +q, q2 = q, and q3 = +q, are...Ch. 19 - The attractive electrostatic force between the...Ch. 19 - Prob. 21PCECh. 19 - A sphere of radius 4.22 cm and uniform surface...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Given that q = +12 C and d = 19...Ch. 19 - Suppose the charge q2 in Figure 19-38 can be moved...Ch. 19 - A point charge q = 0.55 nC is fixed at the origin....Ch. 19 - A point charge q = 0.55 nC is fixed at the origin....Ch. 19 - Find the direction and magnitude of the net...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate (a) Find the direction and...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Two point charges lie on the x...Ch. 19 - A system consists of two positive point charges,...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate The point charges in Figure...Ch. 19 - Referring to the previous problem, suppose that...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate (a) If the nucleus in Example...Ch. 19 - Four point charges are located at the corners of a...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Two identical point charges in...Ch. 19 - Two spheres with uniform surface charge density,...Ch. 19 - Point charges, q1 and q2 are placed on the x axis,...Ch. 19 - Two electric charges are separated by a finite...Ch. 19 - What is the magnitude of the electric field...Ch. 19 - A +5.0-C charge experiences a 0.64-N force in the...Ch. 19 - Two point charges lie on the x axis. A charge of...Ch. 19 - Two point charges lie on the x axis. A charge of...Ch. 19 - The electric field on the dashed line in Figure...Ch. 19 - An object with a charge of 2.1 C and a mass of...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Figure 19-42 shows a system...Ch. 19 - Two point charges of equal magnitude are 8.3 cm...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate A point charge q = +4.7 C is...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Four point charges, each of...Ch. 19 - The electric field at the point x = 5.00 cm and y...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate The electric field lines...Ch. 19 - Referring to Figure 19-43, suppose q2 is not...Ch. 19 - The electric field lines surrounding three charges...Ch. 19 - Make a qualitative sketch of the electric field...Ch. 19 - Sketch the electric field lines for the system of...Ch. 19 - Sketch the electric field lines for the system of...Ch. 19 - Suppose the magnitude of the electric field...Ch. 19 - Predict/Explain Gaussian surface 1 has twice the...Ch. 19 - Suppose the conducting shell in Figure 19-33which...Ch. 19 - Rank the Gaussian surfaces shown in Figure 19-45...Ch. 19 - A uniform electric field of magnitude 35,000 N/C...Ch. 19 - Prob. 61PCECh. 19 - A surface encloses the charges q1 = 3.2 C, q2 =...Ch. 19 - BIO Nerve Cells Nerve cells are long, thin...Ch. 19 - The electric flux through each of the six sides of...Ch. 19 - Consider a spherical Gaussian surface and three...Ch. 19 - The surface charge per area on the outside of a...Ch. 19 - Photovoltaic Field Suppose the field in the...Ch. 19 - A thin wire of infinite extent has a charge per...Ch. 19 - CE Predict/Explain An electron and a proton are...Ch. 19 - CE Predict/Explain In Conceptual Example 19-9,...Ch. 19 - CE Under normal conditions, the electric field at...Ch. 19 - A proton is released from rest in a uniform...Ch. 19 - BIO Ventricular Fibrillation If a charge of 0.30 C...Ch. 19 - A point charge at the origin of a coordinate...Ch. 19 - Prob. 76GPCh. 19 - The Balloon and Your Hair Suppose 7.5 1010...Ch. 19 - The Balloon and the Wall When a charged balloon...Ch. 19 - CE Four lightweight, plastic spheres, labeled A,...Ch. 19 - Find (a) the direction and (b) the magnitude of...Ch. 19 - A small object of mass 0.0150 kg and charge 3.1 C...Ch. 19 - The electric field at a radial distance of 47.7 cm...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Three charges are placed at the...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate BIO Cell Membranes The cell...Ch. 19 - A square with sides of length L has a point charge...Ch. 19 - Two small plastic balls hang from threads of...Ch. 19 - A small sphere with a charge of +2.44 C is...Ch. 19 - Twelve identical point charges q are equally...Ch. 19 - BIO Nerve Impulses When a nerve impulse propagates...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate The Electric Field of the Earth...Ch. 19 - An object of mass m = 2.5 g and charge Q = +42C is...Ch. 19 - Four identical charges, +Q occupy the corners of a...Ch. 19 - Two charges, +q and q, occupy two corners of an...Ch. 19 - Figure 19-52 shows an electron entering a...Ch. 19 - Two identical conducting spheres are separated by...Ch. 19 - Have you ever pulled clothes from a dryer only to...Ch. 19 - Have you ever pulled clothes from a dryer only to...Ch. 19 - The force required to detach a grain of pollen...Ch. 19 - Pollen of the lisianthus plant requires a force 10...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 19-14...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 19-14 In...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 19-16 The...Ch. 19 - Referring to Example 19-16 Suppose the magnitude...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
If someone at the other end of a room smokes a cigarette, you may breathe in some smoke. The movement of smoke ...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Carefully examine the common sedimentary rocks shown In Figure 2.13. Use these photos and the preceding discuss...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Pigeons may exhibit a checkered or plain color pattern. In a series of controlled matings, the following data w...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
9. A student gives a steady push to a ball at the end of a massless, rigid rod for 1 s, causing the ball to rot...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
8. A human maintaining a vegan diet (containing no animal products) would be a:
a. producer
b. primary consume...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
The mammalian trachea and esophagus both connect to the (A) pharynx. (B) stomach. (C) large intestine. (D) rect...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwarda) Use the node-voltage method to find v1, v2, and v3 in the circuit in Fig. P4.14. b) How much power does the 40 V voltage source deliver to the circuit? Figure P4.14 302 202 w w + + + 40 V V1 80 Ω 02 ΣΑΩ 28 A V3 + w w 102 202arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- You're on an interplanetary mission, in an orbit around the Sun. Suppose you make a maneuver that brings your perihelion in closer to the Sun but leaves your aphelion unchanged. Then you must have Question 2 options: sped up at perihelion sped up at aphelion slowed down at perihelion slowed down at aphelionarrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE DO NOT USE LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward་ The position of a particle is described by r = (300e 0.5t) mm and 0 = (0.3t²) rad, where t is in seconds. Part A Determine the magnitude of the particle's velocity at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. v = Value Submit Request Answer Part B ? Units Determine the magnitude of the particle's acceleration at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. a = Value A ? Unitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics Capacitor & Capacitance part 7 (Parallel Plate capacitor) CBSE class 12; Author: LearnoHub - Class 11, 12;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JoW6UstbZ7Y;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY