
a.
To determine:
The piece of DNA is cut by EcoRI, the resulting fragments are separated by gel electrophoresis, and the gel is stained with ethidium bromide. Draw a picture of the bands that will appear on the gel.
Introduction:
EcoRI is type II restriction enzyme.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: The following gel shows that DNA fragments are present after the EcoRI has cleaved at
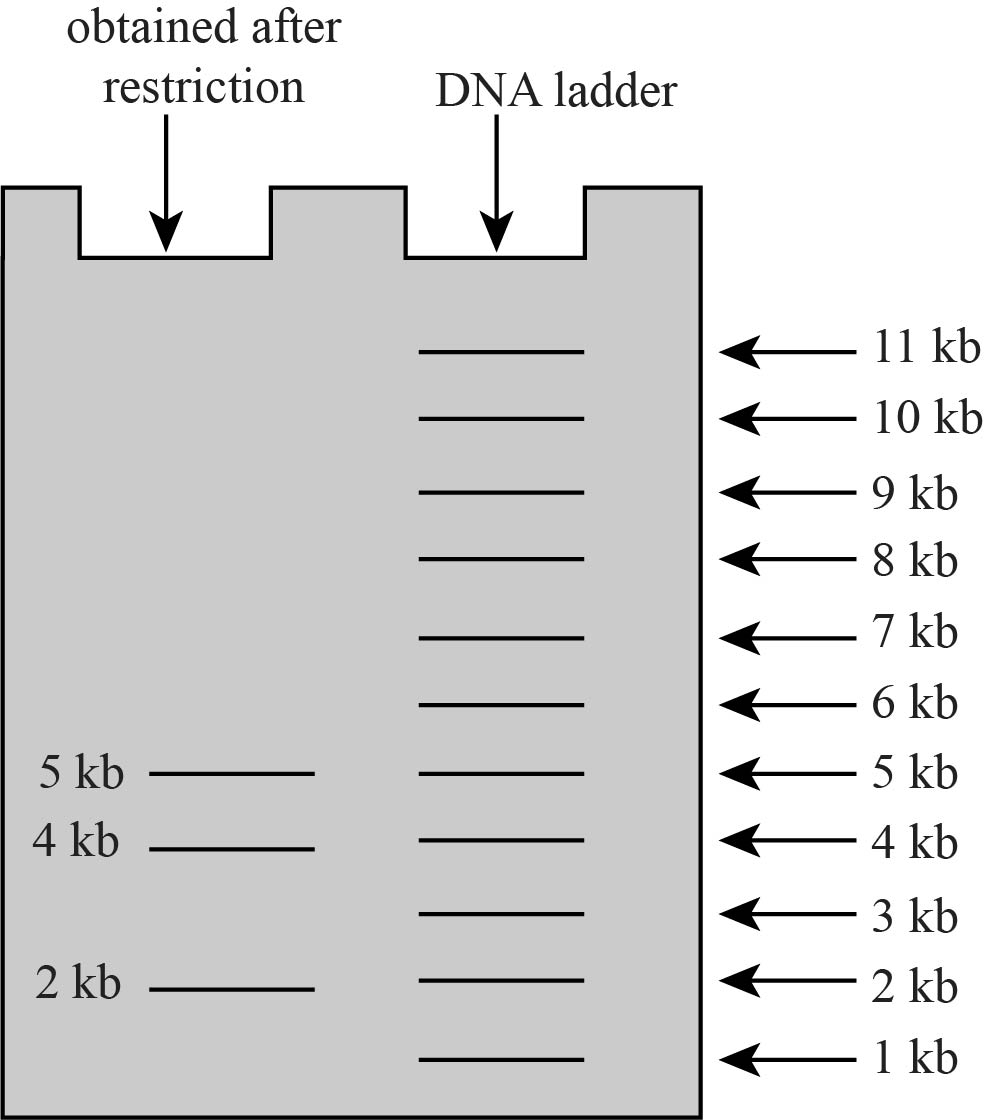
Fig. 1: Gel electrophoresis DNA fragmentation.
After the action of enzyme EcoRI on the DNA, it will produce three fragments of length
b.
To determine:
If a mutation that alters EcoRI site 1 occurs in this piece of DNA, how will the banding pattern on the gel differ from the one that drew in part a?
Introduction:
EcoRI is type II restriction enzyme.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: The following gel on that DNA fragments only two fragments of length is obtained
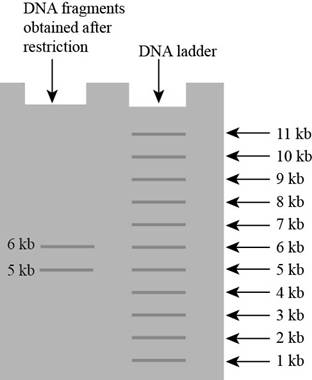
Fig 2 Gel fragmentation
Only two fragments will obtained if the EcoRI site 1 is mutated, two fragments are
c.
To determine:
The difference of banding pattern on the gel that drew in part a if mutations that alter EcoRI sites 1 and 2 occur in this piece of DNA.
Introduction:
EcoRI is type II restriction enzyme.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: The gel electrophoresis after the mutation occurs at both sites.
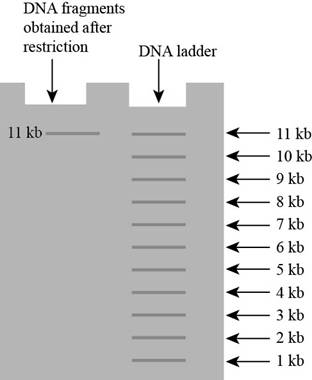
Fig. 3: Gel electrophoresis result
If mutation occur on the both sites, then there will be no cutting and if there will be no cutting then fragment will remain same.
d.
To determine:
The difference of banding pattern on the gel differ from the one that drew in part a if the 1000 bp of DNA were inserted between the two restriction sites.
Introduction:
EcoRI is type II restriction enzyme.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: The gel on that DNA fragments only two fragments of length is obtained
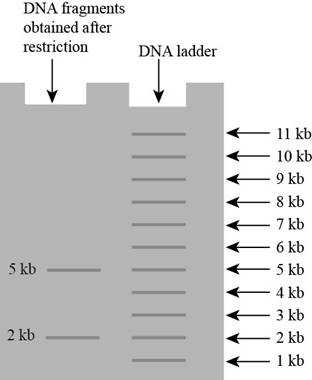
Fig 4: Gel fragmentation
Inserting
e.
To determine:
The difference in the banding pattern on the gel differ from the one that drew in part a if 500 bp of DNA between the two restriction sites were deleted.
Introduction:
EcoRI is type II restriction enzyme.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: The gel on that DNA fragments only three fragments of length are obtained
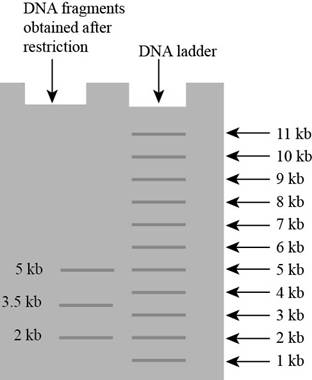
Fig 5 Gel fragmentation
Deleting
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Genetics: A Conceptual Approach
- Outline the negative feedback loop that allows us to maintain a healthy water concentration in our blood. You may use diagram if you wisharrow_forwardGive examples of fat soluble and non-fat soluble hormonesarrow_forwardJust click view full document and register so you can see the whole document. how do i access this. following from the previous question; https://www.bartleby.com/questions-and-answers/hi-hi-with-this-unit-assessment-psy4406-tp4-report-assessment-material-case-stydu-ms-alecia-moore.-o/5e09906a-5101-4297-a8f7-49449b0bb5a7. on Google this image comes up and i have signed/ payed for the service and unable to access the full document. are you able to copy and past to this response. please see the screenshot from google page. unfortunality its not allowing me attch the image can you please show me the mathmetic calculation/ workout for the reult sectionarrow_forward
- Skryf n kortkuns van die Egyptians pyramids vertel ñ story. Maximum 500 woordearrow_forward1.)What cross will result in half homozygous dominant offspring and half heterozygous offspring? 2.) What cross will result in all heterozygous offspring?arrow_forward1.Steroids like testosterone and estrogen are nonpolar and large (~18 carbons). Steroids diffuse through membranes without transporters. Compare and contrast the remaining substances and circle the three substances that can diffuse through a membrane the fastest, without a transporter. Put a square around the other substance that can also diffuse through a membrane (1000x slower but also without a transporter). Molecule Steroid H+ CO₂ Glucose (C6H12O6) H₂O Na+ N₂ Size (Small/Big) Big Nonpolar/Polar/ Nonpolar lonizedarrow_forward
- what are the answer from the bookarrow_forwardwhat is lung cancer why plants removes liquid water intead water vapoursarrow_forward*Example 2: Tracing the path of an autosomal dominant trait Trait: Neurofibromatosis Forms of the trait: The dominant form is neurofibromatosis, caused by the production of an abnormal form of the protein neurofibromin. Affected individuals show spots of abnormal skin pigmentation and non-cancerous tumors that can interfere with the nervous system and cause blindness. Some tumors can convert to a cancerous form. i The recessive form is a normal protein - in other words, no neurofibromatosis.moovi A typical pedigree for a family that carries neurofibromatosis is shown below. Note that carriers are not indicated with half-colored shapes in this chart. Use the letter "N" to indicate the dominant neurofibromatosis allele, and the letter "n" for the normal allele. Nn nn nn 2 nn Nn A 3 N-arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





