
Physics, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134020853
Author: James S. Walker
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 19, Problem 52PCE
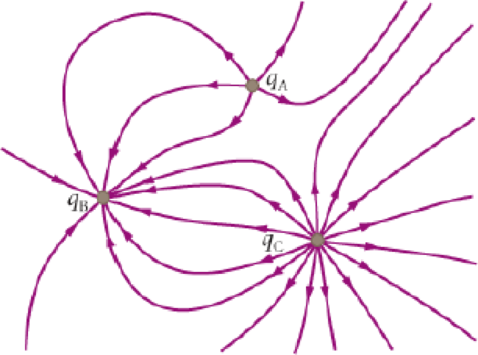
The electric field lines surrounding three charges are shown in Figure 19-44. (a) Which of the charges qA, qB, and qC are positively charged, and which are negatively charged? (b) Rank the charges in order of increasing magnitude.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls
A car in a roller coaster moves along a track that consists of a sequence of ups and
downs. Let the x axis be parallel to the ground and the positive y axis point upward.
In the time interval from t 0 tot = = 4s, the trajectory of the car along a
certain section of the track is given by
7 = A(1 m/s)ti + A [(1 m/s³) t³ - 6(1 m/s²)t²]ĵ
where A is a positive dimensionless constant. At t
car ascending or descending?
=
2.0 S is the roller coaster
Ascending.
Descending.
need help on first part
its not 220
Chapter 19 Solutions
Physics, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Ch. 19.1 - Enhance Your Understanding (Answers given at the...Ch. 19.2 - Enhance Your Understanding (Answers given at the...Ch. 19.3 - Positive and negative charges of equal magnitude...Ch. 19.4 - Enhance Your Understanding (Answers given at the...Ch. 19.5 - The electric field lines for a system of two...Ch. 19.6 - Two conducting spheres of different radii are...Ch. 19.7 - Four Gaussian surfaces (A, B, C, D) are shown in...Ch. 19 - The fact that the electron has a negative charge...Ch. 19 - Explain why a comb that has been rubbed through...Ch. 19 - Small bits of paper are attracted to an...
Ch. 19 - A charged rod is brought near a suspended object,...Ch. 19 - A charged rod is brought near a suspended object,...Ch. 19 - A point charge +Q is fixed at a height H above the...Ch. 19 - A proton moves in a region of constant electric...Ch. 19 - Describe some of the differences between charging...Ch. 19 - A system consists of two charges of equal...Ch. 19 - The force experienced by charge 1 at point A is...Ch. 19 - Can an electric field exist in a vacuum? Explain.Ch. 19 - Gausss law can tell us how much charge is...Ch. 19 - Predict/Explain An electrically neutral object is...Ch. 19 - (a) Based on the materials listed in Table 19-1,...Ch. 19 - This problem refers to the information given in...Ch. 19 - Find the net charge of a system consisting of (a)...Ch. 19 - Find the total electric charge of 2.5 kg of (a)...Ch. 19 - A container holds a gas consisting of 2.85 moles...Ch. 19 - The Charge on Adhesive Tape When adhesive tape is...Ch. 19 - Four pairs of conducting spheres, all with the...Ch. 19 - A system of 1525 particles, each of which is...Ch. 19 - A charge +q and a charge q are placed at opposite...Ch. 19 - Consider the three electric charges, A, B, and C,...Ch. 19 - Predict/Explain Suppose the charged sphere in...Ch. 19 - At what separation is the electrostatic force...Ch. 19 - How much equal charge should be placed on the...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Two point charges, the first...Ch. 19 - When two identical ions are separated by a...Ch. 19 - Given that q = +18 C and d = 21 cm, find the...Ch. 19 - Five point charges, q1 = +q, q2 = +2q q3 = 3q, q4...Ch. 19 - Three charges, q1 = +q, q2 = q, and q3 = +q, are...Ch. 19 - The attractive electrostatic force between the...Ch. 19 - Prob. 21PCECh. 19 - A sphere of radius 4.22 cm and uniform surface...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Given that q = +12 C and d = 19...Ch. 19 - Suppose the charge q2 in Figure 19-38 can be moved...Ch. 19 - A point charge q = 0.55 nC is fixed at the origin....Ch. 19 - A point charge q = 0.55 nC is fixed at the origin....Ch. 19 - Find the direction and magnitude of the net...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate (a) Find the direction and...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Two point charges lie on the x...Ch. 19 - A system consists of two positive point charges,...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate The point charges in Figure...Ch. 19 - Referring to the previous problem, suppose that...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate (a) If the nucleus in Example...Ch. 19 - Four point charges are located at the corners of a...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Two identical point charges in...Ch. 19 - Two spheres with uniform surface charge density,...Ch. 19 - Point charges, q1 and q2 are placed on the x axis,...Ch. 19 - Two electric charges are separated by a finite...Ch. 19 - What is the magnitude of the electric field...Ch. 19 - A +5.0-C charge experiences a 0.64-N force in the...Ch. 19 - Two point charges lie on the x axis. A charge of...Ch. 19 - Two point charges lie on the x axis. A charge of...Ch. 19 - The electric field on the dashed line in Figure...Ch. 19 - An object with a charge of 2.1 C and a mass of...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Figure 19-42 shows a system...Ch. 19 - Two point charges of equal magnitude are 8.3 cm...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate A point charge q = +4.7 C is...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Four point charges, each of...Ch. 19 - The electric field at the point x = 5.00 cm and y...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate The electric field lines...Ch. 19 - Referring to Figure 19-43, suppose q2 is not...Ch. 19 - The electric field lines surrounding three charges...Ch. 19 - Make a qualitative sketch of the electric field...Ch. 19 - Sketch the electric field lines for the system of...Ch. 19 - Sketch the electric field lines for the system of...Ch. 19 - Suppose the magnitude of the electric field...Ch. 19 - Predict/Explain Gaussian surface 1 has twice the...Ch. 19 - Suppose the conducting shell in Figure 19-33which...Ch. 19 - Rank the Gaussian surfaces shown in Figure 19-45...Ch. 19 - A uniform electric field of magnitude 35,000 N/C...Ch. 19 - Prob. 61PCECh. 19 - A surface encloses the charges q1 = 3.2 C, q2 =...Ch. 19 - BIO Nerve Cells Nerve cells are long, thin...Ch. 19 - The electric flux through each of the six sides of...Ch. 19 - Consider a spherical Gaussian surface and three...Ch. 19 - The surface charge per area on the outside of a...Ch. 19 - Photovoltaic Field Suppose the field in the...Ch. 19 - A thin wire of infinite extent has a charge per...Ch. 19 - CE Predict/Explain An electron and a proton are...Ch. 19 - CE Predict/Explain In Conceptual Example 19-9,...Ch. 19 - CE Under normal conditions, the electric field at...Ch. 19 - A proton is released from rest in a uniform...Ch. 19 - BIO Ventricular Fibrillation If a charge of 0.30 C...Ch. 19 - A point charge at the origin of a coordinate...Ch. 19 - Prob. 76GPCh. 19 - The Balloon and Your Hair Suppose 7.5 1010...Ch. 19 - The Balloon and the Wall When a charged balloon...Ch. 19 - CE Four lightweight, plastic spheres, labeled A,...Ch. 19 - Find (a) the direction and (b) the magnitude of...Ch. 19 - A small object of mass 0.0150 kg and charge 3.1 C...Ch. 19 - The electric field at a radial distance of 47.7 cm...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Three charges are placed at the...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate BIO Cell Membranes The cell...Ch. 19 - A square with sides of length L has a point charge...Ch. 19 - Two small plastic balls hang from threads of...Ch. 19 - A small sphere with a charge of +2.44 C is...Ch. 19 - Twelve identical point charges q are equally...Ch. 19 - BIO Nerve Impulses When a nerve impulse propagates...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate The Electric Field of the Earth...Ch. 19 - An object of mass m = 2.5 g and charge Q = +42C is...Ch. 19 - Four identical charges, +Q occupy the corners of a...Ch. 19 - Two charges, +q and q, occupy two corners of an...Ch. 19 - Figure 19-52 shows an electron entering a...Ch. 19 - Two identical conducting spheres are separated by...Ch. 19 - Have you ever pulled clothes from a dryer only to...Ch. 19 - Have you ever pulled clothes from a dryer only to...Ch. 19 - The force required to detach a grain of pollen...Ch. 19 - Pollen of the lisianthus plant requires a force 10...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 19-14...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 19-14 In...Ch. 19 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 19-16 The...Ch. 19 - Referring to Example 19-16 Suppose the magnitude...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
3. What are serous membranes, and what are their functions?
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
15. A woman with severe discoloration of her tooth enamel has four children with a man who has normal tooth ena...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
The number of named species is about ________, but the actual number of species on Earth is estimated to be abo...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Why are BSL-4 suits pressurized? Why not just wear tough regular suits?
