
Concept explainers
Answer the following questions about the given triacylglycerol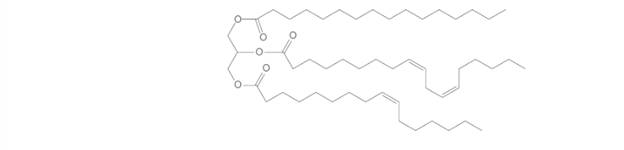
a. What fatty acids are used to form this triacylglycerol?
b. Would you expect this triacylglycerol to be a solid or a liquid at room temperature?
c. What regions are hydrophobic?
d. What regions are hydrophilic?
e. What hydrolysis products are formed when the triacylglycerol is treated with aqueous sulfuric acid?
(a)
Interpretation:
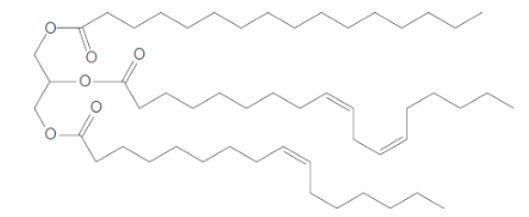
The fatty acids which are used to form the below triacylglycerol needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids are biomolecules that are involved in different biochemical reactions. They are special types of organic molecules which can only be identified with the help of their physical properties, not by the presence of any certain functional group. In general, lipids contain a large number of C-C and C-H bonds with few polar functional groups such as −OH, -SH, etc. For example, triacylglycerol consists of three ester groups whereas Vitamin E is composed of both ether and phenolic groups.
Answer to Problem 50P
In the given triacylglycerol; the fatty acids must be:
Explanation of Solution
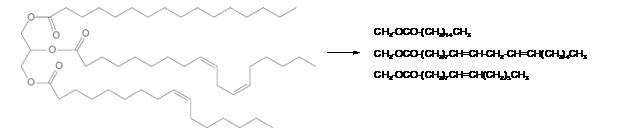
Triacylglycerols are most abundant lipids which are mainly found in animal fat and vegetable oils. They are triesters of glycerol, therefore in the formation of one molecule of triacylglycerol, three molecules of fatty acids react with one molecule of glycerol as given below;
Hence the left side part of hydrocarbon chains is part of fatty acids in the triacylglycerol molecule. The structural formula for the given triacylglycerol is as given below.
In the given triacylglycerol; the fatty acids must be:
(b)
Interpretation:
The physical state of given triacylglycerol needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids are biomolecules that are involved in different biochemical reactions. They are special types of organic molecules which can only be identified with the help of their physical properties, not by the presence of any certain functional group. In general, lipids contain a large number of C-C and C-H bonds with few polar functional groups such as −OH, -SH, etc. For example, triacylglycerol consists of three ester groups whereas Vitamin E is composed of both ether and phenolic groups.
Answer to Problem 50P
The triacylglycerol must be in a liquid state.
Explanation of Solution
In the given triacylglycerol; the fatty acids must be:
Linoleic acid and Palmitoleic acid are unsaturated fatty acids as they have C=C bonds in the long hydrocarbon chain. The unsaturation in fatty acids decreases the melting point of molecule due to bending in the molecule. Since the given triacylglycerol is composed of unsaturated fatty acids, therefore, it should exist in a liquid state.
(c)
Interpretation:
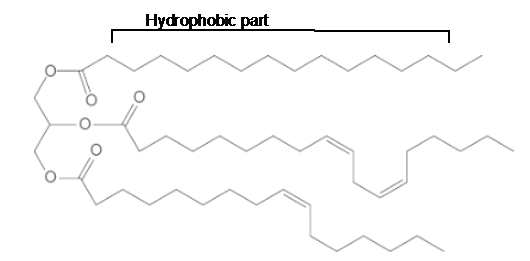
The hydrophobic part of given triacylglycerol needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids are biomolecules that are involved in different biochemical reactions. They are special types of organic molecules which can only be identified with the help of their physical properties, not by the presence of any certain functional group. In general, lipids contain a large number of C-C and C-H bonds with few polar functional groups such as −OH, -SH, etc. For example, triacylglycerol consists of three ester groups whereas Vitamin E is composed of both ether and phenolic groups.
Answer to Problem 50P
The long hydrocarbon chains in the triacylglycerol molecule is hydrophobic part of the molecule.
Explanation of Solution
Triacylglycerols are most abundant lipids which are mainly found in animal fat and vegetable oils. They are triesters of glycerol, therefore in the formation of one molecule of triacylglycerol, three molecules of fatty acids react with one molecule of glycerol as given below;
The long hydrocarbon chains of the triacylglycerol are hydrophobic part as it is non-polar part.
(d)
Interpretation:
The hydrophilic part of given triacylglycerol needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids are biomolecules that are involved in different biochemical reactions. They are special types of organic molecules which can only be identified with the help of their physical properties, not by the presence of any certain functional group. In general, lipids contain a large number of C-C and C-H bonds with few polar functional groups such as −OH, -SH, etc. For example, triacylglycerol consists of three ester groups whereas Vitamin E is composed of both ether and phenolic groups.
Answer to Problem 50P
The ester linkage in the triacylglycerol molecule is hydrophilic part of the molecule.
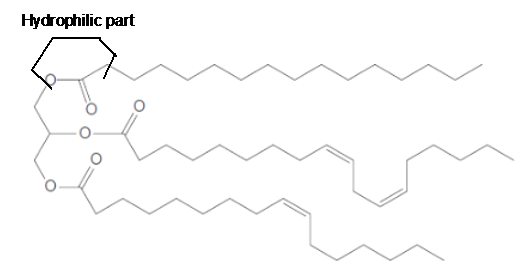
Explanation of Solution
Triacylglycerols are most abundant lipids which are mainly found in animal fat and vegetable oils. They are triesters of glycerol, therefore in the formation of one molecule of triacylglycerol, three molecules of fatty acids react with one molecule of glycerol as given below;
The long hydrocarbon chains of the triacylglycerol are hydrophobic part as it is non-polar part whereas the ester linkage in the molecule is hydrophilic part of the molecule.
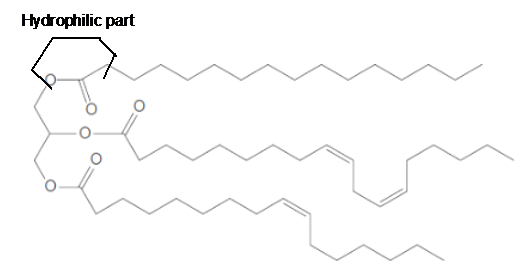
(e)
Interpretation:
The hydrolysis product of given triacylglycerol with aqueous sulfuric acid needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids are biomolecules that are involved in different biochemical reactions. They are special types of organic molecules which can only be identified with the help of their physical properties, not by the presence of any certain functional group. In general, lipids contain a large number of C-C and C-H bonds with few polar functional groups such as −OH, -SH, etc. For example, triacylglycerol consists of three ester groups whereas Vitamin E is composed of both ether and phenolic groups.
Answer to Problem 50P
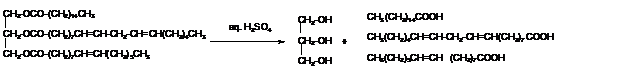
Explanation of Solution
Triacylglycerols are most abundant lipids which are mainly found in animal fat and vegetable oils. They are triesters of glycerol, therefore in the formation of one molecule of triacylglycerol, three molecules of fatty acids react with one molecule of glycerol as given below;
The hydrolysis of triacylglycerol with aqueous sulfuric acid leads to the formation of fatty acid and glycerol molecule.
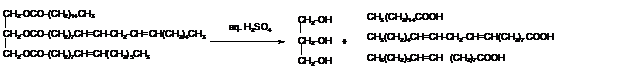
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM-ACCES
- The reaction of 2-oxacyclopentanone with hydrochloric acid in water (i.e., "excess") produces which of the following carboxylic acids?arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardWhat is the name of the major product formed during the reaction between benzoyl chloride and phenol? benzyl ester O phenyl benzoate ○ cyclopentanoate ○ benzyl phenoate ○ benzenecarboxylic acidarrow_forward
- Provide the proper IUPAC or common name for the following compound. Dashes, commas, and spaces must be used correctly.arrow_forwardProvide the proper IUPAC name (only) for the following compound. Dashes, commas, and spaces must be used correctly. HO. OHarrow_forwardQuestion 2 0/1 pts Provide the proper IUPAC name only for the following compound. Dashes, commas, and spaces must be used correctly. HO CH 3 1-methyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxylic acidarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning





