
Concept explainers
(a)
Then the distance ‘d’ to maximise the frequency of oscillation when a small initial displacement is given.
Answer to Problem 19.50P
Distance
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
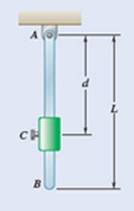
Mass of collar
Mass of rod
Length of rod
The forces corresponding to the rod and collar are shown in the free body diagram below:
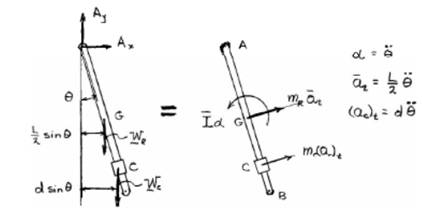
Now, from the equation of motion taking moment about A,
And, moment of inertia of rod is
Compare the above equation with un-damped equation of vibration:
Natural frequency:
To maximise the frequency, we need to take the derivative with respect to d and set it equal to zero.
By solving the above equation we get,
Conclusion:
The distance
(b)
The period of oscillation.
Answer to Problem 19.50P
Period of vibration,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
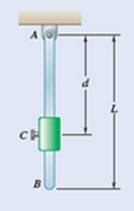
Mass of collar
Mass of rod
Length of rod
The forces corresponding to the rod and collar are shown in the free body diagram below:
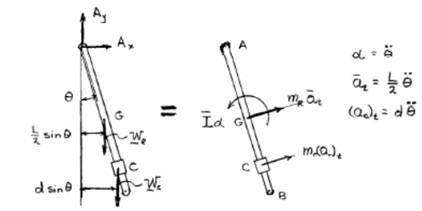
Now, from the equation of motion taking moment about A,
And, moment of inertia of rod is
Compare the above equation with un-damped equation of vibration;
Natural frequency:
To maximise the frequency, we need to take the derivative with respect to d and set it equal to zero.
By solving the above equation we get,
Thus,
Now, natural frequency:
Then, Time period
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,DYNAMICS(LOOSE)-W/ACCESS
- This refrigeration cycle uses R-134a as the working fluid and, for now, assume that it operates on an ideal vapour-compression refrigeration cycle between 0.11 and 1.0 MPa. If the mass flow rate of the refrigerant is 0.075 kg/s, determine What is the rate of heat removal from the refrigerated space? What is the power input to the compressor? What is the rate of heat rejection to the environment? What is the COP of this ideal process? Based on this analysis, what is the cost of electricity to operate the cold room for 1 year? Comment on why this differs to the value above Further data was collected which determined that the working fluid: enters the compressor at 0.11 MPa and -22°C leaves the compressor at 1.0 MPa and 60°C is cooled in the condenser to 0.9 MPa and 20°C is throttled to 0.12 MPa Disregarding any heat transfer or pressure losses in the pipes: What is the rate of heat removal from the refrigerated space? What is the power input to the compressor?…arrow_forward1 The refrigeration capacity of the cold room you are considering is 10 kW. It operates for 24 h/d, 360 days of the year. The average temperature outside the cold room is 30°C and the temperature of the air inside the cold room should be 5°C. What is the maximum coefficient of performance for this refrigeration cycle? What is the minimum work required? and If the price of electricity is 0.008 cents per kJ, what is the minimum cost of electricity to run the cold room for 1 year?arrow_forwardThis refrigeration cycle uses R-134a as the working fluid and, for now, assume that it operates on an ideal vapour-compression refrigeration cycle between 0.11 and 1.0 MPa. If the mass flow rate of the refrigerant is 0.075 kg/s, determine What is the rate of heat removal from the refrigerated space? What is the power input to the compressor? What is the rate of heat rejection to the environment? and What is the COP of this ideal process?arrow_forward
- The figure illustrates the nonpermanent connection of a steel cylinder head to a grade 30 cast-iron pressure vessel using 73 bolts. A confined gasket seal has an effective sealing diameter D of 0.9 m. The cylinder pressure is cycled between a minimum pressure of zero and a maximum pressure p, of 535 kPa. For the specifications given in the table for the specific problem assigned, select a suitable bolt length from the preferred sizes. Use Table A-17 for calculation purposes. Parameter Head thickness, A Cylinder thickness, B Value 16 mm 25 mm Internal diameter of the cylinder, C 0.8 m Gasket sealing diameter, D Bolt circle diameter, E Outer diameter of the cylinder head, F 0.9 m 1.0 m 1.1 m Bolt grade ISO 10.9 Bolt diameter, d 10 mm F E D 111 Find a suitable bolt length. Then, determine the bolt stiffness, material stiffness and stiffness constant of the joint. The bolt length is The bolt stiffness is mm. MN/m. The material stiffness is | The stiffness constant is MN/m.arrow_forwardProblem 3 A rotating shaft of 20 mm diameter is simply supported. The shaft is loaded with a transverse load of 10 kN as shown in the figure. The shaft is made from AISI 1095 hot-rolled steel. The surface has been machined. The shaft operate at temperature T = 450 °C. Consider a reliability factor of 95%. Determine (a) Calculate the reaction forces R₁ and R2* (b) Draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams and determine the maximum bending moment and shear force. 200 mm 20 mm 10,000 N -50 mm- C A B R₁ Not to scale. (c) Determine the critical location of the shaft and the maximum effective stresses, (d) Calculate the static safety factor against yielding. (e) Determined the endurance limit, adjusted as necessary with Marin factors. (f) Calculate the fatigue factor of safety based on achieving infinite life (g) If the fatigue factor of safety is less than 1, then estimate the life of the part in number of rotations, based on the ultimate strength of the material at T = 450 °C.arrow_forwardAn air duct heater consists of an aligned array of electrical heating elements in which the longitudinal and transverse pitches are SL = ST = 24 mm. There are 3 rows of elements in the flow direction (NL = 3) and 4 elements per row (NT = 4). Atmospheric air with an upstream velocity of 12 m/s and a temperature of 25°C moves in cross flow over the elements, which have a diameter of 12 mm, a length of 250 mm, and are maintained at a surface temperature of 350°C. (a) Determine the total rate of heat transfer to the air and the temperature of the air leaving the duct heater. (b) Determine the pressure drop across the element bank and the fan power requirement. (c) Compare the average convection coefficient obtained in your analysis with the value for an isolated (single) element. Explain the difference between the results. (d) What effect would increasing the longitudinal and transverse pitches to 30 mm have on the exit temperature of the air, the total heat rate, and the…arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