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
There are 25 individuals in population 1, all with genotype AA, and there are 40 individuals in population 2, a...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. Which describes our understanding of f...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forwardChildren playing in a playground on the flat roof of a city school lose their ball to the parking lot below. One of the teachers kicks the ball back up to the children as shown in the figure below. The playground is 6.10 m above the parking lot, and the school building's vertical wall is h = 7.40 m high, forming a 1.30 m high railing around the playground. The ball is launched at an angle of 8 = 53.0° above the horizontal at a point d = 24.0 m from the base of the building wall. The ball takes 2.20 s to reach a point vertically above the wall. (Due to the nature of this problem, do not use rounded intermediate values-including answers submitted in WebAssign-in your calculations.) (a) Find the speed (in m/s) at which the ball was launched. 18.1 m/s (b) Find the vertical distance (in m) by which the ball clears the wall. 0.73 ✓ m (c) Find the horizontal distance (in m) from the wall to the point on the roof where the ball lands. 2.68 m (d) What If? If the teacher always launches the ball…arrow_forward
- It is not possible to see very small objects, such as viruses, using an ordinary light microscope. An electron microscope can view such objects using an electron beam instead of a light beam. Electron microscopy has proved invaluable for investigations of viruses, cell membranes and subcellular structures, bacterial surfaces, visual receptors, chloroplasts, and the contractile properties of muscles. The "lenses" of an electron microscope consist of electric and magnetic fields that control the electron beam. As an example of the manipulation of an electron beam, consider an electron traveling away from the origin along the x axis in the xy plane with initial velocity ₁ = vi. As it passes through the region x = 0 to x=d, the electron experiences acceleration a = ai +a, where a and a, are constants. For the case v, = 1.67 x 107 m/s, ax = 8.51 x 1014 m/s², and a = 1.50 x 10¹5 m/s², determine the following at x = d = 0.0100 m. (a) the position of the electron y, = 2.60e1014 m (b) the…arrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forwardneed help with the first partarrow_forward
- A ball is thrown with an initial speed v, at an angle 6, with the horizontal. The horizontal range of the ball is R, and the ball reaches a maximum height R/4. In terms of R and g, find the following. (a) the time interval during which the ball is in motion 2R (b) the ball's speed at the peak of its path v= Rg 2 √ sin 26, V 3 (c) the initial vertical component of its velocity Rg sin ei sin 20 (d) its initial speed Rg √ sin 20 × (e) the angle 6, expressed in terms of arctan of a fraction. 1 (f) Suppose the ball is thrown at the same initial speed found in (d) but at the angle appropriate for reaching the greatest height that it can. Find this height. hmax R2 (g) Suppose the ball is thrown at the same initial speed but at the angle for greatest possible range. Find this maximum horizontal range. Xmax R√3 2arrow_forwardAn outfielder throws a baseball to his catcher in an attempt to throw out a runner at home plate. The ball bounces once before reaching the catcher. Assume the angle at which the bounced ball leaves the ground is the same as the angle at which the outfielder threw it as shown in the figure, but that the ball's speed after the bounce is one-half of what it was before the bounce. 8 (a) Assuming the ball is always thrown with the same initial speed, at what angle & should the fielder throw the ball to make it go the same distance D with one bounce (blue path) as a ball thrown upward at 35.0° with no bounce (green path)? 24 (b) Determine the ratio of the time interval for the one-bounce throw to the flight time for the no-bounce throw. Cone-bounce no-bounce 0.940arrow_forwardA rocket is launched at an angle of 60.0° above the horizontal with an initial speed of 97 m/s. The rocket moves for 3.00 s along its initial line of motion with an acceleration of 28.0 m/s². At this time, its engines fail and the rocket proceeds to move as a projectile. (a) Find the maximum altitude reached by the rocket. 1445.46 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m (b) Find its total time of flight. 36.16 x Your response is within 10% of the correct value. This may be due to roundoff error, or you could have a mistake in your calculation. Carry out all intermediate results to at least four-digit accuracy to minimize roundoff error. s (c) Find its horizontal range. 1753.12 × Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. marrow_forward
- Race car driver is cruising down the street at a constant speed of 28.9 m/s (~65 mph; he has a “lead” foot) when the traffic light in front of him turns red. a) If the driver’s reaction time is 160 ms, how far does he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he begins to slow down? b) If the driver’s combined reaction and movement time is 750 ms, how far do he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he slams on her brakes and car begins to slow down? Please answer parts a-B. Show all work. For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places. DONT FORGET TO DRAW VECTORS! ONLY USE BASIC FORMULAS TAUGHT IN PHYSICS. distance = speed * time.arrow_forwardRace car driver is cruising down the street at a constant speed of 28.9 m/s (~65 mph; he has a “lead” foot) when the traffic light in front of him turns red. a) If the driver’s reaction time is 160 ms, how far does he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he begins to slow down? b) If the driver’s combined reaction and movement time is 750 ms, how far do he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he slams on her brakes and car begins to slow down? c) If the driver’s average rate of acceleration is -9.5 m/s2 as he slows down, how long does it take him to come to a stop (use information about his speed of 28.9 m/s but do NOT use his reaction and movement time in this computation)? Please answer parts a-c. Show all work. For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.…arrow_forwardHow is it that part a is connected to part b? I can't seem to solve either part and don't see the connection between the two.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY