
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by
Answer to Problem 27E
The IUPAC name of the alkyne,
Explanation of Solution
The rules for getting the IUPAC name of alkynes are shown below step by step.
Step-1: Find the longest carbon chain containing the
The given compound is a straight chain compound, so, the full chain will be the longest chain as shown below.
Step-2: Give the numbering to the chain so that the functional group gets the shortest possible number as shown below.
![]()
Figure 1
Step-3: Start naming the compound with proper suffix and prefix.
The given compound contains a five-carbon atom parent chain. The functional group alkyne is present in between carbon number two and three.
For alkynes the suffix used is “yne” and naming for five carbon atoms parent chain is “pent”.
Therefore, the name of the compound is
The IUPAC name is
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC nomenclature. The naming of organic compound is offered by some set of rules to provide each compound with its unique name.
Answer to Problem 27E
The IUPAC name of the alkyne
Explanation of Solution
The rules for getting the IUPAC name of alkynes are shown below step by step.
Step-1: Find the longest carbon chain containing the functional group.
The given compound is a straight chain compound, so, the full chain will be the longest chain as shown below.
Step-2: Give the numbering to the chain so that the functional group gets the shortest possible number as shown below.
![]()
Figure 2
Step-3: Start naming the compound with proper suffix and prefix.
The given compound contains a five-carbon atom parent chain. The functional group alkyne is present in between carbon number one and two.
For alkynes the suffix used is “yne” and naming for five carbon atoms parent chain is “pent”.
Therefore, the name of the compound is
The IUPAC name is
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC nomenclature. The naming of organic compound is offered by some set of rules to provide each compound with its unique name.
Answer to Problem 27E
The IUPAC name of the alkyne,
Explanation of Solution
The rules for getting the IUPAC name of alkynes are shown below step by step.
Step-1: Find the longest carbon chain containing the functional group.
The given compound is a straight-chain compound so the full chain will be the longest chain as shown below.
Step-2: Give the numbering to the chain so that the functional group gets the shortest possible number as shown below.
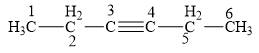
Figure 3
Step-3: Start naming the compound with proper suffix and prefix.
The given compound contains a six-carbon atom parent chain. The function group alkyne is present in between carbon number three and four.
For alkynes the suffix used is “yne” and naming for six carbon atoms parent chain is “hex”.
Therefore the name of the compound is
The IUPAC name is
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC nomenclature. The naming of organic compound is offered by some set of rules to provide each compound with its unique name.
Answer to Problem 27E
The IUPAC name of the alkyne,
Explanation of Solution
The rules for getting the IUPAC name of alkynes are shown below step by step.
Step-1: Find the longest carbon chain containing the functional group.
The given compound is a straight-chain compound so the full chain will be the longest chain as shown below.
Step-2: Give the numbering to the chain so that the functional group gets the shortest possible number as shown below.
![]()
Figure 4
Step-3: Start naming the compound with proper suffix and prefix.
The given compound contains a seven-carbon atom parent chain. The function group alkyne is present in between carbon number two and three.
For alkynes the suffix used is “yne” and naming for seven carbon atoms parent chain is “hept”.
Therefore the name of the compound is
The IUPAC name is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking (8th Edition)
- QUESTION: Find the standard deviation for the 4 different groups 5.298 3.977 223.4 148.7 5.38 4.24 353.7 278.2 5.033 4.044 334.6 268.7 4.706 3.621 305.6 234.4 4.816 3.728 340.0 262.7 4.828 4.496 304.3 283.2 4.993 3.865 244.7 143.6 STDEV = STDEV = STDEV = STDEV =arrow_forwardQUESTION: Fill in the answers in the empty green boxes regarding 'Question 5: Calculating standard error of regression' *The images of the data showing 'coefficients for the standard curve' have been providedarrow_forwardUsing the Nernst equation to calculate nonstandard cell voltage Try Again Your answer is wrong. In addition to checking your math, check that you used the right data and DID NOT round any intermediate calculations. A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 2+ 2+ Sn²+ Ba(s) (aq) + Ba (s) Sn (s) + Ba²+ (aq) →>> Suppose the cell is prepared with 6.10 M Sn 2+ 2+ in one half-cell and 6.62 M Ba in the other. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 1.71 V ☐ x10 ☑ 5 0/5 ? 00. 18 Ararrow_forward
- Question: Find both the b (gradient) and a (y-intercept) value from the list of data below: (x1 -x̄) 370.5 (y1 - ȳ) 5.240 (x2 - x̄) 142.5 (y2 - ȳ) 2.004 (x3 - x̄) 28.5 (y3 - ȳ) 0.390 (x4 - x̄) -85.5 (y4 - ȳ) -1.231 (x5 - x̄) -199.5 (y5 - ȳ) -2.829 (x6 - x̄) -256.5 (y6 - ȳ) -3.575arrow_forwardCalculating standard reaction free energy from standard reduction... Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG° for the following redox reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 3Cu+ (aq) + Cro²¯ (aq) +4H₂O (1) → 3Cu²+ (aq) +Cr(OH)3 (s)+5OH˜¯ (aq) 0 kJ ☐ x10 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid An analytical chemist is titrating 241.7 mL of a 0.4900M solution of methylamine (CH3NH2) with a 0.7800M solution of HNO3. The pK of methylamine is 3.36. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 17.7 mL of the HNO3 solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HNO3 solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = ☑ ? 18 Ararrow_forward
- The following is two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 223.4 148.7 353.7 278.2 334.6 268.7 305.6 234.4 340.0 262.7 304.3 283.2 244.7 143.6 QUESTION: For both groups of data calculate the answers attached in the image.arrow_forwardThe following is a two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 340.0mmol/L 262.7mmol/L QUESTION: For both groups (Regular & Salt Reduced tomato sauce) of data provide answers to the following calculations below: 1. Standard Deviation (Sx) 2. T Values (t0.05,4) 3. 95% Confidence Interval (mmol/L) 4. [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 5. 95% Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardIf we have leucine (2-amino-4-methylpentanoic acid), alanine (2-aminopropanoic acid) and phenylalanine (2-amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid), indicate the tripeptides that can be formed (use the abbreviated symbols Leu., Ala and Phe).arrow_forward
- Briefly state why trifluoroacetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid.arrow_forwardExplain why acid chlorides are more reactive than amides in reactions with nucleophiles.arrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid An analytical chemist is titrating 101.7 mL of a 0.3500M solution of piperidine (C5H10NH) with a 0.05700M solution of HClO4. The pK of piperidine is 2.89. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 682.9 mL of the HClO solution to it. 4 Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HClO solution added. 4 Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = .11 00. 18 Ararrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div





